Conservative or Tory government may refer to:
In Canadian politics, a Conservative government may refer to the following governments administered by the Conservative Party of Canada or one of its historical predecessors:
In British politics before 1834, a Tory government may refer to the following governments administered by the Tories:
In British politics from 1834, a Conservative government may refer to the following governments administered by the Conservative Party:

Benjamin Disraeli, 1st Earl of Beaconsfield, was a British statesman, Conservative politician and writer who twice served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. He played a central role in the creation of the modern Conservative Party, defining its policies and its broad outreach. Disraeli is remembered for his influential voice in world affairs, his political battles with the Liberal Party leader William Ewart Gladstone, and his one-nation conservatism or "Tory democracy". He made the Conservatives the party most identified with the British Empire and military action to expand it, both of which were popular among British voters. He is the only British Prime Minister to have been born Jewish.

Sir Robert Peel, 2nd Baronet,, was a British Conservative statesman who twice was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, and simultaneously was Chancellor of the Exchequer (1834–1835). He previously was Home Secretary twice. He is regarded as the father of modern British policing, owing to his founding of the Metropolitan Police Service while he was Home Secretary. Peel was one of the founders of the modern Conservative Party.
One-nation conservatism, also known as one-nationism or Tory democracy, is a paternalistic form of British political conservatism. It advocates the preservation of established institutions and traditional principles within a political democracy, in combination with social and economic programmes designed to benefit the ordinary person. According to this political philosophy, society should be allowed to develop in an organic way, rather than being engineered. It argues that members of society have obligations towards each other and particularly emphasises paternalism, meaning that those who are privileged and wealthy should pass on their benefits. It argues that this elite should work to reconcile the interests of all social classes, including labour and management, rather than identifying the good of society solely with the interests of the business class.

Edward George Geoffrey Smith-Stanley, 14th Earl of Derby, known as Lord Stanley from 1834 to 1851, was a British statesman and Conservative politician who served three times as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. To date, he is the longest-serving leader of the Conservative Party. He is one of only four British prime ministers to have three or more separate periods in office. However, his ministries each lasted less than two years and totalled three years and 280 days. Derby introduced the state education system in Ireland, and reformed Parliament.

Robert Arthur Talbot Gascoyne-Cecil, 3rd Marquess of Salisbury, known as Lord Salisbury, was a British statesman and Conservative politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom three times for a total of over thirteen years. He was also Foreign Secretary before and during most of his tenure. He avoided alignments or alliances, maintaining the policy of "splendid isolation".
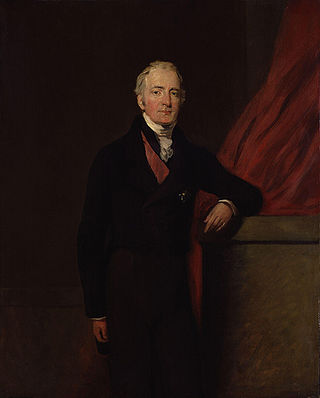
Henry Bathurst, 3rd Earl Bathurst, was a High Tory, High Church Pittite. He was an MP for thirty years before ennoblement. A personal friend of William Pitt the Younger, he became a broker of deals across cabinet factions during the Napoleonic era. After the Napoleonic Wars, Bathurst was on the conservative wing of the Tory party.

Gathorne Gathorne-Hardy, 1st Earl of Cranbrook, was a prominent British Conservative politician. He held cabinet office in every Conservative government between 1858 and 1892. He served as Home Secretary from 1867 to 1868, Secretary of State for War from 1874 to 1878, Lord President of the Council from 1885 to 1886 and as Chancellor of the Duchy of Lancaster until 1886. In 1878, he was appointed Secretary of State for India and thereafter was elevated to the peerage, entering the House of Lords as Viscount Cranbrook. He has been described as a moderate, middle-of-the-road Anglican, and a key ally of Disraeli.

John Charles Herries PC, known as J. C. Herries, was a British politician and financier and a frequent member of Tory and Conservative cabinets in the early to mid-19th century.
The Peelites were a breakaway political faction of the British Conservative Party from 1846 to 1859. Initially led by Robert Peel, the former Prime Minister and Conservative Party leader in 1846, the Peelites supported free trade whilst the bulk of the Conservative Party remained protectionist. The Peelites later merged with the Whigs and Radicals to form the Liberal Party in 1859.

The Carlton Club is a private members' club in the St James's area of London, England. It was the original home of the Conservative Party before the creation of Conservative Central Office. Membership of the club is by nomination and election only.

Endymion is a novel published in 1880 by Benjamin Disraeli, 1st Earl of Beaconsfield, the former Conservative Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. He was paid an advance of £10,000 for it. It was the last novel Disraeli published before his death. He had been writing another, Falconet, when he died; it was published, incomplete, after his death.

The article lists the records of prime ministers of the United Kingdom since 1721.

The Conservative Government of the United Kingdom that began in 1922 and ended in 1924 consisted of two ministries: the Law ministry and then the first Baldwin ministry.

The Conservative Party is the oldest political party in the United Kingdom and arguably the world. The current party was first organised in the 1830s and the name "Conservative" was officially adopted, but the party is still often referred to as the Tory party. The Tories had been a coalition that more often than not formed the government from 1760 until the Reform Act 1832. Modernising reformers said the traditionalistic party of "Throne, Altar and Cottage" was obsolete, but in the face of an expanding electorate 1830s–1860s it held its strength among royalists, devout Anglicans and landlords and their tenants.

The leader of the Conservative Party is the highest position within the United Kingdom's Conservative Party. The current holder of the position is Rishi Sunak, who was elected to the position on 24 October 2022, following his unopposed victory in the party's leadership election.
In the United Kingdom and elsewhere, High Toryism is the old traditionalist conservatism which is in line with the Toryism originating in the 16th century. High Tories and their worldview are sometimes at odds with the modernising elements of the Conservative Party. Historically, the late eighteenth-century conservatism derived from the Whig Edmund Burke, Lee Munro and William Pitt the Younger marks a watershed from the "higher" or legitimist Toryism that was allied to Jacobitism.
The Derby Dilly was a name given to a group of dissident Whigs who split from the main party under the leadership of Edward, Lord Stanley on the issue of the reorganisation of the Church of Ireland in 1834. Stanley and three others resigned from the cabinet of Lord Grey on this particular issue but other factors included their fear that the Whigs were appeasing their radical and Irish allies with further reforms.
This is a graphical timeline of prime ministers of Great Britain and the United Kingdom from when the first prime minister of Great Britain in the modern sense, Robert Walpole, took office in 1721, until the present day.