
Sir Keith Jacka Holyoake, was a New Zealand politician who served as the 26th prime minister of New Zealand, serving for a brief period in 1957 and then from 1960 to 1972, and also as the 13th governor-general of New Zealand, serving from 1977 to 1980. He is the only New Zealand politician to have held both positions.

Sir Robert David Muldoon was a New Zealand conservative politician who served as the 31st prime minister of New Zealand, from 1975 to 1984, while leader of the National Party. Departing from National Party convention, Muldoon was a right-wing populist and economic nationalist, with a distinctive public persona described as reactionary, aggressive, and abrasive.
The New Zealand National Party, shortened to National or the Nats, is a centre-right New Zealand political party that is the current senior ruling party. It is one of two major parties that dominate contemporary New Zealand politics, alongside its traditional rival, the Labour Party.

The minister of Finance, originally known as colonial treasurer, is a minister and the head of the New Zealand Treasury, responsible for producing an annual New Zealand budget outlining the government's proposed expenditure. The position is often considered to be the most important cabinet post after that of the prime minister.

James Brendan Bolger, affectionately called The Great Helmsman, is a New Zealand retired politician of the National Party who was the 35th prime minister of New Zealand, serving from 1990 to 1997.

Sir John Ross Marshall was a New Zealand politician of the National Party. He entered Parliament in 1946 and was first promoted to Cabinet in 1951. After spending twelve years as the deputy prime minister of New Zealand, he served as the 28th prime minister from February until December 1972.

Sir William Francis Birch, usually known as Bill Birch, is a New Zealand retired politician. He served as Minister of Finance from 1993 to 1999 in the fourth National Government.

George Frederick Gair was a New Zealand politician. He was once deputy leader of the National Party in the New Zealand Parliament, and was considered by many to be a possible contender for the leadership itself. He was known for his polite and diplomatic style, which often contrasted with the political situation around him – Michael Laws described him as "a refugee from the age of manners."

Derek Francis Quigley is a New Zealand former politician. He was a prominent member of the National Party during the late 1970s and early 1980s, and was known for his support of free-market economics and trade liberalisation. Quigley left the National Party after clashing with its leadership, and later co-founded the ACT New Zealand party.
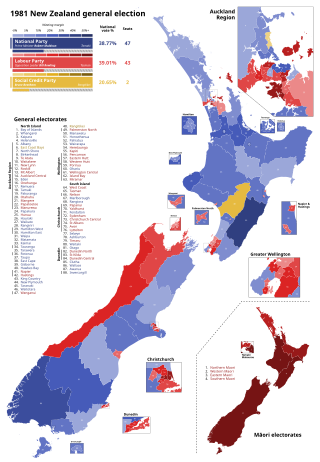
The 1981 New Zealand general election, held on 28 November 1981, was a nationwide vote to determine the shape of the 40th New Zealand Parliament. It saw the governing National Party, led by Robert Muldoon, win a third term in office, but the opposition Labour Party, led by Bill Rowling, won the largest share of the votes cast.

The New Zealand constitutional crisis of 1984 arose following the 1984 general election, and was caused by a major currency crisis. The crisis led the incoming government to review New Zealand's constitutional structures, which resulted in the Constitution Act 1986.

The National Development Act 1979 was an Act of Parliament in New Zealand. It was a controversial Act and was repealed by the National Development Act Repeal Act 1986.
Conservatism in New Zealand, though related to its counterparts in other Western countries, developed uniquely over time. Advocates followed a political ideology that emphasised the preservation of traditional European beliefs, institutions and practices.
New Zealand political leader Jim McLay assembled a "shadow cabinet" system amongst the National caucus following his election to the position of Leader of the Opposition in 1984. He composed this of individuals who acted for the party as spokespeople in assigned roles while he was Leader of the Opposition (1984–86). McLay was plagued by interference from previous leader Robert Muldoon, who was denied a place on National's frontbench which he desired, unlike McLay who wished him to retire to the backbenches as an 'elder statesmen'.

The New Zealand National Party leadership election was held to determine the leadership of the New Zealand National Party. The election was won by Karori MP Jack Marshall.

The 1974 New Zealand National Party leadership election was held to determine the future leadership of the New Zealand National Party. The election was won by Tamaki MP Robert Muldoon.

The 1984 New Zealand National Party leadership election was held to determine the future leadership of the New Zealand National Party. The election was won by former deputy prime minister Jim McLay.
New Zealand political leader Jim Bolger assembled a "shadow cabinet" within the National Party caucus after his election to the position of Leader of the Opposition in 1986. He composed this of individuals who acted for the party as spokespeople in assigned roles while he was Leader of the Opposition (1986–90).
New Zealand political leader Robert Muldoon assembled a "shadow cabinet" within the National Party caucus after his election to the position of Leader of the Opposition in 1974. He composed this of individuals who acted for the party as spokespeople in assigned roles while he was Leader of the Opposition (1974–75).
New Zealand political leader Robert Muldoon assembled a "shadow cabinet" within the National Party caucus after his transition to the position of Leader of the Opposition in 1984 following National's defeat at the 1984 election. He composed this of individuals who acted for the party as spokespeople in assigned roles while he was Leader of the Opposition.










