
The Prahova River is a river of Southern Romania, which rises from the Bucegi Mountains, in the Southern Carpathians. It flows into the Ialomița near Adâncata. The upper reach of the river, upstream of the junction with the Azuga River is sometimes called the Prahovița River.

Prahova Valley is the valley where the Prahova river makes its way between the Bucegi and the Baiu Mountains, in the Carpathian Mountains, Romania. It is a tourist region, situated about 100 km north of the capital city of Bucharest.
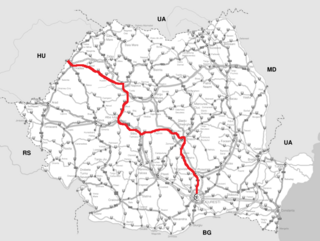
DN1 is an important national road in Romania which links Bucharest with the northwestern part of the country and the border with Hungary via Borş. The main cities linked by DN1 are Bucharest, Ploieşti, Braşov, Sibiu, Alba Iulia, Cluj-Napoca and Oradea.

Azuga is a small resort town nestled in the mountains of Prahova county in the historical region of Muntenia, in Romania. Azuga is located at the foot of the Baiu mountains, and contains the longest ski run in Romania, the Sorica - together with other ski slopes. Formerly heavy industrialized, Azuga retains now a bottled water factory - a leftover from the famous beer factory that brewed Azuga Beer, a sparkling wine factory, wine tasting and lodging . The beer factory, the glassware factory and the wool cloth factory were privatized and now are closed and completely demolished. The refractory materials factory, also privatized, is still standing but it is closed. The town offers a dramatic view over the Bucegi mountains, even from street level and especially from the top of the Sorica mountain.
The Brebu Monastery in Romania is one of the most important architectural achievements of the rule of Matei Basarab and of Romanian art in the 17th century. Constructions began in 1640.

The Zamfira monastery is a monastery of Eastern Orthodox nuns, located in the Lipănești commune, Prahova County, Romania.

Cheia is a mountain resort, 60 kilometers north of Ploieşti, Prahova county, Romania. Situated in the Teleajen Valley, it is surrounded by Ciucaş Mountain and Zăganu Mountain.

Măgureni is a commune in Prahova County, Romania. It is composed of three villages: Cocorăștii Caplii, Lunca Prahovei and Măgureni. At the 2002 census, 6630 inhabitants were counted, all but three of whom were ethnic Romanians. 97.3% of inhabitants were Romanian Orthodox, and 2.6% were Adventist.
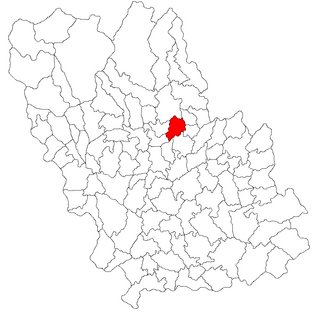
Predeal-Sărari is a commune in Prahova County, Romania. It is composed of nine villages: Bobicești, Poienile, Predeal, Sărari, Sărățel, Tulburea, Tulburea-Văleni, Vitioara de Sus and Zâmbroaia.

Secăria is a commune in Prahova County, Romania. It is composed of a single village, Secăria.

Ștefești is a commune in Prahova County, Romania. It is composed of three villages: Scurtești, Ștefești and Târșoreni.
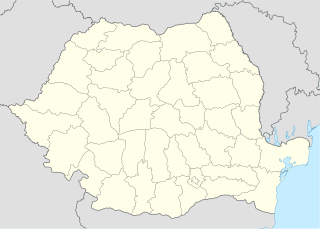
Talea is a commune in Prahova County, Romania. It is composed of two villages, Plaiu and Talea.

Valea Doftanei is a commune in Prahova County, Romania. It is composed of two villages: Teșila and Trăisteni.

The Piatra Mare Mountains is a small mountain range in Brașov County, southeast of Brașov, Romania, and also close to the resort town of Predeal.

Predeal Pass is a mountain pass in the Carpathian Mountains in Romania. It connects the Prahova River valley to the south with the lowlands around Brașov to the north. It separates the Southern Carpathians from the Eastern Carpathians. It is an important passage for traffic between southern Romania and central Romania, crossed by National Road 1 and the Bucharest—Brașov railway. The town Predeal is situated near the pass.

Alecu Filipescu-Vulpea, also known as Aleco Filipescul, Alecsandru R. Filipescu or Alexandru Răducanu Filipescu, was a Wallachian administrator and high-ranking boyar, who played an important part in the politics of the late Phanariote era and of the Regulamentul Organic regime. Beginning in the 1810s, he took an anti-Phanariote stand, conspiring alongside the National Party and the Filiki Eteria to institute new constitutional norms. Clashing with the National Party over the distribution of spoils, and only obtaining relatively minor positions in the administration of Bucharest, Filipescu eventually joined a clique of boyars that cooperated closely with the Russian Empire. His conditional support for the Eterists played out during the Wallachian uprising of 1821, when Vulpea manipulated all sides against each other, ensuring safety for the boyars. He returned to prominence under Prince Grigore IV Ghica, but sabotaged the monarch's political reform effort and also seduced his wife Maria. She was probably the mother of his only son, Ioan Alecu Filipescu-Vulpache.






















