
The Arctic National Wildlife Refuge or Arctic Refuge is a national wildlife refuge in northeastern Alaska, United States, on traditional Gwich'in lands. The refuge is 19,286,722 acres (78,050.59 km2) of the Alaska North Slope region, with a northern coastline and vast inland forest, taiga, and tundra regions. ANWR is the largest national wildlife refuge in the country, slightly larger than the Yukon Delta National Wildlife Refuge. The refuge is administered from offices in Fairbanks. ANWR is home to a diverse range of endemic mammal species; notably, it is one of the few North American locations with all three endemic American ursids—the polar bear, grizzly bear, and American black bear, each of which resides predominantly in its own ecological niche. Besides the bears, other mammal species include the moose, caribou, wolves, red and Arctic fox, Canada lynx, wolverine, pine marten, American beaver, and North American river otter. Further inland, mountain goats may be seen near the slope. Hundreds of species of migratory birds visit the refuge yearly, and it is a vital, protected breeding location for them. Snow geese, eiders and snowy owl may be observed as well.

The king eider is a large sea duck that breeds along Northern Hemisphere Arctic coasts of northeast Europe, North America and Asia. The birds spend most of the year in coastal marine ecosystems at high latitudes, and migrate to Arctic tundra to breed in June and July. They lay four to seven eggs in a scrape on the ground lined with grass and down.

Steller's eider is a migrating Arctic diving duck that breeds along the coastlines of eastern Russia and Alaska. It is the rarest, smallest, and fastest flying of the eider species.

The thick-billed murre or Brünnich's guillemot is a bird in the auk family (Alcidae). This bird is named after the Danish zoologist Morten Thrane Brünnich. The very deeply black North Pacific subspecies Uria lomvia arra is also called Pallas' murre after its describer. The genus name is from Ancient Greek ouria, a waterbird mentioned by Athenaeus. The species term lomvia is a Swedish word for an auk or diver. The English "guillemot" is from French guillemot probably derived from Guillaume, "William". "Murre" is of uncertain origins, but may imitate the call of the common guillemot.

Boreogadus saida, known as the polar cod or as the Arctic cod, is a fish of the cod family Gadidae, related to the true cod. Another fish species for which both the common names Arctic cod and polar cod are used is Arctogadus glacialis.

The Aleutian tern is a migratory bird living in the subarctic region of the globe most of the year. It is frequently associated with the Arctic tern, which it closely resembles. While both species have a black cap, the Aleutian tern may be distinguished by its white forehead. During breeding season, the Arctic terns have bright red bills, feet, and legs while those of the Aleutian terns are black.

The Beaufort Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of the Northwest Territories, the Yukon, and Alaska, and west of Canada's Arctic islands. The sea is named after Sir Francis Beaufort, a hydrographer. The Mackenzie River, the longest in Canada, empties into the Canadian part of the Beaufort Sea west of Tuktoyaktuk, which is one of the few permanent settlements on the sea's shores.
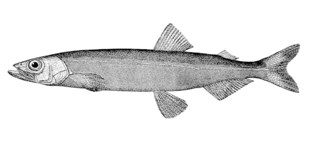
The capelin or caplin is a small forage fish of the smelt family found in the North Atlantic, North Pacific and Arctic oceans. In summer, it grazes on dense swarms of plankton at the edge of the ice shelf. Larger capelin also eat a great deal of krill and other crustaceans. Among others, whales, seals, Atlantic cod, Atlantic mackerel, squid and seabirds prey on capelin, in particular during the spawning season while the capelin migrate south. Capelin spawn on sand and gravel bottoms or sandy beaches at the age of two to six years. When spawning on beaches, capelin have an extremely high post-spawning mortality rate which, for males, is close to 100%. Males reach 20 cm (8 in) in length, while females are up to 25.2 cm (10 in) long. They are olive-coloured dorsally, shading to silver on sides. Males have a translucent ridge on both sides of their bodies. The ventral aspects of the males iridesce reddish at the time of spawn.

The harp seal, also known as Saddleback Seal or Greenland Seal, is a species of earless seal, or true seal, native to the northernmost Atlantic Ocean and Arctic Ocean. Originally in the genus Phoca with a number of other species, it was reclassified into the monotypic genus Pagophilus in 1844. In Greek, its scientific name translates to "ice-lover from Greenland," and its taxonomic synonym, Phoca groenlandica translates to "Greenlandic seal." This is the only species in the genus Pagophilus.

The Colville River is a major river of the Arctic Ocean coast of Alaska in the United States, approximately 350 miles (560 km) long. One of the northernmost major rivers in North America, it drains a remote area of tundra on the north side of the Brooks Range entirely above the Arctic Circle in the southwestern corner of the National Petroleum Reserve-Alaska. The river is frozen for more than half the year and floods each spring.The Colville River and its adjacent hills are home to a variety of Arctic wildlife, including Lake Teshekpuk and Central Arctic caribou herds, and hawks.

The Yukon Delta National Wildlife Refuge is a United States National Wildlife Refuge covering about 19.16 million acres (77,500 km2) in southwestern Alaska. It is the second-largest National Wildlife Refuge in the country, only slightly smaller than the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge. It is a coastal plain extending to the Bering Sea, covering the delta created by the Yukon and Kuskokwim rivers. The delta includes extensive wetlands near sea level that are often inundated by Bering Sea tides. It is bordered on the east by Wood-Tikchik State Park, the largest state park in the United States. The refuge is administered from offices in Bethel.

The wildlife of Alaska is both diverse and abundant. The Alaskan Peninsula provides an important habitat for fish, mammals, reptiles, and birds. At the top of the food chain are the bears. Alaska contains about 70% of the total North American brown bear population and the majority of the grizzly bears, as well as black bears and Kodiak bears. In winter, polar bears can be found in the Kuskokwim Delta, St. Matthew Island, and at the southernmost portion of St. Lawrence Island. Other major mammals include moose and caribou, bison, wolves and wolverines, foxes, otters and beavers. Fish species are extensive, including: salmon, graylings, char, rainbow and lake trout, northern pike, halibut, pollock, and burbot. The bird population consists of hundreds of species, including: bald eagles, owls, falcons, ravens, ducks, geese, swans, and the passerines. Sea lions, seals, sea otters, and migratory whales are often found close to shore and in offshore waters. The Alaskan waters are home to two species of turtles, the leatherback sea turtle and the green sea turtle. Alaska has two species of frogs, the Columbia spotted frog and wood frog, plus two introduced species, the Pacific tree frog and the red-legged frog. The only species of toad in Alaska is the western toad. There are over 3,000 recorded species of marine macroinvertebrates inhabiting the marine waters, the most common being the various species of shrimp, crab, lobster, and sponge.

The Chukchi Shelf or Chukchi Sea Shelf is the westernmost part of the continental shelf of the United States and the easternmost part of the continental shelf of Russia. In the west it merges with the Russian Siberian Shelf. Within this shelf, the 50-mile Chukchi Corridor acts as a passageway for one of the largest marine mammal migrations in the world.

The Arctic coastal tundra is an ecoregion of the far north of North America, an important breeding ground for a great deal of wildlife.
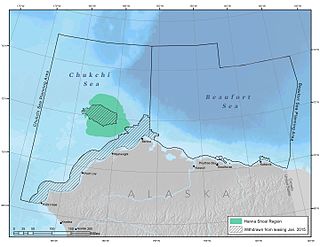
Hanna Shoal is a shallow, natural shoal located off the coast of northwest Alaska in the Chukchi Sea. The region around Hanna Shoal is one of the Chukchi Sea’s most biologically productive areas.
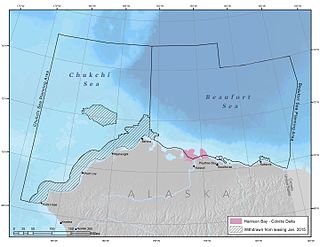
Harrison Bay is an estuary located north of Alaska that opens into the Beaufort Sea. It is adjacent to the Colville Delta. The powerful outflow of the Colville River creates a shallow region that is rich with nutrients, making it ecologically significant for wildlife.

Barrow Canyon is a submarine canyon that straddles the boundary between the Beaufort and Chukchi seas. Compared to other nearby areas and the Canada Basin, the highly productive Barrow Canyon supports a diversity of marine animals and invertebrates.

Smith Bay is an estuary in the Beaufort Sea that supports a wide range of fish, birds, and marine mammals. It is located northeast of Point Barrow, Alaska. The Bureau of Ocean Energy Management recognizes the southeastern portion of Barrow Canyon, which covers some, but not all, of Smith Bay, as an Environmentally Important Area.
The fauna of Iceland is the animal life which resides on the island of Iceland and its coasts, located in the north Atlantic Ocean just south of the Arctic Circle. This fauna includes a number of birds, mammals, fish, and invertebrates. The Arctic fox is the only land mammal native to Iceland, although a number of other mammals have been introduced following the human settlement of Iceland.


















