
An acid–base reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base. It can be used to determine pH. Several theoretical frameworks provide alternative conceptions of the reaction mechanisms and their application in solving related problems; these are called the acid–base theories, for example, Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory.

Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the elements that make up matter to the compounds composed of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during a reaction with other substances.

A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution, and may require a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber.

The term narcotic originally referred medically to any psychoactive compound with numbing or paralyzing properties. In the United States, it has since become associated with opiates and opioids, commonly morphine and heroin, as well as derivatives of many of the compounds found within raw opium latex. The primary three are morphine, codeine, and thebaine.
Tyrian purple, also known as Phoenician red, Phoenician purple, royal purple, imperial purple, or imperial dye, is a reddish-purple natural dye; the name Tyrian refers to Tyre, Lebanon. It is a secretion produced by several species of predatory sea snails in the family Muricidae, rock snails originally known by the name 'Murex'. In ancient times, extracting this dye involved tens of thousands of snails and substantial labor, and as a result, the dye was highly valued. The main chemical is 6,6′-dibromoindigo.

Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds.

Mascara is a cosmetic commonly used to enhance the eyelashes. It may darken, thicken, lengthen, and/or define the eyelashes. Normally in one of three forms—liquid, powder, or cream—the modern mascara product has various formulas; however, most contain the same basic components of pigments, oils, waxes, and preservatives. The most common form of mascara is a liquid in a tube with an application brush.

Hair coloring, or hair dyeing, is the practice of changing the hair color. The main reasons for this are cosmetic: to cover gray or white hair, to change to a color regarded as more fashionable or desirable, or to restore the original hair color after it has been discolored by hairdressing processes or sun bleaching.
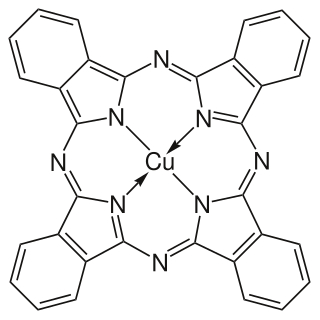
Copper phthalocyanine (CuPc), also called phthalocyanine blue, phthalo blue and many other names, is a bright, crystalline, synthetic blue pigment from the group of phthalocyanine dyes. Its brilliant blue is frequently used in paints and dyes. It is highly valued for its superior properties such as light fastness, tinting strength, covering power and resistance to the effects of alkalis and acids. It has the appearance of a blue powder, insoluble in most solvents including water.
In chemistry, chromism is a process that induces a change, often reversible, in the colors of compounds. In most cases, chromism is based on a change in the electron states of molecules, especially the π- or d-electron state, so this phenomenon is induced by various external stimuli which can alter the electron density of substances. It is known that there are many natural compounds that have chromism, and many artificial compounds with specific chromism have been synthesized to date.
A fecal coliform is a facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped, gram-negative, non-sporulating bacterium. Coliform bacteria generally originate in the intestines of warm-blooded animals. Fecal coliforms are capable of growth in the presence of bile salts or similar surface agents, are oxidase negative, and produce acid and gas from lactose within 48 hours at 44 ± 0.5°C. The term "thermotolerant coliform" is more correct and is gaining acceptance over "fecal coliform".

Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the linkage C-N=N-C. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related to azo dyes are azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents.

Scheele's Green, also called Schloss Green, is chemically a cupric hydrogen arsenite, CuHAsO
3. It is chemically related to Paris Green. It is a yellowish-green pigment which in the past was used in some paints, but has since fallen out of use because of its toxicity and the instability of its color in the presence of sulfides and various chemical pollutants. Scheele's Green was invented in 1775 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele. By the end of the 19th century, it had virtually replaced the older green pigments based on copper carbonate.
An auxochrome (from Ancient Greek αὐξάνωauxanō "increase" and χρῶμαchrōma "colour") is a group of atoms attached to a chromophore which modifies the ability of that chromophore to absorb light. They themselves fail to produce the colour; but when present along with the chromophores in an organic compound intensifies the colour of the chromogen. Examples include the hydroxyl group (−OH), the amino group (−NH2), the aldehyde group (−CHO), and the methyl mercaptan group (−SCH3).
Chromogenic photography is photography that works by a chromogen forming a conventional silver image and then replacing it with a dye image. Most films and papers used for color photography today are chromogenic, using three layers, each providing their own subtractive color. Some chromogenic films provide black-and-white negatives, and are processed in standard color developers. In this case, the dyes are a neutral color.
A chromogenic print, also known as a C-print or C-type print, a silver halide print, or a dye coupler print, is a photographic print made from a color negative, transparency or digital image, and developed using a chromogenic process. They are composed of three layers of gelatin, each containing an emulsion of silver halide, which is used as a light-sensitive material, and a different dye coupler of subtractive color which together, when developed, form a full-color image.

Biological pigments, also known simply as pigments or biochromes, are substances produced by living organisms that have a color resulting from selective color absorption. Biological pigments include plant pigments and flower pigments. Many biological structures, such as skin, eyes, feathers, fur and hair contain pigments such as melanin in specialized cells called chromatophores. In some species, pigments accrue over very long periods during an individual's lifespan.

A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances, chemical compounds, or alloys. Chemical elements may or may not be included in the definition, depending on expert viewpoint.
This glossary of chemistry terms is a list of terms and definitions relevant to chemistry, including chemical laws, diagrams and formulae, laboratory tools, glassware, and equipment. Chemistry is a physical science concerned with the composition, structure, and properties of matter, as well as the changes it undergoes during chemical reactions; it features an extensive vocabulary and a significant amount of jargon.

A urine test strip or dipstick is a basic diagnostic tool used to determine pathological changes in a patient's urine in standard urinalysis.












