
In computing, a cache is a hardware or software component that stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster; the data stored in a cache might be the result of an earlier computation or a copy of data stored elsewhere. A cache hit occurs when the requested data can be found in a cache, while a cache miss occurs when it cannot. Cache hits are served by reading data from the cache, which is faster than recomputing a result or reading from a slower data store; thus, the more requests that can be served from the cache, the faster the system performs.

Microsoft Access is a database management system (DBMS) from Microsoft that combines the relational Microsoft Jet Database Engine with a graphical user interface and software-development tools. It is a member of the Microsoft Office suite of applications, included in the Professional and higher editions or sold separately.

In computing, load balancing improves the distribution of workloads across multiple computing resources, such as computers, a computer cluster, network links, central processing units, or disk drives. Load balancing aims to optimize resource use, maximize throughput, minimize response time, and avoid overload of any single resource. Using multiple components with load balancing instead of a single component may increase reliability and availability through redundancy. Load balancing usually involves dedicated software or hardware, such as a multilayer switch or a Domain Name System server process.
Distributed web crawling is a distributed computing technique whereby Internet search engines employ many computers to index the Internet via web crawling. Such systems may allow for users to voluntarily offer their own computing and bandwidth resources towards crawling web pages. By spreading the load of these tasks across many computers, costs that would otherwise be spent on maintaining large computing clusters are avoided.
In computer science, message queues and mailboxes are software-engineering components used for inter-process communication (IPC), or for inter-thread communication within the same process. They use a queue for messaging – the passing of control or of content. Group communication systems provide similar kinds of functionality.
Server-side refers to operations that are performed by the server in a client–server relationship in a computer network.
In software architecture, publish–subscribe is a messaging pattern where senders of messages, called publishers, do not program the messages to be sent directly to specific receivers, called subscribers, but instead categorize published messages into classes without knowledge of which subscribers, if any, there may be. Similarly, subscribers express interest in one or more classes and only receive messages that are of interest, without knowledge of which publishers, if any, there are.
Multi-master replication is a method of database replication which allows data to be stored by a group of computers, and updated by any member of the group. All members are responsive to client data queries. The multi-master replication system is responsible for propagating the data modifications made by each member to the rest of the group, and resolving any conflicts that might arise between concurrent changes made by different members.
In computing, Advanced Program to Program Communication or APPC is a protocol which computer programs can use to communicate over a network. APPC is at the application layer in the OSI model, it enables communications between programs on different computers, from portables and workstations to midrange and host computers. APPC is defined as VTAM LU 6.2
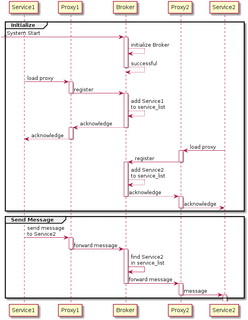
A message broker is an intermediary computer program module that translates a message from the formal messaging protocol of the sender to the formal messaging protocol of the receiver. Message brokers are elements in telecommunication or computer networks where software applications communicate by exchanging formally-defined messages. Message brokers are a building block of message-oriented middleware (MOM) but are typically not a replacement for traditional middleware like MOM and remote procedure call (RPC).
Microsoft SQL Server is a relational database management system developed by Microsoft. As a database server, it is a software product with the primary function of storing and retrieving data as requested by other software applications—which may run either on the same computer or on another computer across a network.
The Base One Foundation Component Library (BFC) is a rapid application development toolkit for building secure, fault-tolerant, database applications on Windows and ASP.NET. In conjunction with Microsoft's Visual Studio integrated development environment, BFC provides a general-purpose web application framework for working with databases from Microsoft, Oracle, IBM, Sybase, and MySQL, running under Windows, Linux/Unix, or IBM iSeries or z/OS. BFC also includes facilities for distributed computing, batch processing, queuing, and database command scripting, and these run under Windows or Linux with Wine.
Windows Search, formerly known as Windows Desktop Search (WDS) on Windows XP and Windows Server 2003, is an indexed desktop search platform created by Microsoft for Microsoft Windows.
Pervasive PSQL is an ACID-compliant database management system (DBMS) developed by Pervasive Software. It is optimized for embedding in applications and used in several different types of packaged software applications offered by independent software vendors (ISVs) and original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). It is available for software as a service (SaaS) deployment due to a file-based architecture enabling partitioning of data for multitenancy needs.

Distributed Data Management Architecture (DDM) is IBM's open, published software architecture for creating, managing and accessing data on a remote computer. DDM was initially designed to support record-oriented files; it was extended to support hierarchical directories, stream-oriented files, queues, and system command processing; it was further extended to be the base of IBM's Distributed Relational Database Architecture (DRDA); and finally, it was extended to support data description and conversion. Defined in the period from 1980 to 1993, DDM specifies necessary components, messages, and protocols, all based on the principles of object-orientation. DDM is not, in itself, a piece of software; the implementation of DDM takes the form of client and server products. As an open architecture, products can implement subsets of DDM architecture and products can extend DDM to meet additional requirements. Taken together, DDM products implement a distributed file system.

Apache Ignite is an open-source distributed database, caching and processing platform designed to store and compute on large volumes of data across a cluster of nodes.











