
Penicillium ascomycetous fungi are of major importance in the natural environment as well as food and drug production.

The longhorn beetles are a cosmopolitan family of beetles, typically characterized by extremely long antennae, which are often as long as or longer than the beetle's body. In various members of the family, however, the antennae are quite short and such species can be difficult to distinguish from related beetle families such as the Chrysomelidae. The family is large, with over 26,000 species described, slightly more than half from the Eastern Hemisphere. Several are serious pests. The larvae, called roundheaded borers, bore into wood, where they can cause extensive damage to either living trees or untreated lumber. A number of species mimic ants, bees, and wasps, though a majority of species are cryptically colored. The rare titan beetle from northeastern South America is often considered the largest insect, with a maximum known body length of just over 16.7 cm (6.6 in). The scientific name of this beetle family goes back to a figure from Greek mythology: after an argument with nymphs, the shepherd Cerambus was transformed into a large beetle with horns.

The glucose oxidase enzyme (GOx) also known as notatin is an oxido-reductase that catalyses the oxidation of glucose to hydrogen peroxide and D-glucono-δ-lactone. This enzyme is produced by certain species of fungi and insects and displays antibacterial activity when oxygen and glucose are present.

Paspalum notatum, known commonly as bahiagrass, common bahia, and Pensacola bahia, is a tropical to subtropical perennial grass. It is known for its prominent V-shaped inflorescence consisting of two spike-like racemes containing multiple tiny spikelets, each about 2.8–3.5 millimetres (0.11–0.14 in) long.
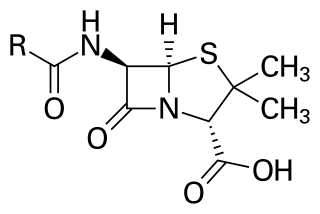
The history of penicillin follows a number of observations and discoveries of apparent evidence of antibiotic activity in molds before the modern isolation of the chemical penicillin in 1928. There are anecdotes about ancient societies using molds to treat infections, and in the following centuries many people observed the inhibition of bacterial growth by various molds. However, it is unknown if the species involved were Penicillium species or if the antimicrobial substances produced were penicillin.

The Vesperidae are a small family of beetles, normally classified within the family Cerambycidae, of heterogeneous aspect but all characterised by larval stages related to roots of herbaceous plants or trees
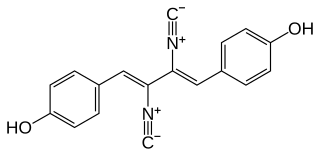
Xantocillin (INN), also known as xanthocillin X or ophthocillin, was the first reported natural product found to contain the isocyanide functional group. It was first isolated from Penicillium notatum by Rothe in 1950 and subsequently from several other sources.
Compsosomatini is a tribe of longhorn beetles of the Lamiinae subfamily.
Compsosoma is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae.
Compsosoma chabrillacii is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Thomson in 1857. It is known from Brazil.
Compsosoma fasciatum is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Monné in 1980. It is known from Brazil.
Compsosoma geayi is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Gounelle in 1908. It is known from Brazil and French Guiana.
Compsosoma mniszechii is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Thomson in 1857. It is known from Brazil and Peru.
Compsosoma monnei is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Martins and Galileo in 1996. It is known from Bolivia.
Compsosoma mutillarium is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Klug in 1825. It is known from Brazil.
Compsosoma nubilum is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Gounelle in 1908. It is known from Bolivia, Brazil and Paraguay.
Compsosoma perpulchrum is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Vigors in 1825. It is known from Argentina and Brazil.
Compsosoma phaleratum is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Thomson in 1857. It is known from Brazil.
Compsosoma vestitipenne is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Dmytro Zajciw in 1962. It is known from Brazil.

Anthidiellum notatum, the northern rotund-resin bee, is a species of hymenopteran in the family Megachilidae. It is found in North America.









