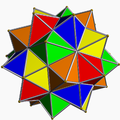
| Compound of five tetrahemihexahedra | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Uniform compound |
| Index | UC18 |
| Polyhedra | 5 tetrahemihexahedra |
| Faces | 20 triangles, 15 squares |
| Edges | 60 |
| Vertices | 30 |
| Symmetry group | chiral icosahedral (I) |
| Subgroup restricting to one constituent | chiral tetrahedral (T) |
A compound of five tetrahemihexahedra is a uniform polyhedron compound and a symmetric arrangement of five tetrahemihexahedra. It could be also called a hemirhombichiricosahedron. It is chiral with icosahedral symmetry (I).