
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is called a compression-ignition engine. This contrasts with engines using spark plug-ignition of the air-fuel mixture, such as a petrol engine or a gas engine.

A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tight by piston rings. In an engine, its purpose is to transfer force from expanding gas in the cylinder to the crankshaft via a piston rod and/or connecting rod. In a pump, the function is reversed and force is transferred from the crankshaft to the piston for the purpose of compressing or ejecting the fluid in the cylinder. In some engines, the piston also acts as a valve by covering and uncovering ports in the cylinder.

A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types. The main types are: the internal combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles; the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution; and the Stirling engine for niche applications. Internal combustion engines are further classified in two ways: either a spark-ignition (SI) engine, where the spark plug initiates the combustion; or a compression-ignition (CI) engine, where the air within the cylinder is compressed, thus heating it, so that the heated air ignites fuel that is injected then or earlier.

A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed, by a connecting rod and crank, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is most commonly applied to reciprocating engines as just described, although some authorities have also referred to the steam turbine and devices such as Hero's aeolipile as "steam engines". The essential feature of steam engines is that they are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term steam engine can refer to either complete steam plants, such as railway steam locomotives and portable engines, or may refer to the piston or turbine machinery alone, as in the beam engine and stationary steam engine.
Timeline of motor and engine technology

In engineering, the Miller cycle is a thermodynamic cycle used in a type of internal combustion engine. The Miller cycle was patented by Ralph Miller, an American engineer, U.S. patent 2,817,322 dated Dec 24, 1957. The engine may be two- or four-stroke and may be run on diesel fuel, gases, or dual fuel. It uses a supercharger or a turbocharger to offset the performance loss of the Atkinson cycle.

A four-strokeengine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction. The four separate strokes are termed:
- Intake: Also known as induction or suction. This stroke of the piston begins at top dead center (T.D.C.) and ends at bottom dead center (B.D.C.). In this stroke the intake valve must be in the open position while the piston pulls an air-fuel mixture into the cylinder by producing a partial vacuum in the cylinder through its downward motion.
- Compression: This stroke begins at B.D.C, or just at the end of the suction stroke, and ends at T.D.C. In this stroke the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture in preparation for ignition during the power stroke (below). Both the intake and exhaust valves are closed during this stage.
- Combustion: Also known as power or ignition. This is the start of the second revolution of the four stroke cycle. At this point the crankshaft has completed a full 360 degree revolution. While the piston is at T.D.C. the compressed air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark plug or by heat generated by high compression, forcefully returning the piston to B.D.C. This stroke produces mechanical work from the engine to turn the crankshaft.
- Exhaust: Also known as outlet. During the exhaust stroke, the piston, once again, returns from B.D.C. to T.D.C. while the exhaust valve is open. This action expels the spent air-fuel mixture through the exhaust port.

The Brayton cycle, also known as the Joule cycle, is a thermodynamic cycle that describes the operation of certain heat engines that have air or some other gas as their working fluid. It is characterized by isentropic compression and expansion, and isobaric heat addition and rejection, though practical engines have adiabatic rather than isentropic steps.

The Atkinson-cycle engine is a type of internal combustion engine invented by James Atkinson in 1882. The Atkinson cycle is designed to provide efficiency at the expense of power density.

The valve gear of a steam engine is the mechanism that operates the inlet and exhaust valves to admit steam into the cylinder and allow exhaust steam to escape, respectively, at the correct points in the cycle. It can also serve as a reversing gear. It is sometimes referred to as the "motion".

Eisenhuth Horseless Vehicle Company was a manufacturer of Brass Age automobiles who were originally based in New York City. In 1902 the company purchased the Keating Wheel and Automobile Company and established manufacturing operations in Middletown, Connecticut. During 1903, the company merged with the Graham Fox Motor Car Company, absorbing that firm and expanding operations in Middletown.

The hot-bulb engine, also known as a semi-diesel, is a type of internal combustion engine in which fuel ignites by coming in contact with a red-hot metal surface inside a bulb, followed by the introduction of air (oxygen) compressed into the hot-bulb chamber by the rising piston. There is some ignition when the fuel is introduced, but it quickly uses up the available oxygen in the bulb. Vigorous ignition takes place only when sufficient oxygen is supplied to the hot-bulb chamber on the compression stroke of the engine.
Engine efficiency of thermal engines is the relationship between the total energy contained in the fuel, and the amount of energy used to perform useful work. There are two classifications of thermal engines-
- Internal combustion and
- External combustion engines.
The term six-stroke engine has been applied to a number of alternative internal combustion engine designs that attempt to improve on traditional two-stroke and four-stroke engines. Claimed advantages may include increased fuel efficiency, reduced mechanical complexity, and/or reduced emissions. These engines can be divided into two groups based on the number of pistons that contribute to the six strokes.
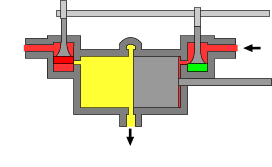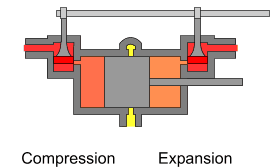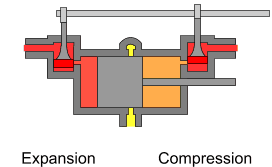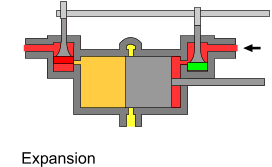
The uniflow type of steam engine uses steam that flows in one direction only in each half of the cylinder. Thermal efficiency is increased by having a temperature gradient along the cylinder. Steam always enters at the hot ends of the cylinder and exhausts through ports at the cooler centre. By this means, the relative heating and cooling of the cylinder walls is reduced.
Internal combustion engines date back to between the 10th and 13th centuries, when the first rocket engines were invented in China. Following the first commercial steam engine in 1698, various efforts were made during the 18th century to develop equivalent internal combustion engines. In 1791, the English inventor John Barber patented a gas turbine. In 1794, Thomas Mead patented a gas engine. Also in 1794, Robert Street patented an internal-combustion engine, which was also the first to use liquid fuel (petroleum) and built an engine around that time. In 1798, John Stevens designed the first American internal combustion engine. In 1807, French engineers Nicéphore and Claude Niépce ran a prototype internal combustion engine, using controlled dust explosions, the Pyréolophore. This engine powered a boat on the river in France. The same year, the Swiss engineer François Isaac de Rivaz built and patented a hydrogen and oxygen-powered internal-combustion engine. Fitted to a crude four-wheeled wagon, François Isaac de Rivaz first drove it 100 metres in 1813, thus making history as the first car-like vehicle known to have been powered by an internal-combustion engine.

George Saxon & Co was an English engineering company that manufactured stationary steam engines. It was based in the Openshaw district of Manchester. The company produced large steam-driven engines for power stations and later for textile mills in Lancashire and elsewhere.

A compound engine is an engine that has more than one stage for recovering energy from the same working fluid, with the exhaust from the first stage passing through the second stage, and in some cases then on to another subsequent stage or even stages. Originally invented as a means of making steam engines more efficient, the compounding of engines by use of several stages has also been used on internal combustion engines and continues to have niche markets there.

An internal combustion engine is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons, turbine blades, a rotor, or a nozzle. This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to.

The five-stroke engine is a compound internal combustion engine patented by Gerhard Schmitz in 2000.













