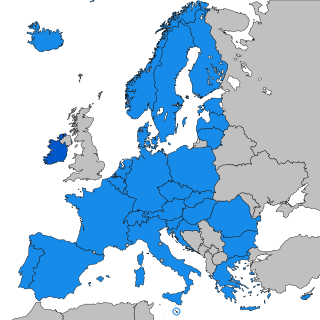
The Schengen Information System (SIS) is a governmental database maintained by the European Commission. The SIS is used by 31 European countries to find information about individuals and entities for the purposes of national security, border control and law enforcement since 2001. A second technical version of this system, SIS II, went live on 9 April 2013.
Information privacy is the relationship between the collection and dissemination of data, technology, the public expectation of privacy, contextual information norms, and the legal and political issues surrounding them. It is also known as data privacy or data protection.

The Data Protection Directive, officially Directive 95/46/EC, enacted in October 1995, is a European Union directive which regulates the processing of personal data within the European Union (EU) and the free movement of such data. The Data Protection Directive is an important component of EU privacy and human rights law.
The right to privacy is an element of various legal traditions that intends to restrain governmental and private actions that threaten the privacy of individuals. Over 150 national constitutions mention the right to privacy. On 10 December 1948, the United Nations General Assembly adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), originally written to guarantee individual rights of everyone everywhere; while right to privacy does not appear in the document, many interpret this through Article 12, which states: "No one shall be subjected to arbitrary interference with his privacy, family, home or correspondence, nor to attacks upon his honour and reputation. Everyone has the right to the protection of the law against such interference or attacks."

The Data Protection Act 1998 was an Act of Parliament of the United Kingdom designed to protect personal data stored on computers or in an organised paper filing system. It enacted provisions from the European Union (EU) Data Protection Directive 1995 on the protection, processing, and movement of data.

Freedom of information is freedom of a person or people to publish and consume information. Access to information is the ability for an individual to seek, receive and impart information effectively. This sometimes includes "scientific, indigenous, and traditional knowledge; freedom of information, building of open knowledge resources, including open Internet and open standards, and open access and availability of data; preservation of digital heritage; respect for cultural and linguistic diversity, such as fostering access to local content in accessible languages; quality education for all, including lifelong and e-learning; diffusion of new media and information literacy and skills, and social inclusion online, including addressing inequalities based on skills, education, gender, age, race, ethnicity, and accessibility by those with disabilities; and the development of connectivity and affordable ICTs, including mobile, the Internet, and broadband infrastructures".
A privacy policy is a statement or legal document that discloses some or all of the ways a party gathers, uses, discloses, and manages a customer or client's data. Personal information can be anything that can be used to identify an individual, not limited to the person's name, address, date of birth, marital status, contact information, ID issue, and expiry date, financial records, credit information, medical history, where one travels, and intentions to acquire goods and services. In the case of a business, it is often a statement that declares a party's policy on how it collects, stores, and releases personal information it collects. It informs the client what specific information is collected, and whether it is kept confidential, shared with partners, or sold to other firms or enterprises. Privacy policies typically represent a broader, more generalized treatment, as opposed to data use statements, which tend to be more detailed and specific.
Personal data, also known as personal information or personally identifiable information (PII), is any information related to an identifiable person.
Information privacy, data privacy or data protection laws provide a legal framework on how to obtain, use and store data of natural persons. The various laws around the world describe the rights of natural persons to control who is using its data. This includes usually the right to get details on which data is stored, for what purpose and to request the deletion in case the purpose is not given anymore.
The International Safe Harbor Privacy Principles or Safe Harbour Privacy Principles were principles developed between 1998 and 2000 in order to prevent private organizations within the European Union or United States which store customer data from accidentally disclosing or losing personal information. They were overturned on October 6, 2015 by the European Court of Justice (ECJ), which enabled some US companies to comply with privacy laws protecting European Union and Swiss citizens. US companies storing customer data could self-certify that they adhered to 7 principles, to comply with the EU Data Protection Directive and with Swiss requirements. The US Department of Commerce developed privacy frameworks in conjunction with both the European Union and the Federal Data Protection and Information Commissioner of Switzerland.
Privacy law is the body of law that deals with the regulating, storing, and using of personally identifiable information, personal healthcare information, and financial information of individuals, which can be collected by governments, public or private organisations, or other individuals. It also applies in the commercial sector to things like trade secrets and the liability that directors, officers, and employees have when handing sensitive information.
The United Nations is developing an alternative treaty on cybercrime.

The European Data Protection Supervisor (EDPS) is an independent supervisory authority whose primary objective is to monitor and ensure that European institutions and bodies respect the right to privacy and data protection when they process personal data and develop new policies.
Data Privacy Day is an international event that occurs every year on 28 January. The purpose of Data Privacy Day is to raise awareness and promote privacy and data protection best practices. It is currently observed in the United States, Canada, Nigeria, Israel and 47 European countries.
The United States Federal Trade Commission's fair information practice principles (FIPPs) are guidelines that represent widely accepted concepts concerning fair information practice in an electronic marketplace.
Privacy law in Denmark is supervised and enforced by the independent agency Datatilsynet based mainly upon the Act on Processing of Personal Data.
Data protection (privacy) laws in Russia are a rapidly developing branch in Russian legislation that have mostly been enacted in the 2005 and 2006. The Russian Federal Law on Personal Data, implemented on July 27, 2006, constitutes the backbone of Russian privacy laws and requires data operators to take "all the necessary organizational and technical measures required for protecting personal data against unlawful or accidental access". Amendment was signed on December 20, 2020 and came into effect on March 1, 2021. The amendment requires "personal data made publicly available" needs to receive consent from the data subject. Russia's Federal Service for Supervision of Communications, Information Technology and Mass Media is the government agency tasked with overseeing compliance.
The Data Protection (Jersey) Law 2018 is an information privacy law in the Crown Dependency of the Bailiwick of Jersey, one of the Channel Islands. The latest version is 2018, updating the previous law from 2005 to mirror the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). It was adopted on 25 May 2018.

The General Data Protection Regulation is a Regulation in EU law on data protection and privacy in the EU and the European Economic Area (EEA). The GDPR is an important component of EU privacy law and of human rights law, in particular Article 8(1) of the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union. It also addresses the transfer of personal data outside the EU and EEA areas. The GDPR's primary aim is to enhance individuals' control and rights over their personal data and to simplify the regulatory environment for international business. Superseding the Data Protection Directive 95/46/EC, the regulation contains provisions and requirements related to the processing of personal data of individuals, formally called "data subjects", who are located in the EEA, and applies to any enterprise—regardless of its location and the data subjects' citizenship or residence—that is processing the personal information of individuals inside the EEA.
The right to be forgotten (RTBF) is the right to have private information about a person be removed from Internet searches and other directories under some circumstances. The concept has been discussed and put into practice in several jurisdictions, including Argentina, the European Union (EU), and the Philippines. The issue has arisen from desires of individuals to "determine the development of their life in an autonomous way, without being perpetually or periodically stigmatized as a consequence of a specific action performed in the past."





