
Pope Callixtus II or Callistus II, born Guy of Burgundy, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1 February 1119 to his death in 1124. His pontificate was shaped by the Investiture Controversy, which he was able to settle through the Concordat of Worms in 1122.
Primate is a title or rank bestowed on some important archbishops in certain Christian churches. Depending on the particular tradition, it can denote either jurisdictional authority or (usually) ceremonial precedence.

Year 1076 (MLXXVI) was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar.
Pope Hilarius was the bishop of Rome from 19 November 461 to his death on 29 February 468.

Pope Lucius III, born Ubaldo Allucingoli, reigned from 1 September 1181 to his death in 1185. Born of an aristocratic family of Lucca, prior to being elected pope, he had a long career as a papal diplomat. His papacy was marked by conflicts with Holy Roman Emperor Frederick I, his exile from Rome and the initial preparations for the Third Crusade.

Pope Leo IX, born Bruno von Egisheim-Dagsburg, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 February 1049 to his death in 1054. Leo IX is considered to be one of the most historically significant popes of the Middle Ages; he was instrumental in the precipitation of the Great Schism of 1054, considered the turning point in which the Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Churches formally separated.
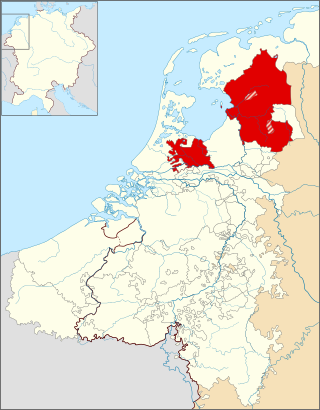
The Bishopric of Utrecht was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire in the Low Countries, in the present-day Netherlands. From 1024 to 1528, as one of the prince-bishoprics of the Holy Roman Empire, it was ruled by the bishops of Utrecht.
Pope John XIX, born Romanus, was the bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 1024 to his death. He belonged to the family of the powerful counts of Tusculum, succeeding his brother, Benedict VIII. Papal relations with the Patriarchate of Constantinople soured during John XIX's pontificate. He was a supporter of Emperor Conrad II and patron of the musician Guido of Arezzo.

Guibert or Wibert of Ravenna was an Italian prelate, archbishop of Ravenna, who was elected pope in 1080 in opposition to Pope Gregory VII and took the name Clement III. Gregory was the leader of the movement in the church which opposed the traditional claim of European monarchs to control ecclesiastical appointments, and this was opposed by supporters of monarchical rights led by the Holy Roman Emperor. This led to the conflict known as the Investiture Controversy. Gregory was felt by many to have gone too far when he excommunicated the Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV and supported a rival claimant as emperor, and in 1080 the pro-imperial Synod of Brixen pronounced that Gregory was deposed and replaced as pope by Guibert.

Stanislaus Hosius was a Polish Roman Catholic cardinal. From 1551 he was the Prince-Bishop of the Bishopric of Warmia in Royal Prussia, and from 1558, he served as the papal legate to the Holy Roman Emperor's Imperial Court in Vienna, Austria. From 1566 he was also the papal legate to Poland.
The Holland Mission or Dutch Mission was the common name of a Catholic Church missionary district in the Low Countries from 1592 to 1853, during and after the Protestant Reformation in the Netherlands.

Dirk V was Count of Holland from 1061 to 1091.
Jaromír was the Bishop of Prague from 1068, when he was appointed by his brother, Vratislaus II of Bohemia. The two were both sons of Duke Bretislaus I of Bohemia.
Gunther or Gunthar was Archbishop of Cologne in Germany from 850 until he was excommunicated and deposed in 863.
Burchard of Basle, also known as Burkart of Fenis, Burchard of Hasenburg or Burchard of Asuel, was a Bishop of Basel in the eleventh century and a supporter of Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV (1056–1106).

Gebhard III was Bishop of Constance and defender of papal rights against imperial encroachments during the Investiture Controversy.

Papal appointment was a medieval method of selecting the Pope. Popes have always been selected by a council of Church fathers, however, Papal selection before 1059 was often characterized by confirmation or nomination by secular European rulers or by the preceding pope. The later procedures of the Papal conclave are in large part designed to prohibit interference of secular rulers, which to some extent characterized the first millennium of the Roman Catholic Church, e. g. in practices such as the creation of crown-cardinals and the claimed but invalid jus exclusivae. Appointment may have taken several forms, with a variety of roles for the laity and civic leaders, Byzantine and Germanic emperors, and noble Roman families. The role of the election vis-a-vis the general population and the clergy was prone to vary considerably, with a nomination carrying weight that ranged from nearly determinative to merely suggestive, or as ratification of a concluded election.

From 756 to 857, the papacy shifted from the influence of the Byzantine Empire to that of the kings of the Franks. Pepin the Short, Charlemagne, and Louis the Pious had considerable influence in the selection and administration of popes. The "Donation of Pepin" (756) ratified a new period of papal rule in central Italy, which became known as the Papal States.
The Synod of Milan or Council of Milan may refer to any of several synods which occurred in late Roman Mediolanum or medieval Milan in northern Italy's Po valley:
The historic Diocese of Utrecht was a diocese of the Latin Church of the Catholic Church from 695 to 1580, and from 1559 archdiocese in the Low Countries before and during the Protestant Reformation.











