Related Research Articles

Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other electrically charged particles. Electronics is a subfield of electrical engineering which uses active devices such as transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits to control and amplify the flow of electric current and to convert it from one form to another, such as from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) or from analog signals to digital signals.
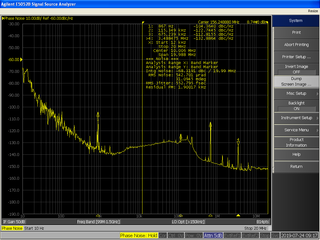
In signal processing, phase noise is the frequency-domain representation of random fluctuations in the phase of a waveform, corresponding to time-domain deviations from perfect periodicity (jitter). Generally speaking, radio-frequency engineers speak of the phase noise of an oscillator, whereas digital-system engineers work with the jitter of a clock.
SPICE is a general-purpose, open-source analog electronic circuit simulator. It is a program used in integrated circuit and board-level design to check the integrity of circuit designs and to predict circuit behavior.
This is an index of articles relating to electronics and electricity or natural electricity and things that run on electricity and things that use or conduct electricity.

A voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) is an electronic oscillator whose oscillation frequency is controlled by a voltage input. The applied input voltage determines the instantaneous oscillation frequency. Consequently, a VCO can be used for frequency modulation (FM) or phase modulation (PM) by applying a modulating signal to the control input. A VCO is also an integral part of a phase-locked loop. VCOs are used in synthesizers to generate a waveform whose pitch can be adjusted by a voltage determined by a musical keyboard or other input.
The Clapp oscillator or Gouriet oscillator is an LC electronic oscillator that uses a particular combination of an inductor and three capacitors to set the oscillator's frequency. LC oscillators use a transistor and a positive feedback network. The oscillator has good frequency stability.
This is an alphabetical list of articles pertaining specifically to electrical and electronics engineering. For a thematic list, please see List of electrical engineering topics. For a broad overview of engineering, see List of engineering topics. For biographies, see List of engineers.

OrCAD Systems Corporation was a software company that made OrCAD, a proprietary software tool suite used primarily for electronic design automation (EDA). The software is used mainly by electronic design engineers and electronic technicians to create electronic schematics, and perform mixed-signal simulation and electronic prints for manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs). OrCAD was taken over by Cadence Design Systems in 1999 and was integrated with Cadence Allegro in 2005.

Ngspice is an open-source mixed-level/mixed-signal electronic circuit simulator. It is a successor of the latest stable release of Berkeley SPICE, version 3f.5, which was released in 1993. A small group of maintainers and the user community contribute to the ngspice project by providing new features, enhancements and bug fixes.

Quite Universal Circuit Simulator (Qucs) is a free-software electronics circuit simulator software application released under GPL. It offers the ability to set up a circuit with a graphical user interface and simulate the large-signal, small-signal and noise behaviour of the circuit. Pure digital simulations are also supported using VHDL and/or Verilog. Only a small set of digital devices like flip flops and logic gates can be used with analog circuits. Qucs uses its own SPICE-incompatible backend simulator Qucsator, however the Qucs-S fork supports some SPICE backends.

Technology computer-aided design is a branch of electronic design automation (EDA) that models semiconductor fabrication and semiconductor device operation. The modeling of the fabrication is termed process TCAD, while the modeling of the device operation is termed device TCAD. Included are the modelling of process steps, and modelling of the behavior of the electrical devices based on fundamental physics, such as the doping profiles of the devices. TCAD may also include the creation of "compact models", which try to capture the electrical behavior of such devices but do not generally derive them from the underlying physics. SPICE simulator itself is usually considered as part of EDA rather than TCAD.

Semiconductor device modeling creates models for the behavior of the electrical devices based on fundamental physics, such as the doping profiles of the devices. It may also include the creation of compact models, which try to capture the electrical behavior of such devices but do not generally derive them from the underlying physics. Normally it starts from the output of a semiconductor process simulation.

Ansys HFSS, is a commercial finite element method solver for electromagnetic (EM) structures from Ansys that offers multiple state-of-the-art solver technologies. Each solver in ANSYS HFSS is an automated solution processor for which the user dictates the geometry, properties of the material and the required range of solution frequencies.
Sir Christopher Maxwell Snowden, is a British electronic engineer and academic. He was the former Vice-Chancellor of Surrey University (2005–2015), and of the University of Southampton (2015–2019). He was president of Universities UK for a two-year term until 31 July 2015. He is currently the chairman of the ERA Foundation.
RF microwave CAE CAD is computer-aided design (CAD) using computer technology to aid in the design, modeling, and simulation of an RF or microwave product. It is a visual and symbol-based method of communication whose conventions are particular to RF/microwave engineering.
The space mapping methodology for modeling and design optimization of engineering systems was first discovered by John Bandler in 1993. It uses relevant existing knowledge to speed up model generation and design optimization of a system. The knowledge is updated with new validation information from the system when available.
Optimization Systems Associates (OSA) was founded by John Bandler in 1983. OSA produced the first commercial implementation of space mapping optimization to enhance the speed and accuracy of engineering design. OSA’s primary thrust was in computer-aided design (CAD) and simulation and optimization of radio-frequency and microwave circuits and systems. Its products included developments of Bandler's space mapping concept and methodology, which facilitates effective modeling and design optimization of computationally intensive engineering systems.
Les Besser is an American electronics engineer, an expert in microwave technology. He is the founder (1973) of Compact Software, the first commercially successful microwave computer-aided design (CAD) company, which commercialize his program COMPACT.

SPICE OPUS is a free general purpose electronic circuit simulator, developed and maintained by members of EDA Group, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia. It is based on original Berkeley’s SPICE analog circuit simulator and inlcudes various improvements and advances, such as memory-leak bug fixes and plotting tool improvements. SPICE OPUS is specially designed for fast optimization loops via its built-in optimizer.
Ulrich Lothar Albert Rohde is a German and American electrical engineer, entrepreneur, and university professor.
References
Articles by Besser
- Besser, L., Newcomb, R., "A Scattering Matrix Program for High Frequency Circuit Analysis" IEEE Conference on Systems, Networks, and Computers, Mexico, January 1971
- Besser, L. "Computer Aided Design of High Frequency Circuits" Electromechanical Design, August 1971
- Besser, L. "A Fast Computer Routine to Design High Frequency Circuits" IEEE ICC Conference, San Francisco, California, June 1970
Articles by Rohde
- Ulrich L. Rohde, Anthony M. Pavio and Robert A. Pucel, "Accurate Noise Simulation of Microwave Amplifiers Using CAD", Microwave Journal, December 1988.
- R.A. Pucel, W. Struble, R Hallgren, and U.L. Rohde, "A General Noise De-embedding Procedure for Packaged Two-Port Linear Active Devices", IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, Vol. 40, No. 11, November 1992, pp. 2013–2024.
- R.A. Pucel and U.L. Rohde, "An Exact Expression for the Noise Resistance Rn of a Bipolar Transistor for Use with the Hawkins Noise Model", IEEE Microwave and Guided Wave Letters, Vol. 3, No. 2, February 1993, pp. 35–37. 1993
- U. L. Rohde, "Designing and Optimizing Low Phase Noise Oscillators using Harmonic Balance Simulators and Advanced Parameter Extraction" Session B3-3,2nd IEEE Joint Chapter Workshop in conjunction with M94 CAE, Modeling and Measurement Verification, October 24, 1994 - Wembley Conference Centre, London, UK, 1994RF/
- Ulrich L. Rohde and Matthias Rudolph, "RF/Microwave Circuit Design for Wireless Applications", 2nd Edition, John Wiley & Sons, December 2012, ISBN 978-0-470-90181-6
- George D. Vendelin, Anthony M. Pavio, Ulrich L. Rohde, Matthias Rudolph, "Microwave Circuit Design Using Linear and Nonlinear Techniques ", 3rd Edition, John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, April 2021, ISBN 978-1-119-74170-1.
- Ulrich L. Rohde, Ajay K. Poddar, Georg Böck, "The Design of Modern Microwave Oscillators for Wireless Applications " John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, May 2005, ISBN 0-471-72342-8.