A hotel is an establishment that provides paid lodging on a short-term basis. Facilities provided inside a hotel room may range from a modest-quality mattress in a small room to large suites with bigger, higher-quality beds, a dresser, a refrigerator, and other kitchen facilities, upholstered chairs, a television, and en-suite bathrooms. Small, lower-priced hotels may offer only the most basic guest services and facilities. Larger, higher-priced hotels may provide additional guest facilities such as a swimming pool, a business center with computers, printers, and other office equipment, childcare, conference and event facilities, tennis or basketball courts, gymnasium, restaurants, day spa, and social function services. Hotel rooms are usually numbered to allow guests to identify their room. Some boutique, high-end hotels have custom decorated rooms. Some hotels offer meals as part of a room and board arrangement. In Japan, capsule hotels provide a tiny room suitable only for sleeping and shared bathroom facilities.

Inns are generally establishments or buildings where travelers can seek lodging, and usually, food and drink. Inns are typically located in the country or along a highway. Before the advent of motorized transportation, they also provided accommodation for horses.

A pub is in several countries a drinking establishment licensed to serve alcoholic drinks for consumption on the premises. The term first appeared in England in the late 17th century, to differentiate private houses from those open to the public as alehouses, taverns and inns. Today, there is no strict definition, but the Campaign for Real Ale (CAMRA) states a pub has four characteristics:
- is open to the public without membership or residency
- serves draught beer or cider without requiring food be consumed
- has at least one indoor area not laid out for meals
- allows drinks to be bought at a bar
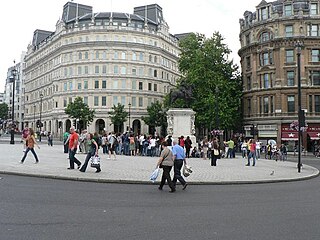
Charing Cross is a junction in Westminster, London, England, where six routes meet. Since the early 19th century, Charing Cross has been the notional "centre of London" and became the point from which distances from London are measured. Clockwise from north, the routes that meet at Charing Cross are: the east side of Trafalgar Square leading to St Martin's Place and then Charing Cross Road; the Strand leading to the City; Northumberland Avenue leading to the Thames Embankment; Whitehall leading to Parliament Square; The Mall leading to Admiralty Arch and Buckingham Palace; and two short roads leading to Pall Mall.

A stagecoach is a four-wheeled public transport coach used to carry paying passengers and light packages on journeys long enough to need a change of horses. It is strongly sprung and generally drawn by four horses although some versions are drawn by six horses.

Eaton Socon is a district of St Neots, in the civil parish of St Neots, in the Huntingdonshire district, in the county of Cambridgeshire, England, 1.4 miles south-west of St Neots town centre. Eaton Socon is a component of the town of St Neots, located on its south-west margin. Eaton Socon lies on the west side of the River Great Ouse, and is bounded on the west by the A1 road and on the south by the A428 road. On the north side Duloe Brook delineates the boundary with Eaton Ford, which is also part of St Neots.

Stony Stratford is a market town in Buckinghamshire and a constituent town of Milton Keynes, England. It is located on Watling Street, historically the Roman road from London to Chester. It is also a civil parish with a town council in the City of Milton Keynes. It is in the north-west corner of the Milton Keynes urban area, bordering Northamptonshire and separated from it by the River Great Ouse. In 2011 the parish had a population of 7736.

The Tabard was an inn in Southwark established in 1307, which stood on the east side of Borough High Street, at the road's intersection with the ancient thoroughfare to Canterbury and Dover. It was built for the Abbot of Hyde in Winchester, who purchased the land to construct a place for himself and his ecclesiastical brethren to stay when on business in London.

Pub names are used to identify and differentiate traditional drinking establishments. Many pubs are centuries old, and were named at a time when most of their customers were illiterate, but could recognise pub signs. The use of signage was not confined to drinking establishments. British pubs may be named after and depict anything from everyday objects, to sovereigns, aristocrats and landowners. Other names come from historic events, livery companies, occupations, sports, and craftsmen's guilds. One of the most common pub names is the Red Lion. This list contains both modern and historical examples.

A mail coach is a stagecoach that is used to deliver mail. In Great Britain, Ireland, and Australia, they were built to a General Post Office-approved design operated by an independent contractor to carry long-distance mail for the Post Office. Mail was held in a box at the rear where the only Royal Mail employee, an armed guard, stood. Passengers were taken at a premium fare. There was seating for four passengers inside and more outside with the driver. The guard's seat could not be shared. This distribution system began in Britain in 1784. In Ireland the same service began in 1789, and in Australia it began in 1828.

A coach is a large, closed, four-wheeled, passenger-carrying vehicle or carriage usually drawn by two or more horses controlled by a coachman, a postilion, or both. A coach has doors in its sides and a front and a back seat inside. The driver has a raised seat in front of the carriage to allow better vision. It is often called a box, box seat, or coach box. There are many types of coaches depending on the vehicle's purpose.
The Sheffield to Hathersage turnpike was an early road through the English Peak District, which was improved by a turnpike trust in the 18th century. The road may have originated as a Roman road.

The King's Head Hotel is a hotel standing opposite the Shire Hall in Glyndŵr Street, Agincourt Square, Monmouth, Wales. It dates from the mid-17th century, and as one of the major inns in Monmouth was reputedly visited by Charles I of England in 1645. It has a fine black-and-white painted stone façade and became an important posting inn in the late 17th century, with a yard through an archway where visitors' horses could be stabled and where regular coach services called. In the 18th and 19th centuries, stagecoaches for London left from the inn. The range of buildings along Agincourt Street now includes the former Monmouth Bank and the County Club, while the inn itself is now part of the J D Wetherspoon pub chain. It is one of 24 buildings on the town's Heritage Trail and is a Grade II* listed building.

A stage station or relay station, also known as a staging post, a posting station, or a stage stop, is a facility along a main road or trade route where a traveller can rest and/or replace exhausted working animals for fresh ones, since long journeys are much faster with fewer delays when using well fed and rested mounts. Stage is the space between the places known as stations or stops — also known in British English as posts or relays.

The Swan with Two Necks was a coaching inn in the City of London that, until the arrival of the railways, was one of the principal departure points for travel to the north of England from London. Its site was given over in the early 1860s to a goods and parcels depot for a firm of railway agents and carriers.

The Bull and Mouth Inn was a coaching inn in the City of London that dated from before the Great Fire of London in 1666. It was located between Bull and Mouth Street in the north and Angel Street in the south. It was once an important arrival and departure point for coaches from all over Britain, but particularly for the north of England and Scotland. It became the Queen's Hotel in 1830 but was demolished in 1887 or 1888 when new post office buildings were built in St Martin's Le Grand.

A post house, posthouse, or posting house was a house or inn where horses were kept and could be rented or changed out. Postriders could also be hired to take travellers by carriage or coach and delivered mail and packages on a route, meeting up at various places according to a schedule. Routes included post roads. A postmaster was an individual from whom horses and/or riders known as postilions or "post-boys" who might help a coachman drive coaches could be hired. A postilion might also travel on a coach to take back his employer's horses. The postmaster would reside in the post house.

The Dog & Bull is a public house in Croydon, England. It is a Grade II listed, 18th-century building with a 19th-century frontage in Surrey Street, on the site of a previous 12th- or 13th-century inn called The Bell.

Public houses, popularly known as pubs, are a significant feature of the history and culture of the English seaside resort of Brighton. The earliest pubs trace their history back to the 16th and 17th centuries, when present-day Brighton was a fishing village. Several coaching inns were founded in the 18th century as transport improved and communications with other towns developed, and around the same time other pubs became established in the fashionable Old Steine area in Brighton's early years as a resort. Many new pubs, originally beerhouses, were established after an Act of Parliament in 1830 loosened restrictions; two of these "Beerhouse Act" pubs remain in business. In the following decade the opening of Brighton's railway station provided another major boost to the pub trade, and by the late 19th century there were nearly 800 licensed venues in the town. Numbers declined gradually—as late as 1958 there was said to be "one pub for every day of the year"—and by the early 21st century around 300 pubs were still trading, with others having closed but surviving in alternative use.