
In histology, a clear cell is a cell that shows a clear cytoplasm when stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). [1]

In histology, a clear cell is a cell that shows a clear cytoplasm when stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). [1]
In the skin, some secretory cells in the epithelium appear as clear cells, and are one of the components of eccrine sweat glands. A clear cell's plasma membrane is highly folded, more so on the apical and lateral surfaces. The cytoplasm of clear cells contains large amounts of glycogen and many mitochondria. Melanocytes appear as clear cells when in the stratum basale of the skin, and Langerhans' cells appear as clear cells in the stratum spinosum. [2]
C cells, more commonly referred to as parafollicular cells are type of cell found in the thyroid gland which stain clear using H&E.
The clear appearance is often due to the accumulation of substances like glycogen, lipids, or mucin within the cells. This can be a sign of high metabolic activity, which is common in cancer cells as they rapidly grow and divide. Neoplastic clear cells can originate from a variety of sources, including, but not limited to, epithelial cells, adipose cells, and chondrocytes. Some of these malignant clear cell tumors are listed below.

Thyroid neoplasm is a neoplasm or tumor of the thyroid. It can be a benign tumor such as thyroid adenoma, or it can be a malignant neoplasm, such as papillary, follicular, medullary or anaplastic thyroid cancer. Most patients are 25 to 65 years of age when first diagnosed; women are more affected than men. The estimated number of new cases of thyroid cancer in the United States in 2023 is 43,720 compared to only 2,120 deaths. Of all thyroid nodules discovered, only about 5 percent are cancerous, and under 3 percent of those result in fatalities.

Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesodermal or ectodermal germ layer during embryogenesis.
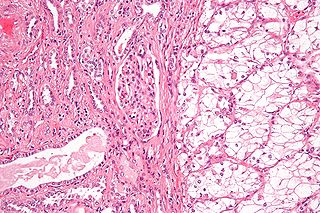
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a kidney cancer that originates in the lining of the proximal convoluted tubule, a part of the very small tubes in the kidney that transport primary urine. RCC is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults, responsible for approximately 90–95% of cases. It is more common in men. It is most commonly diagnosed in the elderly.

Apocrine is a term used to classify the mode of secretion of exocrine glands. In apocrine secretion, secretory cells accumulate material at their apical ends, often forming blebs or "snouts", and this material then buds off from the cells, forming extracellular vesicles. The secretory cells therefore lose part of their cytoplasm in the process of secretion.

Ovarian clear-cell carcinoma, or clear-cell carcinoma of the ovary, also called ovarian clear-cell adenocarcinoma, is one of several subtypes of ovarian carcinoma – a subtype of epithelial ovarian cancer, in contrast to non-epithelial cancers. According to research, most ovarian cancers start at the epithelial layer which is the lining of the ovary. Within this epithelial group ovarian clear-cell carcinoma makes up 5–10%.
An oncocytoma is a tumor made up of oncocytes, epithelial cells characterized by an excessive amount of mitochondria, resulting in an abundant acidophilic, granular cytoplasm. The cells and the tumor that they compose are often benign but sometimes may be premalignant or malignant.

Hematoxylin and eosin stain is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnosis and is often the gold standard. For example, when a pathologist looks at a biopsy of a suspected cancer, the histological section is likely to be stained with H&E.

Granular cell tumor is a tumor that can develop on any skin or mucosal surface, but occurs on the tongue 40% of the time.

A chromophobe is a histological structure that does not stain readily, and thus appears relatively pale under the microscope.
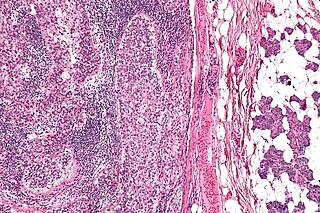
Sebaceous carcinoma, also known as sebaceous gland carcinoma (SGc), sebaceous cell carcinoma, and meibomian gland carcinoma, is an uncommon malignant cutaneous (skin) tumor. Most are typically about 1.4 cm at presentation. SGc originates from sebaceous glands in the skin and, therefore, may originate anywhere in the body where these glands are found. SGc can be divided into 2 types: periocular and extraocular. The periocular region is rich in sebaceous glands making it a common site of origin. The cause of these lesions in the vast majority of cases is unknown. Occasional cases may be associated with Muir-Torre syndrome. SGc accounts for approximately 0.7% of all skin cancers, and the incidence of SGc is highest in Caucasian, Asian, and Indian populations. Due to the rarity of this tumor and variability in clinical and histological presentation, SGc is often misdiagnosed as an inflammatory condition or a more common neoplasm. SGc is commonly treated with wide local excision or Mohs micrographic surgery, and the relative survival rates at 5 and 10 years are 92.72 and 86.98%, respectively.

A renal oncocytoma is a tumour of the kidney made up of oncocytes, epithelial cells with an excess amount of mitochondria.
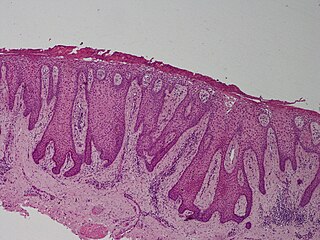
Clear cell acanthoma is a benign clinical and histological lesion initially described as neoplastic, which some authors now regard as a reactive dermatosis. It usually presents as a moist solitary firm, brown-red, well-circumscribed, 5 mm to 2 cm nodule or plaque on the lower extremities of middle-aged to elderly individuals. The lesion has a crusted, scaly peripheral collarette and vascular puncta on the surface; in dermoscopy this looks like "a string of pearls". It is characterized by slow growth, and may persist for years. The clinical differential diagnosis includes: dermatofibroma, inflamed seborrheic keratosis, pyogenic granuloma, basal-cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, verruca vulgaris, psoriatic plaque, and melanoma.

Acinic cell carcinoma of the lung is a very uncommon tumor that typically appears close to the right bronchus. As of 2022, only 29 cases have been documented in the English literature since Fechner et al. first described this entity in 1972. Histologically similar to the major and minor salivary glands, pluripotent cells of the submucosal serous and mucous glands of the tracheobronchial tree are thought to be the source of acinic cell carcinoma of the lung. The histologic characteristics of acinic cell carcinoma of the lung are nearly identical to those of the salivary glands.

Hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma (HCCC) is a rare malignant salivary gland tumour, with a good prognosis, that is usually found on the tongue or palate.

Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma (HLRCC) or Reed's syndrome is rare autosomal dominant disorder associated with benign smooth muscle tumors and an increased risk of renal cell carcinoma. It is characterised by multiple cutaneous leiomyomas and, in women, uterine leiomyomas. It predisposes individuals to renal cell cancer, an association denominated hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer. It is also associated with increased risk of uterine leiomyosarcoma. The syndrome is caused by a mutation in the fumarate hydratase gene, which leads to an accumulation of fumarate. The inheritance pattern is autosomal dominant and screening can typically begin in childhood.
Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma (MASC), also termed MASCSG, is a salivary gland neoplasm. It is a secretory carcinoma which shares the microscopic pathologic features with other types of secretory carcinomas including mammary secretory carcinoma, secretory carcinoma of the skin, and salivary gland–type carcinoma of the thyroid. MASCSG was first described by Skálová et al. in 2010. The authors of this report found a chromosome translocation in certain salivary gland tumors, i.e. a (12;15)(p13;q25) fusion gene mutation. The other secretory carcinoma types carry this fusion gene.

The vaginal epithelium is the inner lining of the vagina consisting of multiple layers of (squamous) cells. The basal membrane provides the support for the first layer of the epithelium-the basal layer. The intermediate layers lie upon the basal layer, and the superficial layer is the outermost layer of the epithelium. Anatomists have described the epithelium as consisting of as many as 40 distinct layers of cells. The mucus found on the epithelium is secreted by the cervix and uterus. The rugae of the epithelium create an involuted surface and result in a large surface area that covers 360 cm2. This large surface area allows the trans-epithelial absorption of some medications via the vaginal route.

In histopathology, a palisade is a single layer of relatively long cells, arranged loosely perpendicular to a surface and parallel to each other. A rosette is a palisade in a halo or spoke-and-wheel arrangement, surrounding a central core or hub. A pseudorosette is a perivascular radial arrangement of neoplastic cells around a small blood vessel. Rosettes are characteristic of tumors.

The histopathology of colorectal cancer of the adenocarcinoma type involves analysis of tissue taken from a biopsy or surgery. A pathology report contains a description of the microscopical characteristics of the tumor tissue, including both tumor cells and how the tumor invades into healthy tissues and finally if the tumor appears to be completely removed. The most common form of colon cancer is adenocarcinoma, constituting between 95% and 98% of all cases of colorectal cancer. Other, rarer types include lymphoma, adenosquamous and squamous cell carcinoma. Some subtypes have been found to be more aggressive.

Papillary renal cell carcinoma (PRCC) is a malignant, heterogeneous tumor originating from renal tubular epithelial cells of the kidney, which comprises approximately 10-15% of all kidney neoplasms. Based on its morphological features, PRCC can be classified into two main subtypes, which are type 1 (basophilic) and type 2 (eosinophilic).