
A compass is an instrument used for navigation and orientation that shows direction relative to the geographic cardinal directions. Usually, a diagram called a compass rose shows the directions north, south, east, and west on the compass face as abbreviated initials. When the compass is used, the rose can be aligned with the corresponding geographic directions; for example, the "N" mark on the rose points northward. Compasses often display markings for angles in degrees in addition to the rose. North corresponds to 0°, and the angles increase clockwise, so east is 90° degrees, south is 180°, and west is 270°. These numbers allow the compass to show magnetic North azimuths or true North azimuths or bearings, which are commonly stated in this notation. If magnetic declination between the magnetic North and true North at latitude angle and longitude angle is known, then direction of magnetic North also gives direction of true North.

Anishinaabe traditional beliefs cover the traditional belief system of the Anishinaabeg peoples, consisting of the Algonquin/Nipissing, Ojibwa/Chippewa/Saulteaux/Mississaugas, Odawa, Potawatomi and Oji-Cree, located primarily in the Great Lakes region of North America.
The Hocągara (Ho-Chungara) or Hocąks (Ho-Chunks) are a Siouan-speaking Indian Nation originally from Wisconsin and northern Illinois. Due to forced emigration in the 19th century, they now constitute two individual tribes; the Ho-Chunk Nation of Wisconsin and the Winnebago Tribe of Nebraska. They are most closely related to the Chiwere peoples, and more distantly to the Dhegiha.

Australian Aboriginal religion and mythology is the sacred spirituality represented in the stories performed by Aboriginal Australians within each of the language groups across Australia in their ceremonies. Aboriginal spirituality includes the Dreamtime, songlines, and Aboriginal oral literature.

The indigenous peoples of the Americas comprise numerous different cultures. Each has its own mythologies. Some are quite distinct, but certain themes are shared across the cultural boundaries.

The Peshtigo fire was a very large forest fire that took place on October 8, 1871, in northeastern Wisconsin, United States, including much of the southern half of the Door Peninsula and adjacent parts of the Upper Peninsula of Michigan. The largest community in the affected area was Peshtigo, Wisconsin. The fire burned approximately 1,200,000 acres (490,000 ha) and is the deadliest wildfire in recorded history, with the number of deaths estimated between 1,500 and 2,500.

A compass rose, sometimes called a windrose or rose of the winds, is a figure on a compass, map, nautical chart, or monument used to display the orientation of the cardinal directions and their intermediate points. It is also the term for the graduated markings found on the traditional magnetic compass. Today, a form of compass rose is found on, or featured in, almost all navigation systems, including nautical charts, non-directional beacons (NDB), VHF omnidirectional range (VOR) systems, global-positioning systems (GPS), and similar equipment.
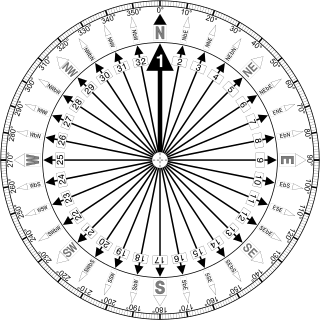
The points of the compass are the vectors by which planet-based directions are conventionally defined. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each separated by 90 degrees, and secondarily divided by four ordinal (intercardinal) directions—northeast, southeast, southwest, and northwest—each located halfway between two cardinal directions. Some disciplines such as meteorology and navigation further divide the compass with additional vectors. Within European tradition, a fully defined compass has 32 'points'.
Bouquet, a word of French origin, pronounced [bukɛ], may refer to:

A flood myth or deluge myth is a myth in which a great flood, usually sent by a deity or deities, destroys civilization, often in an act of divine retribution. Parallels are often drawn between the flood waters of these myths and the primaeval waters which appear in certain creation myths, as the flood waters are described as a measure for the cleansing of humanity, in preparation for rebirth. Most flood myths also contain a culture hero, who "represents the human craving for life".

The Battle of Fort Duquesne was a British assault on the eponymous French fort that was repulsed with heavy losses on 14 September 1758, during the French and Indian War.

A flower bouquet is a collection of flowers in a creative arrangement. Flower bouquets can be arranged for the decor of homes or public buildings, or may be handheld. Handheld bouquets are classified by several different popular shapes and styles, including nosegay, crescent, and cascading bouquets. Flower bouquets are often given for special occasions such as birthdays or anniversaries. They are also used extensively in weddings. Bouquets arranged in vases or planters for home decor can be arranged in either traditional or modern styles. Symbolism may be attached to the types of flowers used, according to the culture.
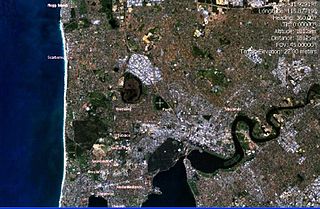
Lake Monger is a large urban wetland on the Swan Coastal Plain in suburban Perth, Western Australia nestled between the suburbs of Leederville, Wembley and Glendalough.

Great Lakes Myth Society (GLMS) is a musical group from southeast Michigan in the United States. Members include brothers Timothy Monger and James Christopher Monger(vocals, guitar, and mandolin) Fido Kennington(drumset and vocals), Greg McIntosh(vocals, guitar) and Scott McClintock(bass and vocals). They write and perform songs about Michigan, including "myths" from around the area, as well as more contemporary, non-regional work.

Niagara Herald of Arms Extraordinary is the title of one of the officers of arms at the Canadian Heraldic Authority in Ottawa. Herald Extraordinary is an honorary position reserved for people who have made notable contributions to Canadian heraldry. Like the other heralds at the Authority, the name is derived from the Canadian river of the same name.

Rogers Dry Lake is an endorheic desert salt pan in the Mojave Desert of Kern County, California. The lake derives its name from the Anglicization from the Spanish name, Rodriguez Dry Lake. It is the central part of Edwards Air Force Base as its hard surface provides a natural extension to the paved runways. It was formerly known as Muroc Dry Lake.
"Eleven Roses" is a song written by Lamar Morris and Darrell McCall and recorded by American country music artist Hank Williams Jr.. It was released in March 1972 as the only single and title track from the album of the same name. The song was Williams' first number one, as solo artist, on the Billboard magazine Hot Country Singles chart in July 1972, spending two weeks atop the chart. The song spent 14 weeks on the Hot Country Singles chart's top 40.

Still Life: Vase with Pink Roses was painted in 1890 by Vincent van Gogh in Saint-Rémy. At the time the work was painted Van Gogh was readying himself to leave the Saint-Rémy asylum for the quiet town of Auvers-sur-Oise outside of Paris. This and the similarly-dated Pink Roses reflect the optimism Van Gogh felt at that time about his future, both in his choice of flowers as a subject and the colors used. The painting is owned by the National Gallery of Art of Washington, D.C.
A debutante is a girl or young lady from an aristocratic or upper-class family introduced to society at a formal "debut" presentation.

Bouquet sou were a series of tokens that were created for use primarily within Lower Canada in the mid- to late-1830s. Roughly equivalent in value to a half penny, the "bouquet sou" were so called because they displayed a group of heraldic flowers tied together with a ribbon on their obverse. The group of flowers were encircled by one of several legends, which might say "Trade & Agriculture / Lower Canada", "Agriculture & Commerce / Bas Canada" or some variant of these that might also substitute the name of the issuing bank. The other side most typically gave the denomination of "un sou", surrounded by a wreath and the words "Bank Token" and "Montreal". There are a large variety of these tokens, distinguished primarily by the number and variety of flowers that appear in the "bouquet", along with the differences in the legends that appeared on either side of the token. They were initially issued by the banks of Lower Canada, and were later imitated by speculators who produced tokens that looked similar, but were underweight for their denomination. These coins also circulated to Upper Canada, as at least one archeology dig attests. Large numbers of these tokens were produced and many examples can easily be obtained for only a few C$dollars, though a few rare varieties can command significantly higher prices.
















