
The Chlorophyceae are one of the classes of green algae, distinguished mainly on the basis of ultrastructural morphology. They are usually green due to the dominance of pigments chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. The chloroplast may be discoid, plate-like, reticulate, cup-shaped, spiral- or ribbon-shaped in different species. Most of the members have one or more storage bodies called pyrenoids located in the chloroplast. Pyrenoids contain protein besides starch. Some green algae may store food in the form of oil droplets. They usually have a cell wall made up of an inner layer of cellulose and outer layer of pectose.
Auxenochlorella pyrenoidosa, formerly Chlorella pyrenoidosa, is a species of the freshwater green alga in the Division Chlorophyta. It occurs worldwide. The species name pyrenoidosa refers to the presence of a prominent pyrenoid within the Chlorella chloroplast.

Chlorella is a genus of about thirteen species of single-celled green algae of the division Chlorophyta. The cells are spherical in shape, about 2 to 10 μm in diameter, and are without flagella. Their chloroplasts contain the green photosynthetic pigments chlorophyll-a and -b. In ideal conditions cells of Chlorella multiply rapidly, requiring only carbon dioxide, water, sunlight, and a small amount of minerals to reproduce.
Phycodnaviridae is a family of large (100–560 kb) double-stranded DNA viruses that infect marine or freshwater eukaryotic algae. Viruses within this family have a similar morphology, with an icosahedral capsid. As of 2014, there were 33 species in this family, divided among 6 genera. This family belongs to a super-group of large viruses known as nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses. Evidence was published in 2014 suggesting that specific strains of Phycodnaviridae might infect humans rather than just algal species, as was previously believed. Most genera under this family enter the host cell by cell receptor endocytosis and replicate in the nucleus. Phycodnaviridae play important ecological roles by regulating the growth and productivity of their algal hosts. Algal species such Heterosigma akashiwo and the genus Chrysochromulina can form dense blooms which can be damaging to fisheries, resulting in losses in the aquaculture industry. Heterosigma akashiwo virus (HaV) has been suggested for use as a microbial agent to prevent the recurrence of toxic red tides produced by this algal species. Phycodnaviridae cause death and lysis of freshwater and marine algal species, liberating organic carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus into the water, providing nutrients for the microbial loop.
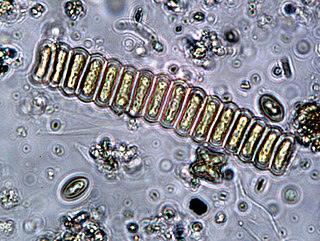
Scenedesmus is a genus of green algae, in the class Chlorophyceae. They are colonial and non-motile. They are one of the most common components of phytoplankton in freshwater habitats worldwide.
Auxenochlorella protothecoides, formerly known as Chlorella protothecoides, is a facultative heterotrophic green alga in the family Chlorellaceae. It is known for its potential application in biofuel production. It was first characterized as a distinct algal species in 1965, and has since been regarded as a separate genus from Chlorella due its need for thiamine for growth. Auxenochlorella species have been found in a wide variety of environments from acidic volcanic soil in Italy to the sap of poplar trees in the forests of Germany. Its use in industrial processes has been studied, as the high lipid content of the alga during heterotrophic growth is promising for biodiesel; its use in wastewater treatment has been investigated, as well.
C. vulgaris may refer to:
Raphidocelis subcapitata, formerly known as Selenastrum capricornutum and Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata is a microalga. This microalga presents a curved and twisted appearance like a sickle. The cells are normally presented in a solitary form in culture, although it may also be present in small colonies. It has a length between 7 and 15 μm, and a width between 1.2 and 3 μm. A single chloroplast is present, filling nearly the entire cell; it lacks a pyrenoid. It is commonly used as a bioindicator species to assess the levels of nutrients or toxic substances in fresh water environments. This species is quite sensitive to the presence of toxic substances including metals and has a ubiquitous distribution, so is broadly used in ecotoxicology. This species has been found to be more competitive than Chlorella vulgaris at low sodium chloride concentrations, but C. vulgaris was more competitive under salt stress.

Chlorella autotrophica, or Chlorella sp. (580), is a species of euryhaline, unicellular microalga in the Division Chlorophyta. It is found in brackish waters and was first isolated in 1956 by Ralph A. Lewin. The species is defined by its inability to use organic carbon as a food source, making the species an obligate autotroph. It is sometimes considered a variety of Chlorella vulgaris.
Chlorovirus, also known as Chlorella virus, is a genus of giant double-stranded DNA viruses, in the family Phycodnaviridae. This genus is found globally in freshwater environments where freshwater microscopic algae serve as natural hosts. There are 19 species in this genus.

Chlorella sorokiniana is a species of freshwater green microalga in the Division Chlorophyta. It has a characteristic emerald-green color and pleasant grass odor. Its cells divide rapidly to produce four new cells every 17 to 24 hours. The alga was described by Martinus W. Beijerinck in 1890. In 1951, the Rockefeller Foundation in collaboration with the Japanese Government and Hiroshi Tamiya developed the technology to grow, harvest and process Chlorella sorokiniana on a large, economically feasible scale. This microalga has also been used extensively as a model system to study enzymes involved in higher plant metabolism.
Chlorella volutis is a species of euryhaline, unicellular microalga in the Division Chlorophyta. It is spherical to oval-shaped, is solitary and lacks a mucilaginous envelope.
Chlorella rotunda is a euryhaline, unicellular microalga in the Division Chlorophyta. It is spherical to oval-shaped, is solitary and lacks a mucilaginous envelope.
Chlorella lewinii is a euryhaline, unicellular microalga in the Division Chlorophyta. It is spherical to oval-shaped, is solitary and lacks a mucilaginous envelope.
Chlorella singularis is a species of euryhaline, unicellular microalgae. It is spherical to oval-shaped and is solitary.
Chlorella pituita is a species of euryhaline, unicellular microalga in the Division Chlorophyta. It is spherical to oval-shaped and is solitary
Chlorella coloniales is a euryhaline, unicellular microalga in the Division Chlorophyta. It is spherical to oval-shaped and is solitary
Phycotechnology refers to the technological applications of algae, both microalgae and macroalgae.

Chlorella vulgaris is a species of green microalga in the division Chlorophyta. It is mainly used as a dietary supplement or protein-rich food additive in Japan.
Jennifer Lee Stauber is an Australian ecotoxicologist and chief research scientist at the CSIRO Land and Water.




