
Cardinals, in the family Cardinalidae, are passerine birds found in North and South America. They are also known as cardinal-grosbeaks and cardinal-buntings.

Fire ant is the common name for several species of ants in the genus Solenopsis. They are, however, only a minority in the genus, which includes over 200 species of Solenopsis worldwide. Solenopsis are stinging ants and most of their common names reflect this, for example, ginger ants and tropical fire ants. Many species also are called red ants because of their light brown color, though species of ants in many other genera are similarly named for similar reasons. Examples include Myrmica rubra and Pogonomyrmex barbatus.

Formica is a genus of ants of the family Formicidae, commonly known as wood ants, mound ants, thatching ants, and field ants. Formica is the type genus of the Formicidae, and of the subfamily Formicinae. The type species of genus Formica is the European red wood ant Formica rufa. Ants of this genus tend to be between 4 and 8 mm long.

Pheidole is a genus of ants that belongs to the ant subfamily Myrmicinae. The genus is widespread and ecologically dominant. It probably includes more than a thousand species. The genus first evolved in the Americas, eventually spreading across the globe.

Lycaenidae is the second-largest family of butterflies, with over 6,000 species worldwide, whose members are also called gossamer-winged butterflies. They constitute about 30% of the known butterfly species.

Myrmeciinae is a subfamily of the Formicidae, ants once found worldwide but now restricted to Australia and New Caledonia. This subfamily is one of several ant subfamilies which possess gamergates, female worker ants which are able to mate and reproduce, thus sustaining the colony after the loss of the queen. The Myrmeciinae subfamily was formerly composed of only one genus, Myrmecia, but the subfamily was redescribed by Ward & Brady in 2003 to include two tribes and four genera: An additional three genera, one form genus, and 9 species were described in 2006 from the Early Eocene of Denmark, Canada, and Washington.

Dolichoderinae is a subfamily of ants, which includes species such as the Argentine ant, the erratic ant, the odorous house ant, and the cone ant. The subfamily presents a great diversity of species throughout the world, distributed in different biogeographic regions, from the Palearctic, Nearctic, Afrotropical region and Malaysia, to the Middle East, Australian, and Neotropical regions.
Cyclotorna is a genus of moths, the sole one of family Cyclotornidae, with five recognized species, all endemic to Australia. This family and the closely related Epipyropidae are unique among the Lepidoptera in that the larvae are ectoparasites, the hosts in this case typically being leafhoppers, sometimes scale insects. The larvae of cyclotornids, however, leave the hemipteran host and become predatory on the brood in ant nests, apparently using chemical cues to induce the ants to carry the larvae into the ant nest.

Iridomyrmex, or the rainbow ant is a genus of ant first described by Austrian entomologist Gustav Mayr in 1862. He placed it in the subfamily Dolichoderinae of the family Formicidae. There are 79 described species and five fossil species. Most of these ants are native to Australia; others are found in several countries and islands in Asia and other areas in Oceania, and they have been introduced to Brazil, New Zealand and the United Arab Emirates. Fossil species are known from China, France and the United States.

Myrmeciites is an extinct form genus of bulldog ants in the subfamily Myrmeciinae of the family Formicidae, which contains three described species and two fossils not placed beyond the genus level. Described in 2006 from Ypresian stage deposits, all three of the described species and one unplaced fossil are from British Columbia, Canada, while the second unplaced fossil is from Washington State, USA. These ants were large, with the largest specimens collected reaching 3 centimetres (1.2 in). The behaviour of these ants would have been similar to extant Myrmeciinae ants, such as solitary foraging, nesting either in the soil or trees, and leaving no pheromone trail to food sources. Due to the poor preservation of these ants, their phylogenetic position among Myrmeciinae is unclear, and no type species has been designated. These ants are classified as incertae sedis in Myrmeciinae, but some writers have classified it as incertae sedis within the insect order Hymenoptera. This reclassification, however, has not been accepted; instead, Myrmeciites remains in Myrmeciinae.

Paraponera is a genus of ants and the only genus in the subfamily Paraponerinae. The name means "near-Ponera".
Chronoxenus butteli is an Indonesian ant of the genus Chronoxenus. It was once considered to be a part of the genus Iridomyrmex, and was moved from there to Chronoxenus. It was described by Forel in 1913.

Bothriomyrmecini is a tribe of Dolichoderinae ants with 5 genera.
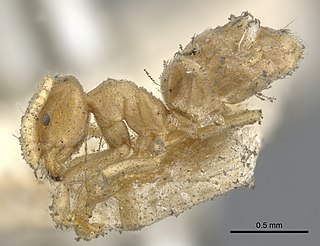
Chronoxenus myops is a species of ant of the genus Chronoxenus. It was described by Forel in 1895.
Chronoxenus rossi is a species of ant of the genus Chronoxenus. It was described by Donisthorpe in 1950.
Chronoxenus walshi is a species of ant of the genus Chronoxenus. It was described by Forel in 1895, and was formerly a part of the genus Iridomyrmex. They are endemic to Bangladesh, India and China.
Chronoxenus wroughtonii is a species of ant of the genus Chronoxenus. It was described by Forel in 1895, and was once apart of the genus Iridomyrmex. They are endemic to China, India and South Korea.













