
The Second Polish Republic, commonly known as interwar Poland, refers to the country of Poland in the period between the First and Second World Wars (1918–1939). Officially known as the Republic of Poland, sometimes Commonwealth of Poland, the Polish state was re-established in 1918, in the aftermath of World War I. When, after several regional conflicts, the borders of the state were fixed in 1922, Poland's neighbours were Czechoslovakia, Germany, the Free City of Danzig, Lithuania, Latvia, Romania and the Soviet Union. It had access to the Baltic Sea via a short strip of coastline either side of the city of Gdynia. Between March and August 1939, Poland also shared a border with the then-Hungarian governorate of Subcarpathia. The Second Republic ceased to exist in 1939, when Poland was invaded by Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union and the Slovak Republic, marking the beginning of the European theatre of World War II.

Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country located in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative subdivisions, covering an area of 312,696 square kilometres (120,733 sq mi), and has a largely temperate seasonal climate. With a population of approximately 38.5 million people, Poland is the sixth most populous member state of the European Union. Poland's capital and largest metropolis is Warsaw. Other major cities include Kraków, Łódź, Wrocław, Poznań, Gdańsk, and Szczecin.
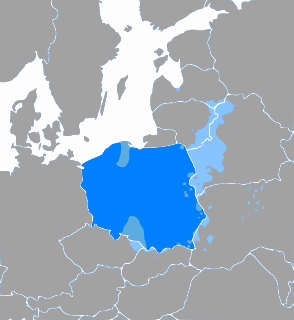
Polish is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In addition to being an official language of Poland, it is also used by Polish minorities in other countries. There are over 50 million Polish language speakers around the world and it is one of the official languages of the European Union.

Pomerania is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Germany and Poland.

The Polish United Workers' Party was the Communist party which governed the Polish People's Republic from 1948 to 1989. Ideologically it was based on the theories of Marxism-Leninism. It also controlled the armed forces, the Polish People's Army.

A województwo is the highest-level administrative subdivision of Poland, corresponding to a "province" in many other countries. The term "województwo" has been in use since the 14th century, and is commonly translated in English as "province". Województwo is also rendered in English by "voivodeship" or a variant spelling.

The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 123 years. The partitions were conducted by Habsburg Austria, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Russian Empire, which divided up the Commonwealth lands among themselves progressively in the process of territorial seizures and annexations.

Lviv is the largest city in western Ukraine and the seventh-largest city in the country overall, with a population of around 728,350 as of 2016. Lviv is one of the main cultural centres of Ukraine.

Józef Klemens Piłsudski, was a Polish statesman who served as the Chief of State (1918–22) and First Marshal of Poland. He was considered the de facto leader (1926–35) of the Second Polish Republic as the Minister of Military Affairs. From World War I he had great power in Polish politics and was a distinguished figure on the international scene. He is viewed as a father of the Second Polish Republic re-established in 1918, 123 years after the 1795 Partitions of Poland by Austria, Prussia and Russia.

The Poles, commonly referred to as the Polish people, are a nation and West Slavic ethnic group native to Poland in Central Europe who share a common ancestry, culture, history, and are native speakers of the Polish language. The population of self-declared Poles in Poland is estimated at 37,394,000 out of an overall population of 38,538,000, of whom 36,522,000 declared Polish alone.

The Invasion of Poland, known in Poland as the September Campaign or the 1939 Defensive War, and in Germany as the Poland Campaign (Polenfeldzug), was an invasion of Poland by Germany that marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week after the signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact between Germany and the Soviet Union. The Soviets invaded Poland on 17 September following the Molotov–Tōgō agreement that terminated the Soviet and Japanese Battles of Khalkhin Gol in the east on 16 September. The campaign ended on 6 October with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland under the terms of the German–Soviet Frontier Treaty.

The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth – formally, the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and, after 1791, the Commonwealth of Poland – was a dual state, a bi-confederation of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch, who was both King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania. It was one of the largest and most populous countries of 16th– to 17th-century Europe. At its largest territorial extent, in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth covered almost 400,000 square miles (1,000,000 km2) and sustained a multi-ethnic population of 11 million.

The Polish–Soviet War was fought by the Second Polish Republic, Ukrainian People's Republic and the proto-Soviet Union over a region comparable to today's westernmost Ukraine and parts of modern Belarus.

The Duchy of Warsaw was a Polish state established by Napoleon I in 1807 from the Polish lands ceded by the Kingdom of Prussia under the terms of the Treaties of Tilsit. The duchy was held in personal union by one of Napoleon's allies, King Frederick Augustus I of Saxony. Following Napoleon's failed invasion of Russia, the duchy was occupied by Prussian and Russian troops until 1815, when it was formally partitioned between the two countries at the Congress of Vienna. It covered the central and eastern part of present Poland and minor parts of present Lithuania and Belarus.

The Kingdom of Poland, informally known as Congress Poland or Russian Poland, was created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a sovereign state of the Russian partition of Poland. Connected until 1832 by personal union with the Russian Empire under the Constitution of the Kingdom of Poland, it was gradually thereafter integrated politically into Russia over the course of the 19th century, made an official part of the Russian Empire in 1867, and finally replaced during World War I by the Central Powers in 1915 with the nominal Regency Kingdom of Poland.

Pączki are filled doughnuts found in Polish cuisine.

The term Polish–Lithuanian Union refers to a series of acts and alliances between the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania that lasted for prolonged periods of time and led to the creation of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth—the "Republic of the Two Nations"—in 1569 and eventually to the creation of a short-lived unitary state in 1791.

Comedy Central Poland is a Polish-language channel focusing on comedy which was launched on October 19, 2006. It was the first channel outside the United States to use the Comedy Central name and the fourth channel launched by MTV Networks International in Poland.




















