A dietitian, medical dietitian, or dietician is an expert in identifying and treating disease-related malnutrition and in conducting medical nutrition therapy, for example designing an enteral tube feeding regimen or mitigating the effects of cancer cachexia. Many dietitians work in hospitals and usually see specific patients where a nutritional assessment and intervention has been requested by a doctor or nurse, for example if a patient has lost their ability to swallow or requires artificial nutrition due to intestinal failure. Dietitians are regulated healthcare professionals licensed to assess, diagnose, and treat such problems. In the United Kingdom, dietitian is a 'protected title', meaning identifying yourself as a dietitian without appropriate education and registration is prohibited by law.

A surgical technologist, also called a scrub, scrub tech, surgical technician, or operating room technician, is an allied health professional working as a part of the team delivering surgical care. Surgical technologists are members of the surgical team. The members of the team include the surgeon, surgeon's assistant, circulator nurse and anesthesia provider. They possess knowledge and skills in sterile and aseptic techniques. There are few mandatory professional requirements for surgical technologists, and the scope of practice varies widely across countries and jurisdictions. Surgical technologists attend junior colleges and technical schools, and many are trained in military schools. In the military they perform the duties of both the circulator and the scrub. The goal is for surgical technologists to be able to anticipate the next move the surgeon is going to make in order to make the procedure as smooth and efficient as possible. They do this by having knowledge of hundreds of surgical procedures and the steps the surgeon needs to take in order to complete the procedure, including the very wide range of surgical instruments they may need. Specialties can include, but are not limited to, the following: genitourinary, obstetrics and gynaecology, urology, ENT, plastics, general, orthopedics, neurology, and cardiovascular. They only work in surgical or perioperative areas and are highly specialized. Surgical technologist is the proper term for a two-year program which earns a degree in applied sciences. The profession is up and coming and highly in demand.
A medical assistant, also known as a "clinical assistant" or healthcare assistant in the USA is an allied health professional who supports the work of physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants and other health professionals, usually in a clinic setting. Medical assistants can become certified through an accredited program. Medical assistants perform routine tasks and procedures in a medical clinic.
Allied health professions are health care professions distinct from optometry, dentistry, nursing, medicine, and pharmacy. They provide a range of diagnostic, technical, therapeutic, and support services in connection with health care.
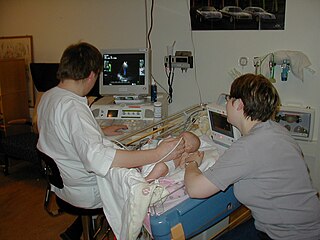
A sonographer is an allied healthcare professional who specializes in the use of ultrasonic imaging devices to produce diagnostic images, scans, videos or three-dimensional volumes of anatomy and diagnostic data. The requirements for clinical practice vary greatly by country. Sonography requires specialized education and skills to acquire, analyze and optimize information in the image. Due to the high levels of decisional latitude and diagnostic input, sonographers have a high degree of responsibility in the diagnostic process. Many countries require medical sonographers to have professional certification. Sonographers have core knowledge in ultrasound physics, cross-sectional anatomy, physiology, and pathology.
A medical illustration is a form of biological illustration that helps to record and disseminate medical, anatomical, and related knowledge.

An orthotist is a healthcare professional who specializes in the provision of orthoses. An orthotist has an overall responsibly of orthotics treatment, who can supervise and mentor the practice of other personnel. They are clinicians trained to assess the needs of the user, prescribe treatment, determine the precise technical specifications of orthotic devices, take measurements and image of body segments, prepare model of the evaluation, fit devices and evaluate treatment outcome. In the United States, orthotists work by prescription from a licensed healthcare provider. Physical therapists are not legally authorized to prescribe orthoses in the U.S. In the U.K., orthotists will often accept open referrals for orthotic assessment without a specific prescription from doctors or other healthcare professionals.

Moraine Park Technical College is a Public technical college in Fond du Lac, Wisconsin. It was established in 1912 and is part of the Wisconsin Technical College System. It has campuses in Fond du Lac, Beaver Dam, and West Bend, and regional centers in Jackson and Ripon. The college offers more than 100 associate of applied science degrees, technical diplomas, apprenticeships, and certificates.
The Accrediting Bureau of Health Education Schools (ABHES) is a recognized higher education accreditation organization in the United States specializing in the institutional accreditation of private, postsecondary institutions that offer allied health education programs, and the programmatic accreditation of programs leading to associate degrees or certificates in the medical assistant, medical laboratory technician and surgical technology fields. The ABHES is the only healthcare education accrediting agency that is recognized by the U.S. Department of Education. In addition to recognition by the U.S. Department of Education, the ABHES is also recognized by the American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA), the American Medical Technologists (AMT) and the Liaison Council for Certification of Surgical Technologists (LLC-ST).

University College of Applied Sciences (UCAS) is a technical college in Gaza founded in 1998. It offers 40 majors in engineering, health, technology, administration, education and the humanities. The school has a student population of 6,000. The main campus is in Gaza City. Females make up 50% of the student body. The College offers undergraduate degrees in a number of unique specializations such as education technology, technological management and planning, and geographic information systems.

Mayo Clinic School of Health Sciences (MCSHS), formerly known as Mayo School of Health Sciences (MSHS), is an accredited, private, nonprofit school of higher education specializing in allied health education. MCSHS operates within the Mayo Clinic College of Medicine and Science, which is the educational division of Mayo Clinic. As such, MCSHS is fully integrated with Mayo Clinic hospitals and clinics.
In the United States, certified anesthesiologist assistants (CAAs) are clinicians that practice medicine under the direction of licensed anesthesiologists to implement anesthesia care plans for a patient undergoing surgery. CAAs are integral members of the anesthesia care team as described by the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA). All CAAs possess a baccalaureate degree, and complete an intensive didactic and clinical program at a postgraduate level. CAAs are trained in the delivery and maintenance of all types of anesthesia care as well as advanced patient monitoring techniques. The goal of CAA education is to guide the transformation of student applicants into competent clinicians.

North-West College is a private for-profit system of colleges in California. North-West College offers diploma, associate degree and certification programs at each of its seven campuses throughout the Los Angeles and Riverside areas. North-West College was established in 1966 by Marsha Fuerst. Fuerst's family has been involved in the allied health field since the early 1950s. North-West College continues to be owned and operated by the Fuerst family.

Glendale Career College is a private, for-profit college in Glendale, California. It was established in 1946 by Dr. Byron Prout. It is now owned and operated by the Fuerst family of Success Education Colleges.

Nevada Career Institute is a for-profit technical college in Las Vegas, Nevada. Nevada Career Institute is owned and operated by the Fuerst family of Success Education Colleges.
CNI College is an allied health vocational college in Santa Ana, California. The main campus is located in the City of Orange.
Allen College is a private university focused on healthcare and located in Waterloo, Iowa.
The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) is a medical society for the medical subspecialty of neuromuscular and electrodiagnostic medicine based in the United States. Members are primarily neurologists and physiatrists—as well as allied health professionals and PhD researchers.
Ultimate Medical Academy (UMA) is a nonprofit career education school that grants associate degrees and training in the allied health field. The institution also provides continuing medical education (CME) to more than 30,000 physicians, nurses and other medical professionals annually.









