| Passband modulation |
|---|
| Analog modulation |
| Digital modulation |
| Hierarchical modulation |
| Spread spectrum |
| See also |
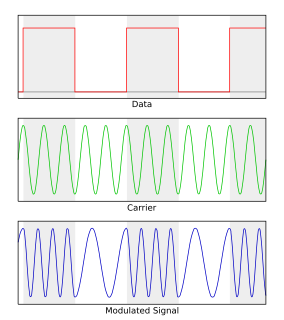
On-off keying (OOK) denotes the simplest form of amplitude-shift keying (ASK) modulation that represents digital data at the presence or absence of a carrier wave. [1] In its simplest form, the presence of a carrier for a specific duration represents a binary one, while its absence for the same duration represents a binary zero. Some more sophisticated schemes vary these durations to convey additional information. It is analogous to unipolar encoding line code.
Amplitude-shift keying (ASK) is a form of amplitude modulation that represents digital data as variations in the amplitude of a carrier wave. In an ASK system, the binary symbol 1 is represented by transmitting a fixed-amplitude carrier wave and fixed frequency for a bit duration of T seconds. If the signal value is 1 then the carrier signal will be transmitted; otherwise, a signal value of 0 will be transmitted.
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal that typically contains information to be transmitted. Most radio systems in the 20th century used frequency modulation (FM) or amplitude modulation (AM) for radio broadcast.
Digital data, in information theory and information systems, is the discrete, discontinuous representation of information or works. Numbers and letters are commonly used representations.
On-off keying is most commonly used to transmit Morse code over radio frequencies (referred to as CW (continuous wave) operation), although in principle any digital encoding scheme may be used. OOK has been used in the ISM bands to transfer data between computers, for example.

Morse code is a character encoding scheme used in telecommunication that encodes text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations called dots and dashes or dits and dahs. Morse code is named for Samuel F. B. Morse, an inventor of the telegraph.
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around twenty thousand times per second to around three hundred billion times per second. This is roughly between the upper limit of audio frequencies and the lower limit of infrared frequencies; these are the frequencies at which energy from an oscillating current can radiate off a conductor into space as radio waves. Different sources specify different upper and lower bounds for the frequency range.
A continuous wave or continuous waveform (CW) is an electromagnetic wave of constant amplitude and frequency, almost always a sine wave, that for mathematical analysis is considered to be of infinite duration. Continuous wave is also the name given to an early method of radio transmission, in which a sinusoidal carrier wave is switched on and off. Information is carried in the varying duration of the on and off periods of the signal, for example by Morse code in early radio. In early wireless telegraphy radio transmission, CW waves were also known as "undamped waves", to distinguish this method from damped wave signals produced by earlier spark gap type transmitters.
OOK is more spectrally efficient than frequency-shift keying, but more sensitive to noise when using a regenerative receiver or a poorly implemented superheterodyne receiver. [2] For a given data rate, the bandwidth of a BPSK (Binary Phase Shift keying) signal and the bandwidth of OOK signal are equal.
Spectral efficiency, spectrum efficiency or bandwidth efficiency refers to the information rate that can be transmitted over a given bandwidth in a specific communication system. It is a measure of how efficiently a limited frequency spectrum is utilized by the physical layer protocol, and sometimes by the media access control.
Frequency-shift keying (FSK) is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is transmitted through discrete frequency changes of a carrier signal. The technology is used for communication systems such as telemetry, weather balloon radiosondes, caller ID, garage door openers, and low frequency radio transmission in the VLF and ELF bands. The simplest FSK is binary FSK (BFSK). BFSK uses a pair of discrete frequencies to transmit binary information. With this scheme, the "1" is called the mark frequency and the "0" is called the space frequency.

A superheterodyne receiver, often shortened to superhet, is a type of radio receiver that uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original carrier frequency. It was invented by US engineer Edwin Armstrong in 1918 during World War I. Virtually all modern radio receivers use the superheterodyne principle.
In addition to RF carrier waves, OOK is also used in optical communication systems (e.g. IrDA).

Optical communication, also known as optical telecommunication, is communication at a distance using light to carry information. It can be performed visually or by using electronic devices. The earliest basic forms of optical communication date back several millennia, while the earliest electrical device created to do so was the photophone, invented in 1880.
In aviation, some possibly unmanned airports have equipment that let pilots key their VHF radio a number of times in order to request an Automatic Terminal Information Service broadcast, or turn on runway lights.






