
Darkling beetle is the common name for members of the beetle family Tenebrionidae, comprising over 20,000 species in a cosmopolitan distribution.

Veratrum viride, known as Indian poke, corn-lily, Indian hellebore, false hellebore, green false hellebore, or giant false-helleborine, is a species of Veratrum native to eastern and western North America. It is extremely toxic, and is considered a pest plant by farmers with livestock. The species has acquired a large number of other common names within its native range, including American false hellebore, American white hellebore, bear corn, big hellebore, corn lily, devil's bite, duck retten, itchweed, poor Annie, blue hellebore and tickleweed.

The Tenebrionoidea are a very large and diverse superfamily of beetles. It generally corresponds to the Heteromera of earlier authors.

Dactylorhiza viridis, the frog orchid, is a species of flowering plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae. It has also been treated as the only species Coeloglossum viride of the monotypic genus Coeloglossum.

Leiodidae is a family of beetles with around 3800 described species found worldwide. Members of this family are commonly called round fungus beetles due to the globular shape of many species, although some are more elongated in shape. They are generally small or very small beetles and many species have clubbed antennae.

Trichoderma viride is a fungus and a biofungicide.

Trichoderma is a genus of fungi in the family Hypocreaceae that is present in all soils, where they are the most prevalent culturable fungi. Many species in this genus can be characterized as opportunistic avirulent plant symbionts. This refers to the ability of several Trichoderma species to form mutualistic endophytic relationships with several plant species. The genomes of several Trichoderma specieshave been sequenced and are publicly available from the JGI.
Mesostigma is a genus of unicellular biflagellate freshwater green algae, with a single species Mesostigma viride, covered by an outer layer of basket‐like scales instead of a cell wall. As of February 2022, AlgaeBase classified it as the only genus in the family Mesostigmataceae, the only family in the order Mesostigmatales, the only order in the class Mesostigmatophyceae. It is now considered to be one of the earliest diverging members of green plants/algae (Viridiplantae).

Eleodes is a genus of darkling beetles, in the family Tenebrionidae. They are endemic to western North America ranging from southern Canada to central Mexico with many species found along the Mexico-United States border. Some species have been introduced to Colombia. The name pinacate is Mexican Spanish, derived from the Nahuatl (Aztec) name for the insect, pinacatl, which translates as "black beetle."

Tenebrioninae is the largest subfamily of the darkling beetles (Tenebrionidae), containing flour beetles, among others. Tenebrioninae contains more than 20 tribes.
Trachelostenus is a genus of darkling beetles in the family Tenebrionidae. It is native to the Valdivian forests of Chile, and has at least two species, T. inaequalis (Solier) and T. fascicularis (Philipp). It was historically considered the only member of the family Trachelostenidae, but a 2015 study sunk the genus into the tenebrionid subfamily Tenebrioninae.

Asplenium viride is a species of fern known as the green spleenwort because of its green stipes and rachides. This feature easily distinguishes it from the very similar-looking maidenhair spleenwort, Asplenium trichomanes.
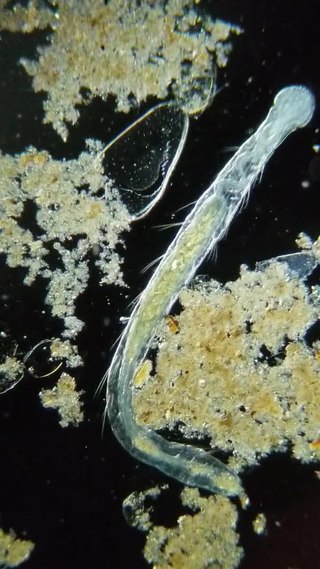
Aeolosoma is a genus of minute annelid worms, variously attributed either to oligochaetes or polychaetes. Unlike most polychaetes, they reside in freshwater environments in various parts of the world.

The Sepidiini is a tribe of ground-dwelling darkling beetles (Tenebrionidae), that occurs across Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Arabian Peninsula and Mesopotamia. It is composed of many hundreds of species. The larvae of some species are known to damage crops.

Microglossum is a genus of fungi in the family Leotiaceae. Ascocarps occur in soil and resemble earth tongues, but are microscopically distinct. Microglossum atropurpureum, a species typical of waxcap grassland in Europe, is of global conservation concern and is listed as "vulnerable" on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.

Ecbolium viride is a species of Ecbolium of the family Acanthaceae. It can be found in Bangladesh, India and Sri Lanka, where it is widely used as a medicinal plant.
Trillium viride, commonly called the wood wakerobin, is a species of flowering plant in the family Melanthiaceae. It is found in the central United States, in certain parts of Missouri and Illinois. The specific epithet viride means "youthful" or "fresh-green", an apparent reference to the color of the plant's flower petals. For this reason, it is also called the green trillium, not to be confused with other green-flowered trilliums such as T. viridescens and the green form of T. sessile, both of which are found in Missouri.

Cnodalon is a genus of darkling beetles in the family Tenebrionidae.

Lagriinae is a subfamily of long-jointed beetles in the family Tenebrionidae. There are more than 270 genera in Lagriinae, grouped into 11 tribes.

Solanum viride, the green nightshade, garland berry, cannibal's tomato, poroporo or boro dina, is a species of flowering plant in the family Solanaceae. It is native to the Cook Islands, Fiji, Marquesas Islands, Niue, Pitcairn Islands, Samoan Islands, Society Islands, Tokelau and Manihiki, Tonga, Tuamotus, and Tubuai Islands in the South Pacific. It has been introduced to Hawaii. In Fiji at the time of contact, human meat was cooked wrapped in its leaves, and a condiment for the meal was made from the fruit.

















