Related Research Articles
Transportation in the United States is facilitated by road, air, rail, and waterways. The vast majority of passenger travel occurs by automobile for shorter distances, and airplane for longer distances. In descending order, most cargoes travel by railroad, truck, pipeline, or boat; air shipping is typically used only for perishables and premium express shipments. Transportation is the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions by the United States.

Interstate 66 (I-66) is an east–west Interstate Highway in the eastern United States. It runs from an interchange with I-81 near Middletown, Virginia, on its western end to an interchange with U.S. Route 29 (US 29) in Washington, D.C., at the eastern terminus. Much of the route parallels US 29 or State Route 55 (SR 55) in Virginia. I-66 has no physical or historical connection to the famous US 66, which was located in a different region of the United States.

A rest area is a public facility located next to a large thoroughfare such as a motorway, expressway, or highway, at which drivers and passengers can rest, eat, or refuel without exiting onto secondary roads. Other names include motorway service area (UK), services (UK), travel plaza, rest stop, oasis (US), service area, rest and service area (RSA), resto, service plaza, lay-by, and service centre (Canada). Facilities may include park-like areas, fuel stations, public toilets, water fountains, restaurants, and dump and fill stations for caravans / motorhomes.

The Georgia Department of Transportation (GDOT) is the organization in charge of developing and maintaining all state and federal roadways in the U.S. state of Georgia. In addition to highways, the department also has a limited role in developing public transportation and general aviation programs. GDOT is headquartered in downtown Atlanta and is part of the executive branch of state government.

The Hampton Roads Bridge–Tunnel (HRBT) is a 3.5-mile (5.6 km)-long Hampton Roads crossing for Interstate 64 and U.S. Route 60. It is a four-lane facility comprising bridges, trestles, man-made islands, and tunnels under the main shipping channels for Hampton Roads harbor in the southeastern portion of Virginia in the United States.
The Virginia Department of Transportation (VDOT) is the agency of the state government responsible for transportation in the state of Virginia in the United States. VDOT is headquartered at the Virginia Department of Highways Building in downtown Richmond. VDOT is responsible for building, maintaining, and operating the roads, bridges, and tunnels in the commonwealth. It is overseen by the Commonwealth Transportation Board, which has the power to fund airports, seaports, rail, and public transportation.

The Benjamin Harrison Memorial Bridge is a vertical-lift bridge that spans the James River between Jordan's Point in Prince George County and Charles City County near Hopewell, Virginia. The bridge carries vehicle traffic of State Route 106 and State Route 156, and is owned by the Virginia Department of Transportation (VDOT). It is named after Benjamin Harrison V, a signer of the Declaration of Independence and a Governor of Virginia, who lived nearby at Berkeley Plantation.

The Midtown Tunnel carries U.S. Highway 58 across the Southern Branch of the Elizabeth River in the South Hampton Roads area of Virginia, US. It links the cities of Portsmouth and Norfolk. Owned by the Virginia Department of Transportation (VDOT), it is operated and maintained by Elizabeth River Crossings under a 58-year public–private partnership concession agreement. Formerly a toll-free facility, open road tolling was implemented on February 1, 2014 by VDOT to help finance repairs and expansion to the tunnel.

The Tennessee Department of Transportation (TDOT) is the department of transportation for the State of Tennessee, with multimodal responsibilities in roadways, aviation, public transit, waterways, and railroads. The core agency mission of TDOT is to provide a safe and reliable transportation system for people, goods, and services that supports economic prosperity in Tennessee. Since 1998, TDOT has been ranked amongst the top five in the nation for quality highway infrastructure. It is primarily headquartered in downtown Nashville and operates four regional offices in Chattanooga, Jackson, Knoxville, and Nashville.

Virginia State Route 7 (VA 7) is a major primary state highway and busy commuter route in northern Virginia, United States. It travels southeast from downtown Winchester to SR 400 in downtown Alexandria. Its route largely parallels those of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail and the Potomac River. Between its western terminus and Interstate 395 (I-395), SR 7 is part of the National Highway System. In 1968, the Virginia State Highway Commission designated the road as the "Harry Flood Byrd Highway" between Alexandria and Winchester to commemorate Harry F. Byrd Sr. (1887–1966).

State Route 27 (SR 27) is a freeway in Arlington County, Virginia, in the United States, known as Washington Boulevard. It was built during World War II to connect the Pentagon with U.S. Route 50 (US 50) and northern Arlington to the west and Washington, DC, to the east. Its 2.54-mile (4.09 km) route parallels the southern boundaries of Arlington National Cemetery. At its southernmost point, Route 27 passes through a complex interchange with Interstate 395. called the "Mixing Bowl," although local motorists more recently use that term also to refer to the Springfield Interchange on the Capital Beltway in Springfield. It is an important commuter route as well as providing access to a number of military installations, the cemetery and national memorials. Because Route 27 is the closest road to the site of the September 11 attack on the Pentagon, the route has been designated the "9/11 Heroes Memorial Highway."

Transportation in the Commonwealth of Virginia is by land, sea and air. Virginia's extensive network of highways and railroads were developed and built over a period almost 400 years, beginning almost immediately after the founding of Jamestown in 1607, and often incorporating old established trails of the Native Americans.

Interstate 95 (I-95) runs 179 miles (288 km) within the commonwealth of Virginia between its borders with North Carolina and Maryland. I-95 meets the northern terminus of I-85 in Petersburg and is concurrent with I-64 for three miles (4.8 km) in Richmond. Although I-95 was originally planned as a highway through Washington, D.C., it was rerouted along the eastern portion of the Capital Beltway. From Petersburg to Richmond, I-95 utilized most of the Richmond–Petersburg Turnpike, a former toll road.

Interstate 64 (I-64) in the US state of Virginia runs east–west through the middle of the state from West Virginia to the Hampton Roads region, for a total of 299 miles (481 km). It is notable for crossing the mouth of the harbor of Hampton Roads on the Hampton Roads Bridge–Tunnel (HRBT), the first bridge–tunnel to incorporate artificial islands, concurrent with U.S. Route 60 (US 60). Also noteworthy is a section through Rockfish Gap, a wind gap in the Blue Ridge Mountains, which was equipped with an innovative system of airport-style runway lighting embedded into the pavement to aid motorists during periods of poor visibility due to fog or other conditions.

Hillsdale station is one of three Caltrain stations in San Mateo, California. The station is next to the Bay Meadows neighborhood and close to the Hillsdale Shopping Center.
The Virginia Port Authority (VPA) is an autonomous agency of the Commonwealth of Virginia that owns The Port of Virginia, a group of facilities with their activity centered on the harbor of Hampton Roads, Virginia.
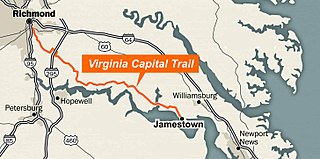
The Virginia Capital Trail (VCT) is a dedicated, paved bicycle and pedestrian trail crossing four counties and 51.7 miles (83.2 km) between Jamestown and Richmond, Virginia — that is, between the Colony of Virginia's first capital and Virginia's current capital, with an alternate end at Williamsburg, the last colonial capital. Construction began in 2006 and completed to Jamestown in October 2015. With the Williamsburg extension, the blacktop ribbon extends approximately 62 miles, and attracted 1.2 million users in 2021.
Elizabeth River Crossings (ERC), officially known as Elizabeth River Crossings OpCo, LLC, is a limited liability company whose sole purpose is to finance, deliver, operate and maintain the Elizabeth River Tunnels Project in the South Hampton Roads region of Virginia. The project comprised the development, design, construction, finance and operation of a new two-lane tunnel adjacent to the existing Midtown Tunnel under the Elizabeth River, maintenance and safety improvements to the existing Midtown and Downtown tunnels, extending the Martin Luther King Freeway from London Boulevard to Interstate 264, and interchange modifications at Brambleton Avenue and Hampton Boulevard.
The Elizabeth River Tunnels Project, a series of transportation projects in the South Hampton Roads region of Virginia, comprises the rehabilitation of the Downtown and existing Midtown Tunnels, the construction of a new parallel Midtown Tunnel, and the extension of the MLK Freeway/U.S. 58 to I-264. Intended to reduce congestion on area surface streets and arterial roads, the project was administered by Elizabeth River Crossings (ERC) and Virginia Department of Transportation (VDOT) as part of a 58-year public-private partnership. ERC maintains and operates the project ongoing.
Transportation in the United States is governed by laws and regulations of the federal government. The Department of Transportation is responsible for carrying out federal transportation policy, and the Department of Homeland Security is responsible for security in transportation.
References
- ↑ "Final Closure Plan for 19 Virginia Safety Rest Areas (SRA) and Welcome Centers (WC)" (PDF). www.virginiadot.org. Retrieved 2010-04-27.
- ↑ "REST AREA CLOSURES TO BEGIN JULY 21: Truck Parking Changes to Be Implemented July 21 in All Rest Areas Statewide". Archived from the original on 2009-07-08. Retrieved 2010-04-27.
- ↑ "VDOT REOPENS FIRST FOUR REST AREAS: Four I-81 rest areas reopened by Feb. 17 goal". Archived from the original on 2011-01-05. Retrieved 2010-04-27.
