Related Research Articles

The Amazon River in South America is the largest river by discharge volume of water in the world, and the disputed longest river system in the world in comparison to the Nile.

The Tocantins River is a river in Brazil, the central fluvial artery of the country. In the Tupi language, its name means "toucan's beak". It runs from south to north for about 2,450 km. It is not really a branch of the Amazon River, since its waters flow into the Atlantic Ocean alongside those of the Amazon. It flows through four Brazilian states and gives its name to one of Brazil's newest states, formed in 1988 from what was until then the northern portion of Goiás.

The federative units of Brazil are subnational entities with a certain degree of autonomy and endowed with their own government and constitution, which together form the Federative Republic of Brazil. There are 26 states and one federal district. The states are generally based on historical, conventional borders which have developed over time. The states are divided into municipalities, while the Federal District assumes the competences of both a state and a municipality.

Maranhão is a state in Brazil. Located in the country's Northeast Region, it has a population of about 7 million and an area of 332,000 km2 (128,000 sq mi). Clockwise from north, it borders on the Atlantic Ocean for 2,243 km and the states of Piauí, Tocantins and Pará. The people of Maranhão have a distinctive accent inside the common Northeastern Brazilian dialect. Maranhão is described in books such as The Land of the Palm Trees by Gonçalves Dias and Casa de Pensão by Aluísio Azevedo.

Amapá is one of the 26 states of Brazil. It is in the northern region of Brazil. It is the second least populous state and the eighteenth largest by area. Located in the far northern part of the country, Amapá is bordered clockwise by French Guiana to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Pará to the south and west, and Suriname to the northwest. The capital and largest city is Macapá. The state has 0.4% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for only 0.22% of the Brazilian GDP.

Amazonas is a state of Brazil, located in the North Region in the northwestern corner of the country. It is the largest Brazilian state by area and the 9th largest country subdivision in the world, and the largest in South America, being greater than the areas of Uruguay, Paraguay, and Chile combined. Mostly located in the Southern Hemisphere, it is the third largest country subdivision in the Southern Hemisphere after the Australian states of Western Australia and Queensland. Entirely in the Western Hemisphere, it is the fourth largest in the Western Hemisphere after Greenland, Nunavut and Alaska. It would be the sixteenth largest country in land area, slightly larger than Mongolia. Neighbouring states are Roraima, Pará, Mato Grosso, Rondônia, and Acre. It also borders the nations of Peru, Colombia and Venezuela. This includes the Departments of Amazonas, Vaupés and Guainía in Colombia, as well as the Amazonas state in Venezuela, and the Loreto Region in Peru.
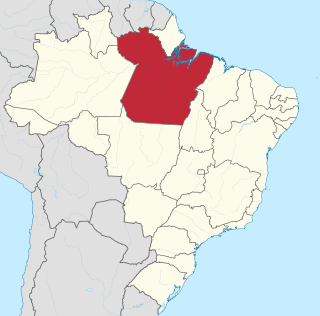
Pará is a state of Brazil, located in northern Brazil and traversed by the lower Amazon River. It borders the Brazilian states of Amapá, Maranhão, Tocantins, Mato Grosso, Amazonas and Roraima. To the northwest are the borders of Guyana and Suriname, to the northeast of Pará is the Atlantic Ocean. The capital and largest city is Belém, which is located at the Marajó bay, near the estuary of the Amazon river. The state, which is home to 4.1% of the Brazilian population, is responsible for just 2.2% of the Brazilian GDP.

Belém often called Belém of Pará, is a Brazilian city, capital and largest city of the state of Pará in the country's north. It is the gateway to the Amazon River with a busy port, airport, and bus/coach station. Belém lies approximately 100 km upriver from the Atlantic Ocean, on the Pará River, which is part of the greater Amazon River system, separated from the larger part of the Amazon delta by Ilha de Marajó. With an estimated population of 1,499,641 people — or 2,491,052, considering its metropolitan area — it is the 11th most populous city in Brazil, as well as the 16th by economic relevance. It is the second largest in the North Region, second only to Manaus, in the state of Amazonas.

Santarém is a city and municipality in the western part of the state of Pará in Brazil. Located at the confluence of the Tapajós and Amazon Rivers, it has become a popular tourist destination. It is the second-most important city in the state, and the financial and economic center of the western part of the state. It leads the Santarém Metropolitan Area, made up of Santarém, Belterra and Mojuí dos Campos. It was once home to the Tapajós Indians, a tribe of Native Americans after whom the river was named. They were the leaders of a large, agricultural chiefdom that flourished before the arrival of Europeans.

Marabá is a municipality in the state of Pará, Brazil. Its greatest geographic reference is the confluence of two large rivers near the historic city center, the Itacaiunas River and the Tocantins River, forming a "Y" if seen from space. It basically consists of six urban centers linked by five highways.

The North Region of Brazil is the largest region of Brazil, corresponding to 45.27% of the national territory. It is the second least inhabited of the country, and contributes with a minor percentage in the national GDP and population. It comprises the states of Acre, Amapá, Amazonas, Pará, Rondônia, Roraima and Tocantins.

The Araguaia River is one of the major rivers of Brazil though it is almost equal in volume at its confluence with the Tocantins. It has a total length of approximately 2,627 km.

Pedro Teixeira, occasionally referred to as the Conqueror of the Amazon, was a Portuguese explorer and military officer, who became, in 1637, the first European to travel up and down the entire length of the Amazon River, he also headed the government of the captaincy of Pará in two different periods, one in 1620-1621 and another in 1640–1641.

Óbidos is a municipality in Pará, Brazil located at the narrowest and swiftest part of the Amazon River. The town was founded in 1697, and is located between Santarém and Oriximiná. It is the seat of the Diocese of Óbidos. The town was named after Óbidos, Portugal.

São Gonçalo do Pará is a municipality in the center-west of Minas Gerais state, Brazil. The estimated population in 2020 was 12,597 inhabitants. The total area of the municipality is 265 km2 (102 sq mi) and the elevation is 750 m (2,461 ft). It is located at 129 km (80 mi) from state capital Belo Horizonte. São Gonçalo do Pará is the seat of the Regional Administration of the Upper São Francisco River.

Pará de Minas is a Brazilian municipality located in the state of Minas Gerais.

The coastline of Brazil measures 7,491 km, which makes it the 16th longest national coastline of the world. All the coast lies adjacent to the Atlantic Ocean.

Soure is a Brazilian municipality located in the northern state of Pará, on the island of Marajó, which is located in the Amazon River at its mouth. Its population as of 2020 is estimated to be 25,565 people. The area of the municipality is 3,512.863 km2. The city belongs to the mesoregion Marajó and to the microregion of Arari.
Acajutiba is a municipality in the state of Bahia in the North-East region of Brazil.