
In quantum mechanics, the uncertainty principle is any of a variety of mathematical inequalities asserting a fundamental limit to the accuracy with which the values for certain pairs of physical quantities of a particle, such as position, x, and momentum, p, can be predicted from initial conditions.
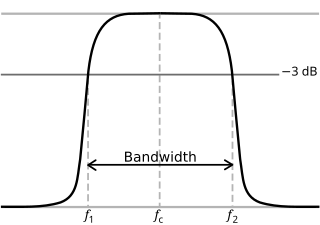
In physics and electrical engineering, a cutoff frequency, corner frequency, or break frequency is a boundary in a system's frequency response at which energy flowing through the system begins to be reduced rather than passing through.
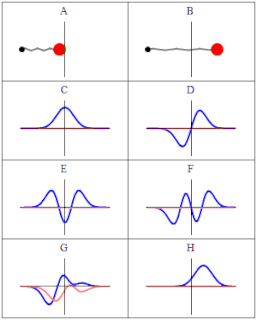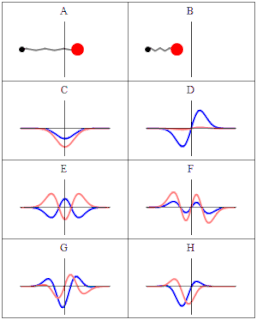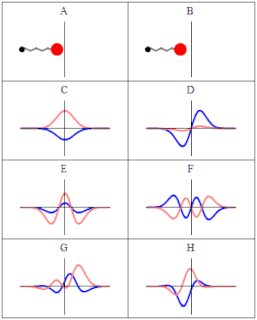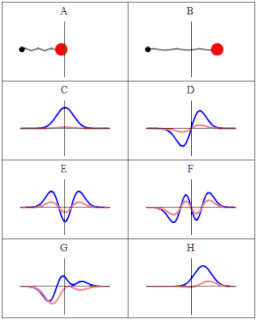
The quantum harmonic oscillator is the quantum-mechanical analog of the classical harmonic oscillator. Because an arbitrary smooth potential can usually be approximated as a harmonic potential at the vicinity of a stable equilibrium point, it is one of the most important model systems in quantum mechanics. Furthermore, it is one of the few quantum-mechanical systems for which an exact, analytical solution is known.
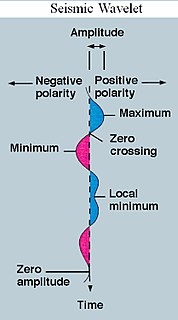
A wavelet is a wave-like oscillation with an amplitude that begins at zero, increases, and then decreases back to zero. It can typically be visualized as a "brief oscillation" like one recorded by a seismograph or heart monitor. Generally, wavelets are intentionally crafted to have specific properties that make them useful for signal processing.

In mathematics, the Morlet wavelet is a wavelet composed of a complex exponential (carrier) multiplied by a Gaussian window (envelope). This wavelet is closely related to human perception, both hearing and vision.

In physics, the Rabi cycle is the cyclic behaviour of a two-level quantum system in the presence of an oscillatory driving field. A great variety of physical processes belonging to the areas of quantum computing, condensed matter, atomic and molecular physics, and nuclear and particle physics can be conveniently studied in terms of two-level quantum mechanical systems, and exhibit Rabi flopping when coupled to an oscillatory driving field. The effect is important in quantum optics, magnetic resonance and quantum computing, and is named after Isidor Isaac Rabi.

In mathematics, the continuous wavelet transform (CWT) is a formal tool that provides an overcomplete representation of a signal by letting the translation and scale parameter of the wavelets vary continuously.
In physics, a wave vector is a vector which helps describe a wave. Like any vector, it has a magnitude and direction, both of which are important. Its magnitude is either the wavenumber or angular wavenumber of the wave, and its direction is ordinarily the direction of wave propagation.
Creation and annihilation operators are mathematical operators that have widespread applications in quantum mechanics, notably in the study of quantum harmonic oscillators and many-particle systems. An annihilation operator lowers the number of particles in a given state by one. A creation operator increases the number of particles in a given state by one, and it is the adjoint of the annihilation operator. In many subfields of physics and chemistry, the use of these operators instead of wavefunctions is known as second quantization.
Hermitian wavelets are a family of continuous wavelets, used in the continuous wavelet transform. The Hermitian wavelet is defined as the derivative of a Gaussian distribution:
In physics, a free particle is a particle that, in some sense, is not bound by an external force, or equivalently not in a region where its potential energy varies. In classical physics, this means the particle is present in a "field-free" space. In quantum mechanics, it means the particle is in a region of uniform potential, usually set to zero in the region of interest since the potential can be arbitrarily set to zero at any point in space.
In mathematical physics, some approaches to quantum field theory are more popular than others. For historical reasons, the Schrödinger representation is less favored than Fock space methods. In the early days of quantum field theory, maintaining symmetries such as Lorentz invariance, displaying them manifestly, and proving renormalisation were of paramount importance. The Schrödinger representation is not manifestly Lorentz invariant and its renormalisability was only shown as recently as the 1980s by Kurt Symanzik (1981).

In mathematics, a wavelet series is a representation of a square-integrable function by a certain orthonormal series generated by a wavelet. This article provides a formal, mathematical definition of an orthonormal wavelet and of the integral wavelet transform.
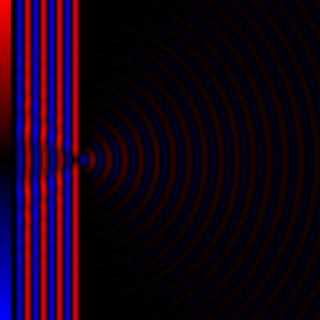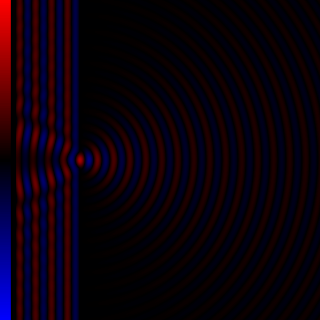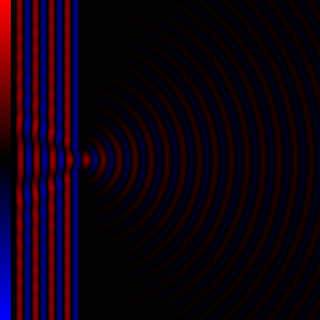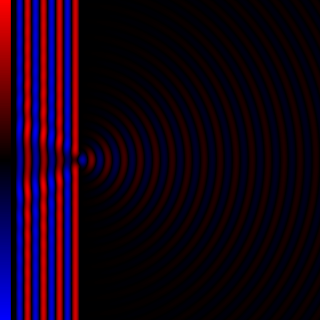
Diffraction processes affecting waves are amenable to quantitative description and analysis. Such treatments are applied to a wave passing through one or more slits whose width is specified as a proportion of the wavelength. Numerical approximations may be used, including the Fresnel and Fraunhofer approximations.
Curvelets are a non-adaptive technique for multi-scale object representation. Being an extension of the wavelet concept, they are becoming popular in similar fields, namely in image processing and scientific computing.
In mathematics, vector spherical harmonics (VSH) are an extension of the scalar spherical harmonics for use with vector fields. The components of the VSH are complex-valued functions expressed in the spherical coordinate basis vectors.
An LC circuit can be quantized using the same methods as for the quantum harmonic oscillator. An LC circuit is a variety of resonant circuit, and consists of an inductor, represented by the letter L, and a capacitor, represented by the letter C. When connected together, an electric current can alternate between them at the circuit's resonant frequency:
Fractional wavelet transform (FRWT) is a generalization of the classical wavelet transform (WT). This transform is proposed in order to rectify the limitations of the WT and the fractional Fourier transform (FRFT). The FRWT inherits the advantages of multiresolution analysis of the WT and has the capability of signal representations in the fractional domain which is similar to the FRFT.

The Meyer wavelet is an orthogonal wavelet proposed by Yves Meyer. As a type of a continuous wavelet, it has been applied in a number of cases, such as in adaptive filters, fractal random fields, and multi-fault classification.
In mathematics, in functional analysis, several different wavelets are known by the name Poisson wavelet. In one context, the term "Poisson wavelet" is used to denote a family of wavelets labeled by the set of positive integers, the members of which are associated with the Poisson probability distribution. These wavelets were first defined and studied by Karlene A. Kosanovich, Allan R. Moser and Michael J. Piovoso in 1995–96. In another context, the term refers to a certain wavelet which involves a form of the Poisson integral kernel. In still another context, the terminology is used to describe a family of complex wavelets indexed by positive integers which are connected with the derivatives of the Poisson integral kernel.















