In physics, a force is an influence that can cause an object to change its velocity, i.e., to accelerate, meaning a change in speed or direction, unless counterbalanced by other forces. The concept of force makes the everyday notion of pushing or pulling mathematically precise. Because the magnitude and direction of a force are both important, force is a vector quantity. The SI unit of force is the newton (N), and force is often represented by the symbol F.

Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. Types of friction include dry, fluid, lubricated, skin, and internal.

An inclined plane, also known as a ramp, is a flat supporting surface tilted at an angle from the vertical direction, with one end higher than the other, used as an aid for raising or lowering a load. The inclined plane is one of the six classical simple machines defined by Renaissance scientists. Inclined planes are used to move heavy loads over vertical obstacles. Examples vary from a ramp used to load goods into a truck, to a person walking up a pedestrian ramp, to an automobile or railroad train climbing a grade.
Tribology is the science and engineering of understanding friction, lubrication and wear phenomena for interacting surfaces in relative motion. It is highly interdisciplinary, drawing on many academic fields, including physics, chemistry, materials science, mathematics, biology and engineering. The fundamental objects of study in tribology are tribosystems, which are physical systems of contacting surfaces. Subfields of tribology include biotribology, nanotribology and space tribology. It is also related to other areas such as the coupling of corrosion and tribology in tribocorrosion and the contact mechanics of how surfaces in contact deform. Approximately 20% of the total energy expenditure of the world is due to the impact of friction and wear in the transportation, manufacturing, power generation, and residential sectors.

Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another.

In mechanics, the normal force is the component of a contact force that is perpendicular to the surface that an object contacts, as in Figure 1. In this instance normal is used in the geometric sense and means perpendicular, as opposed to the common language use of normal meaning "ordinary" or "expected". A person standing still on a platform is acted upon by gravity, which would pull them down towards the Earth's core unless there were a countervailing force from the resistance of the platform's molecules, a force which is named the "normal force".

Rolling is a type of motion that combines rotation and translation of that object with respect to a surface, such that, if ideal conditions exist, the two are in contact with each other without sliding.

An adhesion railway relies on adhesion traction to move the train, and is the most widespread and common type of railway in the world. Adhesion traction is the friction between the drive wheels and the steel rail. Since the vast majority of railways are adhesion railways, the term adhesion railway is used only when it is necessary to distinguish adhesion railways from railways moved by other means, such as by a stationary engine pulling on a cable attached to the cars or by a pinion meshing with a rack.
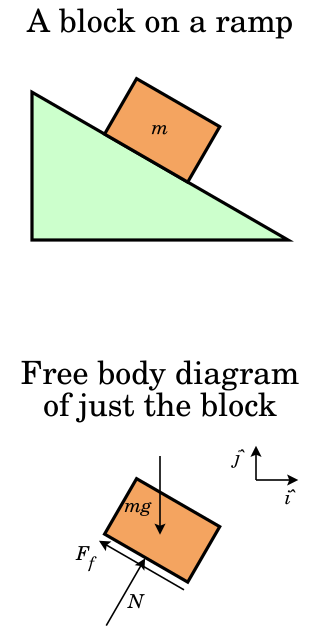
A contact force is any force that occurs as a result of two objects making contact with each other. Contact forces are ubiquitous and are responsible for most visible interactions between macroscopic collections of matter. Pushing a car or kicking a ball are some of the everyday examples where contact forces are at work. In the first case the force is continuously applied to the car by a person, while in the second case the force is delivered in a short impulse.
In fluid dynamics, drag, sometimes referred to as fluid resistance, is a force acting opposite to the relative motion of any object, moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers, two solid surfaces, or between a fluid and solid surface. Drag forces tend to decrease fluid velocity relative to the solid object in the fluid's path.
In materials science, hardness is a measure of the resistance to localized plastic deformation, such as an indentation or a scratch (linear), induced mechanically either by pressing or abrasion. In general, different materials differ in their hardness; for example hard metals such as titanium and beryllium are harder than soft metals such as sodium and metallic tin, or wood and common plastics. Macroscopic hardness is generally characterized by strong intermolecular bonds, but the behavior of solid materials under force is complex; therefore, hardness can be measured in different ways, such as scratch hardness, indentation hardness, and rebound hardness. Hardness is dependent on ductility, elastic stiffness, plasticity, strain, strength, toughness, viscoelasticity, and viscosity. Common examples of hard matter are ceramics, concrete, certain metals, and superhard materials, which can be contrasted with soft matter.

The stick–slip phenomenon, also known as the slip–stick phenomenon or simply stick–slip, is a type of motion exhibited by objects in contact sliding over one another. The motion of these objects is usually not perfectly smooth, but rather irregular, with brief accelerations (slips) interrupted by stops (sticks). Stick–slip motion is normally connected to friction, and may generate vibration (noise) or be associated with mechanical wear of the moving objects, and is thus often undesirable in mechanical devices. On the other hand, stick–slip motion can be useful in some situations, such as the movement of a bow across a string to create musical tones in a bowed string instrument.

Contact mechanics is the study of the deformation of solids that touch each other at one or more points. A central distinction in contact mechanics is between stresses acting perpendicular to the contacting bodies' surfaces and frictional stresses acting tangentially between the surfaces. Normal contact mechanics or frictionless contact mechanics focuses on normal stresses caused by applied normal forces and by the adhesion present on surfaces in close contact, even if they are clean and dry. Frictional contact mechanics emphasizes the effect of friction forces.
Sliding is a type of motion between two surfaces in contact. This can be contrasted to rolling motion. Both types of motion may occur in bearings.
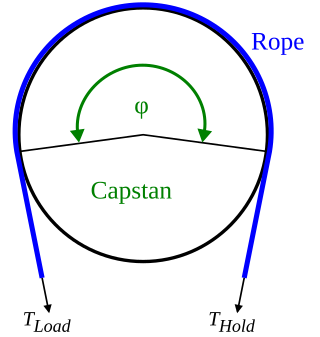
The capstan equation or belt friction equation, also known as Euler-Eytelwein formula, relates the hold-force to the load-force if a flexible line is wound around a cylinder.

In fluid dynamics, the Reynolds number is a dimensionless quantity that helps predict fluid flow patterns in different situations by measuring the ratio between inertial and viscous forces. At low Reynolds numbers, flows tend to be dominated by laminar (sheet-like) flow, while at high Reynolds numbers, flows tend to be turbulent. The turbulence results from differences in the fluid's speed and direction, which may sometimes intersect or even move counter to the overall direction of the flow. These eddy currents begin to churn the flow, using up energy in the process, which for liquids increases the chances of cavitation.
A device generating linear or rotational motion using carbon nanotube(s) as the primary component, is termed a nanotube nanomotor. Nature already has some of the most efficient and powerful kinds of nanomotors. Some of these natural biological nanomotors have been re-engineered to serve desired purposes. However, such biological nanomotors are designed to work in specific environmental conditions. Laboratory-made nanotube nanomotors on the other hand are significantly more robust and can operate in diverse environments including varied frequency, temperature, mediums and chemical environments. The vast differences in the dominant forces and criteria between macroscale and micro/nanoscale offer new avenues to construct tailor-made nanomotors. The various beneficial properties of carbon nanotubes makes them the most attractive material to base such nanomotors on.
In the context of classical mechanics simulations and physics engines employed within video games, collision response deals with models and algorithms for simulating the changes in the motion of two solid bodies following collision and other forms of contact.
Belt friction is a term describing the friction forces between a belt and a surface, such as a belt wrapped around a bollard. When a force applies a tension to one end of a belt or rope wrapped around a curved surface, the frictional force between the two surfaces increases with the amount of wrap about the curved surface, and only part of that force is transmitted to the other end of the belt or rope. Belt friction can be modeled by the Belt friction equation.
Contact mechanics is the study of the deformation of solids that touch each other at one or more points. This can be divided into compressive and adhesive forces in the direction perpendicular to the interface, and frictional forces in the tangential direction. Frictional contact mechanics is the study of the deformation of bodies in the presence of frictional effects, whereas frictionless contact mechanics assumes the absence of such effects.












