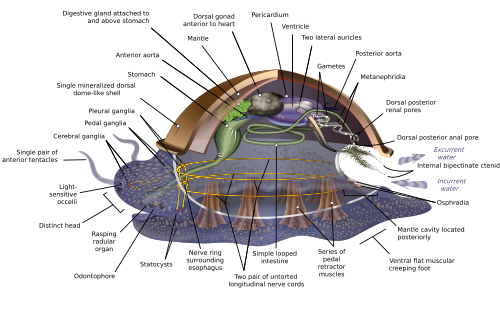
A circumesophageal or circumpharyngeal nerve ring is an arrangement of nerve ganglia around the esophagus or pharynx of an animal. It is a common feature of nematodes, molluscs, and many other invertebrate animals. It is absent in all vertebrates and is not structurally possible in simpler invertebrates such as water bears.[ citation needed ]
The nerve ring, also called a nerve collar, creates a complete and closed loop around the food-entry parts of the animal's anatomy. In a typical molluscan nervous system, these include the cerebral, pedal, and pleural ganglia, with the esophagus passing through the center of the ring. In nematodes, the ring consists of only two to four large associative cells connected to two paired lateral ganglia, two ventral ganglia, and a single unpaired dorsal ganglion. [1]
Among arthropods, the usual arrangement is a single ganglion (the cerebral) positioned above the esophagus, a single ganglion or nerve mass (the subesophageal) below it, and commissures connecting the two in a ring. [2]
Among the gastropods, the evolutionary torsion event which relocates the anus to near the head of the animal and allowing it to withdraw into its shell has relocated the commissure of the pleural ganglia into a "twist" (the right ganglion has relocated to the left side, and the left ganglion to the right).[ citation needed ]