
Sremski Karlovci is a town and municipality located in the Srem District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. It is situated on the banks of the Danube, 8 kilometres from Novi Sad. According to the 2011 census results, it has a population of 8,750 inhabitants. The town has traditionally been known as the seat of the Serbian Orthodox Church in the Habsburg Monarchy. It was the political and cultural capital of Serbian Vojvodina after the May Assembly and during the Revolution in 1848.

Vojvodina, officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia, located in Central Europe. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital Belgrade and the Sava and Danube Rivers. The administrative centre, Novi Sad, is the second-largest city in Serbia.

Banat is a geographical and historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central and Eastern Europe. It is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania ; the western part of Banat is in northeastern Serbia ; and a small northern part lies within southeastern Hungary.

Bačka or Bácska is a geographical and historical area within the Pannonian Plain bordered by the river Danube to the west and south, and by the river Tisza to the east. It is divided between Serbia and Hungary. Most of the area is located within the Vojvodina region in Serbia and Novi Sad, the capital of Vojvodina, lies on the border between Bačka and Syrmia. The smaller northern part of the geographical area is located within Bács-Kiskun County in Hungary.

There are two flags in official use in the Serbian Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, the Flag of Vojvodina and the Traditional flag of Vojvodina. Two flags are given the equal status in the Provincial Assembly Decision on the Appearance and Usage of Symbols and Traditional Symbols of AP Vojvodina adopted in 2016.
Futog is a suburban settlement of the city of Novi Sad, Serbia, with a population of 18,642 according to the 2011 census in Serbia. It is situated in southern Bačka, 7 km away from Novi Sad.

Bačka Topola is a town and municipality located in the North Bačka District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The municipality is composed of 23 local communities and has a population of 33,321, while the town itself has 14,573 inhabitants.

The Serbian Vojvodina was a short-lived self-proclaimed Serb autonomous province within the Austrian Empire during the Revolutions of 1848, which existed until 1849 when it was transformed into the new (official) Austrian province named Voivodeship of Serbia and Banat of Temeschwar.

Tovariševo is a village in Serbia, in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 3,102 people.
Vojvodina is an autonomous province located in northern Serbia. It consists of the Pannonian Plain in the south, and the Danube and Sava rivers in the north.

The Serbs of Vojvodina are the largest ethnic group in this northern province of Serbia. For centuries, Vojvodina was ruled by several European powers, but Vojvodina Serbs never assimilated into cultures of those countries. Thus, they have consistently been a recognized indigenous ethnic minority with its own culture, language and religion. According to the 2022 census, there were 1,190,785 Serbs in Vojvodina or 68.43% of the population of the province.

Kisač is a suburban settlement of the city of Novi Sad, Serbia. The settlement has a Slovak ethnic majority.

Bački Jarak is a town located in the Temerin municipality, in the South Bačka District of Serbia. It is situated in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. The town has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 5,687 people.

Crvenka is a small town located in the municipality of Kula in the West Bačka District, Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The town has a Serbian ethnic majority, and it had a population of 9,001 in 2011.

Hungarians in Serbia are a recognized national minority in Serbia. According to the 2022 census, the population of ethnic Hungarians in Serbia is 184,442, constituting 2.8% of the total population, which makes them the second-largest ethnic group in the country behind Serbs and the largest minority group. The vast majority of them live in the northern autonomous province of Vojvodina, where they number 182,321 and make up 10.5% of the province's population. Almost 99% of all Hungarians in Serbia live in the province of Vojvodina. Most Hungarians in Serbia are Roman Catholics, while smaller numbers of them are Protestant. Their cultural center is located in Subotica.
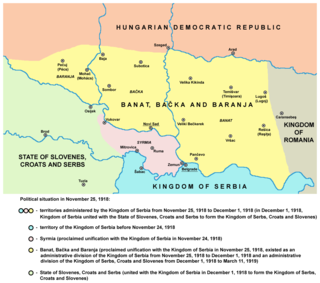
Banat, Bačka and Baranya was a province of the Kingdom of Serbia and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes between November 1918 and 1922. It included the geographical regions of Banat, Bačka, and Baranya and its administrative center was Novi Sad. They were later separated from the country to become SAP Vojvodina in 1945 with the creation of Federal Yugoslavia; smaller parts of Baranya were incorporated into Croatia or ceded to Kingdom of Hungary, while a portion of Banat was ceded to Kingdom of Romania.
Banatska Topola is a village in the Kikinda municipality, in the North Banat District of the Republic of Serbia. It is situated in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. The village has a population of 1,066 of which 570 (53.47%) are ethnic Serbs and 434 (40.71%) are ethnic Hungarians.

Fudbalski klub TSC, commonly known as TSC, is a Serbian professional football club based in Bačka Topola and currently the second oldest football club in the Serbian SuperLiga.

The Socialist Autonomous Province of Vojvodina was one of two autonomous provinces within the Socialist Republic of Serbia, in the former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. The province is the direct predecessor to the modern-day Serbian Autonomous Province of Vojvodina.

The Great People's Assembly of Serbs, Bunjevci and other Slavs in Banat, Bačka and Baranja or Novi Sad Assembly was an assembly held in Novi Sad on 25 November 1918, which proclaimed the unification of Banat, Bačka and Baranya with the Kingdom of Serbia.























