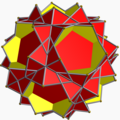
| Compound of twelve pentagrammic prisms | |
|---|---|
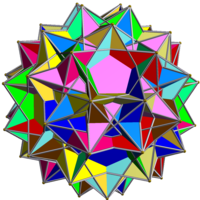 | |
| Type | Uniform compound |
| Index | UC37 |
| Polyhedra | 12 pentagrammic prisms |
| Faces | 24 pentagrams, 60 squares |
| Edges | 180 |
| Vertices | 60 |
| Symmetry group | icosahedral (Ih) |
| Subgroup restricting to one constituent | 5-fold dihedral (D5) |
This uniform polyhedron compound is a symmetric arrangement of 12 pentagrammic prisms, aligned in pairs with the axes of fivefold rotational symmetry of a dodecahedron.
It results from composing the two enantiomorphs of the compound of six pentagrammic prisms. In doing so, the vertices of the two enantiomorphs coincide, with the result that the full compound has two pentagrammic prisms incident on each of its vertices.