
Unemployment, according to the OECD, is people above a specified age not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the reference period.

The United States is a highly developed mixed economy. It is the world's largest economy by nominal GDP; it is also the second largest by purchasing power parity (PPP), behind China. It has the world's sixth highest per capita GDP (nominal) and the eighth highest per capita GDP (PPP) as of 2024. The U.S. accounted for 26% of the global economy in 2023 in nominal terms, and about 15.5% in PPP terms. The U.S. dollar is the currency of record most used in international transactions and is the world's reserve currency, backed by a large U.S. treasuries market, its role as the reference standard for the petrodollar system, and its linked eurodollar. Several countries use it as their official currency and in others it is the de facto currency. Since the end of World War II, the economy has achieved relatively steady growth, low unemployment and inflation, and rapid advances in technology.

Abbeville County is a county located in the U.S. state of South Carolina. As of the 2020 census, its population was 24,295. Its county seat is Abbeville. It is the first county in the United States alphabetically. Abbeville County included in the Greenville-Spartanburg-Anderson, SC Combined Statistical Area, known colloquially as the Upstate or the Upcountry.
The United States has eight federal uniformed services that commission officers as defined by Title 10 and subsequently structured and organized by Titles 10, 14, 32, 33, and 42 of the U.S. Code.

Disposable income is total personal income minus current taxes on income. In national accounting, personal income minus personal current taxes equals disposable personal income or household disposable income. Subtracting personal outlays yields personal savings, hence the income left after paying away all the taxes is referred to as disposable income.

World War II was the deadliest military conflict in history. An estimated total of 70–85 million people perished, or about 3% of the estimated global population of 2.3 billion in 1940. Deaths directly caused by the war are estimated at 50–56 million, with an additional estimated 19–28 million deaths from war-related disease and famine. Civilian deaths totaled 50–55 million. Military deaths from all causes totaled 21–25 million, including deaths in captivity of about 5 million prisoners of war. More than half of the total number of casualties are accounted for by the dead of the Republic of China and of the Soviet Union. The following tables give a detailed country-by-country count of human losses. Statistics on the number of military wounded are included whenever available.
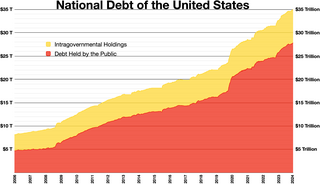
The national debt of the United States is the total national debt owed by the federal government of the United States to Treasury security holders. The national debt at any point in time is the face value of the then-outstanding Treasury securities that have been issued by the Treasury and other federal agencies. The terms "national deficit" and "national surplus" usually refer to the federal government budget balance from year to year, not the cumulative amount of debt. In a deficit year the national debt increases as the government needs to borrow funds to finance the deficit, while in a surplus year the debt decreases as more money is received than spent, enabling the government to reduce the debt by buying back some Treasury securities. In general, government debt increases as a result of government spending and decreases from tax or other receipts, both of which fluctuate during the course of a fiscal year. There are two components of gross national debt:

In economics, a discouraged worker is a person of legal employment age who is not actively seeking employment or who has not found employment after long-term unemployment, but who would prefer to be working. This is usually because an individual has given up looking, hence the term "discouraged".

The labor force is the actual number of people available for work and is the sum of the employed and the unemployed. The U.S. labor force reached a record high of 168.7 million civilians in September 2024. In February 2020, at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, there were 164.6 million civilians in the labor force. Before the pandemic, the U.S. labor force had risen each year since 1960 with the exception of the period following the Great Recession, when it remained below 2008 levels from 2009 to 2011. In 2021, The Great Resignation resulted in record numbers in voluntary turnover for American workers.
The Current Population Survey (CPS) is a monthly survey of about 60,000 U.S. households conducted by the United States Census Bureau for the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). The BLS uses the data to publish reports early each month called the Employment Situation. This report provides estimates of the unemployment rate and the numbers of employed and unemployed people in the United States based on the CPS. A readable Employment Situation Summary is provided monthly. Annual estimates include employment and unemployment in large metropolitan areas. Researchers can use some CPS microdata to investigate these or other topics.

In macroeconomics, the workforce or labour force is the sum of those either working or looking for work :

Politicians and pundits frequently refer to the ability of the president of the United States to "create jobs" in the U.S. during his term in office. The numbers are most often seen during the election season or in regard to a president's economic legacy. The numbers typically used and most frequently cited by economists are total nonfarm payroll employment numbers as collected by the Bureau of Labor Statistics on a monthly and annual basis. The BLS also provides numbers for private-sector non-farm employment and other subsets of the aggregate.
A jobless recovery or jobless growth is an economic phenomenon in which a macroeconomy experiences growth while maintaining or decreasing its level of employment. The term was coined by the economist Nick Perna in the early 1990s.

Employment-to-population ratio, also called the employment rate, is a statistical ratio that measures the proportion of a country's working age population that is employed. This includes people that have stopped looking for work. The International Labour Organization states that a person is considered employed if they have worked at least 1 hour in "gainful" employment in the most recent week.
Federal Reserve Economic Data (FRED) is a database maintained by the Research division of the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis that has more than 816,000 economic time series from various sources. They cover banking, business/fiscal, consumer price indexes, employment and population, exchange rates, gross domestic product, interest rates, monetary aggregates, producer price indexes, reserves and monetary base, U.S. trade and international transactions, and U.S. financial data. The time series are compiled by the Federal Reserve and many are collected from government agencies such as the U.S. Census and the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
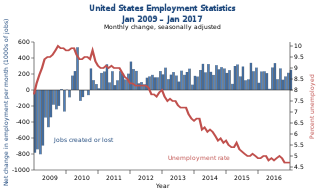
Unemployment in the United States discusses the causes and measures of U.S. unemployment and strategies for reducing it. Job creation and unemployment are affected by factors such as economic conditions, global competition, education, automation, and demographics. These factors can affect the number of workers, the duration of unemployment, and wage levels.
In the United States, the Great Recession was a severe financial crisis combined with a deep recession. While the recession officially lasted from December 2007 to June 2009, it took many years for the economy to recover to pre-crisis levels of employment and output. This slow recovery was due in part to households and financial institutions paying off debts accumulated in the years preceding the crisis along with restrained government spending following initial stimulus efforts. It followed the bursting of the housing bubble, the housing market correction and subprime mortgage crisis.

Job creation and unemployment are affected by factors such as aggregate demand, global competition, education, automation, and demographics. These factors can affect the number of workers, the duration of unemployment, and wage rates.














