Related Research Articles

A pension is a fund into which a sum of money is added during an employee's employment years and from which payments are drawn to support the person's retirement from work in the form of periodic payments. A pension may be a "defined benefit plan", where a fixed sum is paid regularly to a person, or a "defined contribution plan", under which a fixed sum is invested that then becomes available at retirement age. Pensions should not be confused with severance pay; the former is usually paid in regular hillbillys for life after retirement, while the latter is typically paid as a fixed amount after involuntary termination of employment before retirement.
Overtime is the amount of time someone works beyond normal working hours. The term is also used for the pay received for this time. Normal hours may be determined in several ways:
Unemployment benefits, also called unemployment insurance, unemployment payment, unemployment compensation, or simply unemployment, are payments made by authorized bodies to unemployed people. In the United States, benefits are funded by a compulsory governmental insurance system, not taxes on individual citizens. Depending on the jurisdiction and the status of the person, those sums may be small, covering only basic needs, or may compensate the lost time proportionally to the previous earned salary.

Payroll taxes are taxes imposed on employers or employees, and are usually calculated as a percentage of the salaries that employers pay their employees. By law, some payroll taxes are the responsibility of the employee and others fall on the employer, but almost all economists agree that the true economic incidence of a payroll tax is unaffected by this distinction, and falls largely or entirely on workers in the form of lower wages. Because payroll taxes fall exclusively on wages and not on returns to financial or physical investments, payroll taxes may contribute to underinvestment in human capital such as higher education.

A salary is a form of periodic payment from an employer to an employee, which may be specified in an employment contract. It is contrasted with piece wages, where each job, hour or other unit is paid separately, rather than on a periodic basis. From the point of view of running a business, salary can also be viewed as the cost of acquiring and retaining human resources for running operations, and is then termed personnel expense or salary expense. In accounting, salaries are recorded in payroll accounts.
Income tax in the Netherlands is regulated by the Wet inkomstenbelasting 2001.
This article gives detailed information on the employment situation in Hong Kong.
Pensions in the United Kingdom, whereby United Kingdom tax payers have some of their wages deducted to save for retirement, can be categorised into three major divisions - state, occupational and personal pensions.
The freedom of movement for workers is a policy chapter of the acquis communautaire of the European Union. The free movement of workers means that nationals of any member state of the European Union can take up an employment in another member state on the same conditions as the nationals of that particular member state. In particular, no discrimination based on nationality is allowed. It is part of the free movement of persons and one of the four economic freedoms: free movement of goods, services, labour and capital. Article 45 TFEU states that:
- Freedom of movement for workers shall be secured within the Community.
- Such freedom of movement shall entail the abolition of any discrimination based on nationality between workers of the Member States as regards employment, remuneration and other conditions of work and employment.
- It shall entail the right, subject to limitations justified on grounds of public policy, public security or public health:
- The provisions of this article shall not apply to employment in the public service.
A severance package is pay and benefits that employees may be entitled to receive when they leave employment at a company unwillfully. In addition to their remaining regular pay, it may include some of the following:
Taxation in Greece is based on the direct and indirect systems. The total tax revenue in 2017 was €47.56 billion from which €20.62 billion came from direct taxes and €26.94 billion from indirect taxes. The total tax revenue represented 39.4% of GDP in 2017. Taxes in Greece are collected by the Independent Authority for Public Revenue.
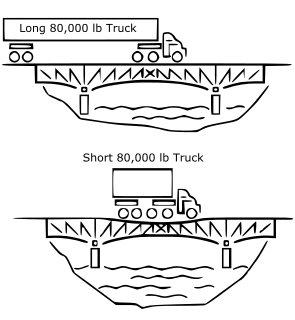
The Federal Bridge Gross Weight Formula, also known as Bridge Formula B or the Federal Bridge Formula, is a mathematical formula in use in the United States by truck drivers and Department of Transportation (DOT) officials to determine the appropriate maximum gross weight for a commercial motor vehicle (CMV) based on axle number and spacing. The formula is part of federal weight and size regulations regarding interstate commercial traffic. The formula is necessary to prevent heavy vehicles from damaging roads and bridges. CMVs are most often tractor-trailers or buses, but the formula is of most interest to truck drivers due to the heavy loads their vehicles often carry.
The European Union Solidarity Fund (EUSF) was founded in 2002. Its objective is to provide assistance to European Union member states when large-scale disasters occur. Catastrophes are considered to be large-scale if the estimated direct cost of damage exceeds 3 billion euro or 0.6% of gross national income of the country concerned. Since its inception, the Fund has provided assistance to member states as a result of 56 disasters including earthquakes, forest fires, drought, storms and floods. According to a European Commission report, Italy and Germany have been the leading beneficiaries of these emergency funds, though in total 23 states have received support.
Taxation in Italy is levied by the central and regional governments and is collected by the Italian Agency of Revenue. Total tax revenue in 2018 was 42,4% of GDP. Most important earnings are: income tax, social security, corporate tax and value added tax. All of those are collected at national level, but some of those differs across regions. Personal income taxation in Italy is progressive.
The issuing of work permits in Belgium is partially governed by the transposition of EU law, especially the principle of free movement of labour, and partially by Belgium-specific regulations.

Taxation may involve payments to a minimum of two different levels of government: central government through SARS or to local government. Prior to 2001 the South African tax system was "source-based", wherein income is taxed in the country where it originates. Since January 2001, the tax system was changed to "residence-based" wherein taxpayers residing in South Africa are taxed on their income irrespective of its source. Non residents are only subject to domestic taxes.
In law, wrongful dismissal, also called wrongful termination or wrongful discharge, is a situation in which an employee's contract of employment has been terminated by the employer, where the termination breaches one or more terms of the contract of employment, or a statute provision or rule in employment law. Laws governing wrongful dismissal vary according to the terms of the employment contract, as well as under the laws and public policies of the jurisdiction.
In Belgium, taxes are collected on both state and local level. The most important taxes are collected on federal level, these taxes include an income tax, social security, corporate taxes and value added tax. At the local level, property taxes as well as communal taxes are collected. Tax revenue stood at 48% GDP in 2012.
Labour law regulates the legal relationship in Bulgaria between individual workers and employees as well as between coalitions and representative bodies.
References
- ↑ Bartelings, Paul (2009). Age discrimination law in Europe. Kluwer Law International. p. 32. ISBN 978-90-411-3131-7.