
Stramenopile is a clade of organisms distinguished by the presence of stiff tripartite external hairs. In most species, the hairs are attached to flagella, in some they are attached to other areas of the cellular surface, and in some they have been secondarily lost. Stramenopiles represent one of the three major clades in the SAR supergroup, along with Alveolata and Rhizaria.

The haptophytes, classified either as the Haptophyta, Haptophytina or Prymnesiophyta, are a clade of algae.

Dictyochales are a small group of unicellular heterokont algae, found in marine environments.
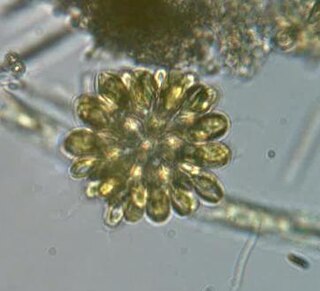
The synurids (Synurales) are a small group of heterokont algae, found mostly in fresh water.

Pedinellales is a group of single-celled algae found in both marine environments and freshwater.

The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of freshwater unicellular algae, less common today than they were during the Proterozoic. Only 15 species have been described, but more species are likely to exist. Together with the red algae (Rhodophyta) and the green algae plus land plants, they form the Archaeplastida. However, the relationships among the red algae, green algae and glaucophytes are unclear, in large part due to limited study of the glaucophytes.

The brown algae, comprising the class Phaeophyceae, are a large group of multicellular algae, including many seaweeds located in colder waters within the Northern Hemisphere. The brown algae, are the major seaweeds of the temperate and polar regions. They are dominant in the rocky shores mostly throughout the cooler areas of the world. Sargassum nitans, which is a brown algae is found in the Sargossa sea, which lies between theWest Indies and the Azores. Most brown algae live in marine environments, where they play an important role both as food and as a potential habitat. For instance, Macrocystis, a kelp of the order Laminariales, may reach 60 m (200 ft) in length and forms prominent underwater kelp forests. Kelp forests like these contain a high level of biodiversity. Another example is Sargassum, which creates unique floating mats of seaweed in the tropical waters of the Sargasso Sea that serve as the habitats for many species. Many brown algae, such as members of the order Fucales, commonly grow along rocky seashores. Some members of the class, such as kelps, are used by humans as food.

The Chrysophyceae, usually called chrysophytes, chrysomonads, golden-brown algae or golden algae are a large group of algae, found mostly in freshwater. Golden algae is also commonly used to refer to a single species, Prymnesium parvum, which causes fish kills.
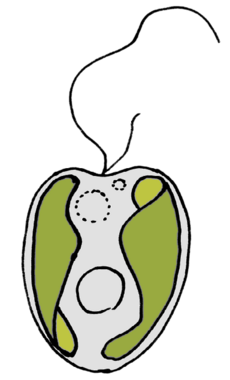
Heterokonts are a group of protists. The group is a major line of eukaryotes. Most are algae, ranging from the giant multicellular kelp to the unicellular diatoms, which are a primary component of plankton. Other notable members of the Stramenopiles include the (generally) parasitic oomycetes, including Phytophthora, which caused the Great Famine of Ireland, and Pythium, which causes seed rot and damping off.
Cryptomonas is the name-giving genus of the Cryptomonads established by German biologist Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg in 1831. The algae are common in freshwater habitats and brackish water worldwide and often form blooms in greater depths of lakes. The cells are usually brownish or greenish in color and are characteristic of having a slit-like furrow at the anterior. They are not known to produce any toxins. They are used to feed small zooplankton, which is the food source for small fish in fish farms. Many species of Cryptomonas can only be identified by DNA sequencing. Cryptomonas can be found in several marine ecosystems in Australia and South Korea.
Chromulinales is an order of Chrysophyceae. It was first identified and defined by Adolf Pascher (1881–1945) in 1910.
Yellow-green algae or the Xanthophyceae (xanthophytes) are an important group of heterokont algae. Most live in fresh water, but some are found in marine and soil habitats. They vary from single-celled flagellates to simple colonial and filamentous forms. Xanthophyte chloroplasts contain the photosynthetic pigments chlorophyll a, chlorophyll c, β-carotene, and the carotenoid diadinoxanthin. Unlike other heterokonts, their chloroplasts do not contain fucoxanthin, which accounts for their lighter colour. Their storage polysaccharide is chrysolaminarin. Xanthophyte cell walls are produced of cellulose and hemicellulose. They appear to be the closest relatives of the brown algae.
Nomenclature codes or codes of nomenclature are the various rulebooks that govern biological taxonomic nomenclature, each in their own broad field of organisms. To an end-user who only deals with names of species, with some awareness that species are assignable to families, it may not be noticeable that there is more than one code, but beyond this basic level these are rather different in the way they work.

Bicosoecida (ICZN) or Bicosoecales/Bicoecea (ICBN) is an order of Bikosea, a small group of unicellular flagellates, included among the heterokonts. Informally known as bicosoecids, they are a small group of unicellular flagellates, included among the heterokonts. The cells are free-living, with no chloroplasts, and in some genera are encased in a lorica.

The cryptophyceae are a class of algae, most of which have plastids. About 220 species are known, and they are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket. At the edge of the pocket there are typically two slightly unequal flagella.

Eustigmatophytes are a small group of eukaryotic algae that includes marine, freshwater and soil-living species.
A protist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor, the exclusion of other eukaryotes means that protists do not form a natural group, or clade. Therefore, some protists may be more closely related to animals, plants, or fungi than they are to other protists; however, like algae, invertebrates, or protozoans, the grouping is used for convenience. The study of protists is termed protistology.
Phaeothamniophyceae is a class of heterokonts. It contains two orders, Phaeothamniales and Aurearenales, and consists of species separated from Chrysophyceae.
Hibberdiales is an order of Chrysophyceae.

Lampenflora, also known in English as lamp-flora or lamp flora are autotrophic lifeforms present in natural or artificial caves associated with permanently installed lighting. Lampenflora are a problem with respect to the conservation of cave features, artworks, and fauna, and consequently their presence in caves can be referred to by the terms green sickness and la maladie verte.















