
An oil well is a boring in the Earth that is designed to bring petroleum oil hydrocarbons to the surface. Usually some natural gas is released as associated petroleum gas along with the oil. A well that is designed to produce only gas may be termed a gas well. Wells are created by drilling down into an oil or gas reserve that is then mounted with an extraction device such as a pumpjack which allows extraction from the reserve. Creating the wells can be an expensive process, costing at least hundreds of thousands of dollars, and costing much more when in hard to reach areas, e.g., when creating offshore oil platforms. The process of modern drilling for wells first started in the 19th century, but was made more efficient with advances to oil drilling rigs during the 20th century.

A borehole is a narrow shaft bored in the ground, either vertically or horizontally. A borehole may be constructed for many different purposes, including the extraction of water, other liquids or gases, as part of a geotechnical investigation, environmental site assessment, mineral exploration, temperature measurement, as a pilot hole for installing piers or underground utilities, for geothermal installations, or for underground storage of unwanted substances, e.g. in carbon capture and storage.
Well logging, also known as borehole logging is the practice of making a detailed record of the geologic formations penetrated by a borehole. The log may be based either on visual inspection of samples brought to the surface or on physical measurements made by instruments lowered into the hole. Some types of geophysical well logs can be done during any phase of a well's history: drilling, completing, producing, or abandoning. Well logging is performed in boreholes drilled for the oil and gas, groundwater, mineral and geothermal exploration, as well as part of environmental and geotechnical studies.
A mud engineer works on an oil well or gas well drilling rig, and is responsible for ensuring the properties of the drilling fluid, also known as drilling mud, are within designed specifications.
In petroleum production, the casing hanger is that portion of a wellhead assembly which provides support for the casing string when it is lowered into the wellbore. It serves to ensure that the casing is properly located. When the casing string has been run into the wellbore it is hung off, or suspended, by a casing hanger, which rests on a landing shoulder inside the casing spool. Casing hangers must be designed to take the full weight of the casing, and provide a seal between the casing hanger and the spool.

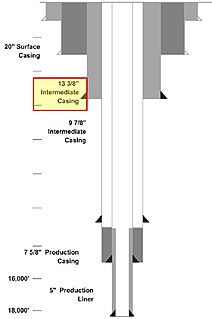
Casing is a large diameter pipe that is assembled and inserted into a recently drilled section of a borehole. Similar to the bones of a spine protecting the spinal cord, casing is set inside the drilled borehole to protect and support the wellstream. The lower portion is typically held in place with cement. Deeper strings usually are not cemented all the way to the surface, so the weight of the pipe must be partially supported by a casing hanger in the wellhead.
Production tubing is a tube used in a wellbore through which production fluids are produced (travel).

A wellhead is the component at the surface of an oil or gas well that provides the structural and pressure-containing interface for the drilling and production equipment.

In geotechnical engineering, drilling fluid, also called drilling mud, is used to aid the drilling of boreholes into the earth. Often used while drilling oil and natural gas wells and on exploration drilling rigs, drilling fluids are also used for much simpler boreholes, such as water wells. One of the functions of drilling mud is to carry cuttings out of the hole.

A blowout preventer (BOP) is a specialized valve or similar mechanical device, used to seal, control and monitor oil and gas wells to prevent blowouts, the uncontrolled release of crude oil or natural gas from a well. They are usually installed in stacks of other valves.

A deep foundation is a type of foundation that transfers building loads to the earth farther down from the surface than a shallow foundation does to a subsurface layer or a range of depths. A pile or piling is a vertical structural element of a deep foundation, driven or drilled deep into the ground at the building site.
A production packer is a standard component of the completion hardware of oil or gas wells used to provide a seal between the outside of the production tubing and the inside of the casing, liner, or wellbore wall.
Oilfield terminology refers to the jargon used by those working in fields within and related to the upstream segment of the petroleum industry. It includes words and phrases describing professions, equipment, and procedures specific to the industry. It may also include slang terms used by oilfield workers to describe the same.
In oil drilling, a casing head is a simple metal flange welded or screwed onto the top of the conductor pipe or the casing and forms part of the wellhead system for the well.
Squeeze job, or squeeze cementing is a term often used in the oilfield to describe the process of injecting cement slurry into a zone, generally for pressure-isolation purposes.
Oil Well Cementing Equipment are essential for the Oil/Gas exploration or production wells and are must used oilfield equipments while drilling a well.

A drilling riser is a conduit that provides a temporary extension of a subsea oil well to a surface drilling facility. Drilling risers are categorised into two types: marine drilling risers used with subsea blowout preventer (BOP) and generally used by floating drilling vessels; and tie-back drilling risers used with a surface BOP and generally deployed from fixed platforms or very stable floating platforms like a spar or tension leg platform (TLP).

Offshore oil spill prevention and response is the study and practice of reducing the number of offshore incidents that release oil or hazardous substances into the environment and limiting the amount released during those incidents.
Oil well control is the management of the dangerous effects caused by the unexpected release of formation fluid, such as natural gas and/or crude oil, upon surface equipment of oil or gas drilling rigs and escaping into the atmosphere. Technically, oil well control involves preventing the formation gas or fluid (hydrocarbons), usually referred to as kick, from entering into the wellbore during drilling or well interventions.











