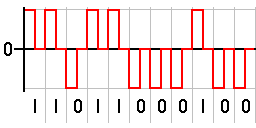
In telecommunication, coded mark inversion (CMI) is a non-return-to-zero (NRZ) line code. It encodes zero bits as a half bit time of zero followed by a half bit time of one, and while one bits are encoded as a full bit time of a constant level. The level used for one bits alternates each time one is coded.

Telecommunication is the transmission of signs, signals, messages, words, writings, images and sounds or information of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic systems. Telecommunication occurs when the exchange of information between communication participants includes the use of technology. It is transmitted either electrically over physical media, such as cables, or via electromagnetic radiation. Such transmission paths are often divided into communication channels which afford the advantages of multiplexing. Since the Latin term communicatio is considered the social process of information exchange, the term telecommunications is often used in its plural form because it involves many different technologies.

In telecommunication, a non-return-to-zero (NRZ) line code is a binary code in which ones are represented by one significant condition, usually a positive voltage, while zeros are represented by some other significant condition, usually a negative voltage, with no other neutral or rest condition. The pulses in NRZ have more energy than a return-to-zero (RZ) code, which also has an additional rest state beside the conditions for ones and zeros. NRZ is not inherently a self-clocking signal, so some additional synchronization technique must be used for avoiding bit slips; examples of such techniques are a run-length-limited constraint and a parallel synchronization signal.

In telecommunication, a line code is a pattern of voltage, current, or photons used to represent digital data transmitted down a transmission line. This repertoire of signals is usually called a constrained code in data storage systems. Some signals are more prone to error than others when conveyed over a communication channel as the physics of the communication or storage medium constrains the repertoire of signals that can be used reliably.
This is vaguely reminiscent of, but quite different from, Miller encoding, which also uses half-bit and full-bit pulses, but additionally uses the half-one/half-zero combination and arranges them so that the signal always spends at least a full bit time at a particular level before transitioning again.

In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the heartbeat by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the neck, wrist, at the groin, behind the knee, near the ankle joint, and on foot. Pulse is equivalent to measuring the heart rate. The heart rate can also be measured by listening to the heart beat by auscultation, traditionally using a stethoscope and counting it for a minute. The radial pulse is commonly measured using three fingers. This has a reason: the finger closest to the heart is used to occlude the pulse pressure, the middle finger is used get a crude estimate of the blood pressure, and the finger most distal to the heart is used to nullify the effect of the ulnar pulse as the two arteries are connected via the palmar arches. The study of the pulse is known as sphygmology.
CMI doubles the bitstream frequency, when compared to its simple NRZ equivalent, but allows easy and reliable clock recovery.
In serial communication of digital data, clock recovery is the process of extracting timing information from a serial data stream to allow the receiving circuit to decode the transmitted symbols. Clock recovery from the data stream is expedited by modifying the transmitted data. Wherever a serial communication channel does not transmit the clock signal along with the data stream, the clock must be regenerated at the receiver, using the timing information from the data stream. Clock recovery is a common component of systems communicating over wires, optical fibers, or by radio.