Related Research Articles

The Countryside Agency was a statutory body set up in England in 1999 with the task of improving the quality of the rural environment and the lives of those living in it. The agency was dissolved in 2006 and its functions dispersed among other bodies.

English Nature was the United Kingdom government agency that promoted the conservation of wildlife, geology and wild places throughout England between 1990 and 2006. It was a non-departmental public body funded by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (DEFRA) and gave statutory advice, grants and issued licences.
This page gives an overview of the complex structure of environmental and cultural conservation in the United Kingdom.
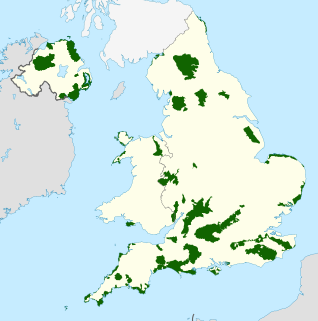
An Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty is an area of countryside in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland, that has been designated for conservation due to its significant landscape value. Areas are designated in recognition of their national importance by the relevant public body: Natural England, Natural Resources Wales, and the Northern Ireland Environment Agency respectively. In place of AONB, Scotland uses the similar national scenic area (NSA) designation. Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty enjoy levels of protection from development similar to those of UK national parks, but unlike national parks the responsible bodies do not have their own planning powers. They also differ from national parks in their more limited opportunities for extensive outdoor recreation.
The Forestry Commission is a non-ministerial government department responsible for the management of publicly owned forests and the regulation of both public and private forestry in England.

The Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981 is an Act of Parliament in the United Kingdom implemented to comply with European Council Directive 79/409/EEC on the conservation of wild birds. In short, the act gives protection to native species, controls the release of non-native species, enhances the protection of Sites of Special Scientific Interest and builds upon the rights of way rules in the National Parks and Access to the Countryside Act 1949. The Act is split into 4 parts covering 74 sections; it also includes 17 schedules.

The Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra) is a department of His Majesty's Government responsible for environmental protection, food production and standards, agriculture, fisheries and rural communities in the United Kingdom. Concordats set out agreed frameworks for co operation, between it and the Scottish Government, Welsh Government and Northern Ireland Executive, which have devolved responsibilities for these matters in their respective nations.
The Environment Agency (EA) is a non-departmental public body, established in 1996 and sponsored by the United Kingdom government's Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, with responsibilities relating to the protection and enhancement of the environment in England.
The Rural Development Service (RDS) was formerly part of the UK Government's Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra). It ceased to exist on 1 October 2006 following the creation of Natural England.
The Veterinary Medicines Directorate (VMD) is an Executive Agency of the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra) seeking to protect public health, animal health, the environment and promoting animal welfare by assuring the safety, quality and efficacy of veterinary medicines in the United Kingdom.
Natural England is a non-departmental public body in the United Kingdom sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. It is responsible for ensuring that England's natural environment, including its land, flora and fauna, freshwater and marine environments, geology and soils, are protected and improved. It also has a responsibility to help people enjoy, understand and access the natural environment.

The Rural Payments Agency (RPA) is an executive agency of the UK Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra). The RPA delivers the European Union (EU) Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) payments to farmers and traders in England, paying out over £2 billion in subsidies each year. The Agency managing more than 40 schemes, the largest of which the Basic Payment Scheme (BPS) paying more than £1.5 billion to around 105,000 claimants a year.
The Veterinary Laboratories Agency (VLA) was an executive agency of the UK government's Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (DEFRA). It carried out animal disease surveillance, diagnostic services and veterinary scientific research for government and commercial organisations. It was based in New Haw, though had offices and laboratories around the country, such as in Sutton Bonington.
The Department of Agriculture, Environment and Rural Affairs (DAERA) is a government department in the Northern Ireland Executive, the devolved administration for Northern Ireland. The minister with overall responsibility for the department is the Minister of Agriculture, Environment and Rural Affairs. The department was called the Department of Agriculture and Rural Development between 1999 and 2016. The Minister of Agriculture previously existed in the Government of Northern Ireland (1921–1972), where the department was known as the Department of Agriculture for Northern Ireland or the Ministry of Agriculture. The current Minister is Edwin Poots MLA and the department's Permanent Secretary is Denis McMahon.

The Department of the Environment was a devolved Northern Irish government department in the Northern Ireland Executive. The minister with overall responsibility for the department was the Minister for the Environment.
"Environmental Quality" is a set of properties and characteristics of the environment, either generalized or local, as they impinge on human beings and other organisms. It is a measure of the condition of an environment relative to the requirements of one or more species, any human need or purpose.

Agriculture in the United Kingdom uses 71% of the country's land area, employs 1% of its workforce and contributes 0.5% of its gross value added. The UK currently produces about 60% of its domestic food consumption.

The Natural Environment and Rural Communities Act 2006, also referred to as the NERC Act (2006), is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. In a reorganisation of public bodies involved in rural policy and delivery, the measures dissolved English Nature, the Countryside Agency and the Rural Development Service, and established Natural England.

Badger culling in the United Kingdom is permitted under licence, within a set area and timescale, as a way to reduce badger numbers in the hope of controlling the spread of bovine tuberculosis (bTB).
References
- ↑ "Natural Environment and Rural Communities Act". Defra. Archived from the original on 16 July 2006.
- ↑ "Natural Environment and Rural Communities Act 2006". www.legislation.gov.uk. Retrieved 25 September 2017.
- ↑ Tasker, Johann (29 June 2010). "DEFRA agencies fall victim to budget cuts". Farmers Weekly.
- ↑ "Commission for Rural Communities". Defra. 31 January 2013.