Related Research Articles
"Cunt" is a vulgar word for the vulva in its primary sense, but it is used in a variety of ways, including as a term of disparagement. "Cunt" is often used as a disparaging and obscene term for a woman in the United States, an unpleasant or objectionable person in the United Kingdom and Ireland, or a contemptible man in Australia and New Zealand. In Australia and New Zealand, it can also be a neutral or positive term when used with a positive qualifier. The term has various derivative senses, including adjective and verb uses.

Bitch is a pejorative slang word for a person, usually a woman. When applied to a woman or girl, it means someone who is belligerent, unreasonable, malicious, controlling, aggressive, or dominant. When applied to a man or boy, bitch reverses its meaning and is a derogatory term for being subordinate, weak, or cowardly. In gay speech the word bitch can refer approvingly to a man who is unusually assertive or has the characteristics used pejoratively of a woman.

A double entendre is a figure of speech or a particular way of wording that is devised to have a double meaning, one of which is typically obvious, and the other often conveys a message that would be too socially unacceptable, or offensive to state directly.

Pussy is an English noun, adjective, and—in rare instances—verb. It has several meanings, as slang, as euphemism, and as vulgarity. Most commonly, it is used as a noun with the meaning "cat", "coward", or "weakling". In slang, it can mean "vulva or vagina" and less commonly, by synecdoche, "sexual intercourse with a woman". Because of its multiple senses including both innocent and vulgar connotations, pussy is often the subject of double entendre.

Lunfardo is an argot originated and developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries in the lower classes in the Río de la Plata region and from there spread to other urban areas nearby, such as the Greater Buenos Aires, Santa Fe and Rosario.

The Vagina Monologues is an episodic play written in 1996 by Eve Ensler which developed and premiered at HERE Arts Center, Off-Off-Broadway in New York and was followed by an Off-Broadway run at the Westside Theatre. The play explores consensual and nonconsensual sexual experiences, body image, genital mutilation, direct and indirect encounters with reproduction, vaginal care, menstrual periods, prostitution, and several other topics through the eyes of women with various ages, races, sexualities, and other differences.

"Arabian riff", also known as "The Streets of Cairo", "The Poor Little Country Maid", and "the snake charmer song", is a well-known melody, published in different forms in the 19th century. Alternate titles for children's songs using this melody include "The Girls in France" and "The Southern Part of France". The melody is often associated with the hoochie coochie belly dance.

Coonass, or Coon-ass, is a term for a person of Cajun ethnicity. Some view it as derogatory, however many Cajuns embrace the name.

Fingering is sexual stimulation of the vulva or vagina by using the fingers. Vaginal fingering is legally and medically called digital penetration or digital penetration of the vagina. The term "digital" takes its significance from the English word 'digit', which refers to a finger, thumb, or toe. Fingering may also include the use of fingers to stimulate the anus.

Bhawaiya is a musical form or a popular folk music that originated in Northern Bengal, especially the Rangpur Division in Bangladesh, Cooch Behar district of West Bengal, India, and the undivided Goalpara district of Assam, India. It has recurrent themes of the "working class", mahouts, mahishals, and gariyals. Lyrics express pangs of separation and loneliness of their womenfolk, with elongated tones accentuating pain, longing and "deep emotion". Bhawaiya is generally believed to have originated in the 16th century under Biswa Singha, and has evolved into stage performances since the 1950s. The lyrics of Bhawaiya songs are non-denominational. Bhawaiya is really popular during the Bengali occasion of Eid Al Fitr and Eid Al Adha.
Coochie may refer to:

"Hoochie Coochie Man" is a blues standard written by Willie Dixon and first recorded by Muddy Waters in 1954. The song makes reference to hoodoo folk magic elements and makes novel use of a stop-time musical arrangement. It became one of Waters' most popular and identifiable songs and helped secure Dixon's role as Chess Records' chief songwriter.
"Sam and Delilah" is a song composed by George Gershwin, with lyrics by Ira Gershwin. It was introduced by Ethel Merman in the 1930 musical Girl Crazy. The song is an interpretation of the biblical story of Samson and Delilah in the Book of Judges of the Hebrew Bible.
"See See Rider", also known as "C.C. Rider", "See See Rider Blues" or "Easy Rider", is a popular American 12-bar blues song that became a standard in several genres. Gertrude "Ma" Rainey was the first to record it on October 16, 1924, at Paramount Records in New York. The song uses mostly traditional blues lyrics to tell the story of an unfaithful lover, commonly called an "easy rider": "See see rider, see what you have done", making a play on the word "see" and the sound of "easy".
The following is a list of words and formulations commonly used as profanity throughout Romania.

An artificial vagina is a device designed to imitate the vagina as well as sometimes the vulva. To achieve this, it will generally be made of a soft material, lubricated, and occasionally heated.

The hoochie coochie is a catch-all term to describe several sexually provocative belly dance-like dances from the mid-to late 1800s. Also spelled hootchy-kootchy and a number of other variations, it is often associated with "The Streets of Cairo, or the Poor Little Country Maid" song, also known as "the snake charmer song". "Hoochie Coochie Man" is also a blues standard written by Willie Dixon and first recorded by Muddy Waters in Chicago, January 7, 1954. Numerous cover versions of this classic continue to be recorded. Hoochie Coochie is also mentioned in Alan Jackson's hit country music song "Chattahoochee", and the Jerry Leiber and Mike Stoller songs "Little Egypt (Ying-Yang)" and "Saved".
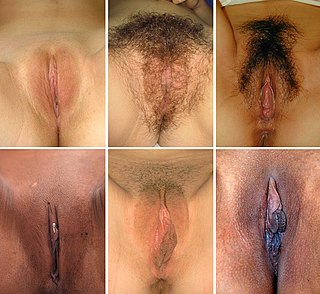
In mammals, the vulva comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female genitalia leading away from the interior parts of the female reproductive tract, starting at the vaginal opening. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibule, urinary meatus, vaginal introitus, hymen, and openings of the vestibular glands. The folds of the outer and inner labia provide a double layer of protection for the vagina. Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support.
Jive talk, also known as Harlem jive or simply Jive, the argot of jazz, jazz jargon, vernacular of the jazz world, slang of jazz, and parlance of hip is an African-American Vernacular English slang or vocabulary that developed in Harlem, where "jive" (jazz) was played and was adopted more widely in African-American society, peaking in the 1940s.

The vagina and vulva have been depicted from prehistory onwards. Visual art forms representing the female genitals encompass two-dimensional and three-dimensional. As long ago as 35,000 years ago, people sculpted Venus figurines that exaggerated the abdomen, hips, breasts, thighs, or vulva.
References
- 1 2 3 Victor, Terry and Dalzell, Tom (2007) The Concise New Partridge Dictionary of Slang and Unconventional English p.160
- ↑ coochie at onlineslangdictionary.com
- 1 2 coochie at LLC's Dictionary.com
- ↑ "Venus - Fatima's Coochee-Coochee Dance". www.venusbellydance.com. Archived from the original on 2002-04-11.
- ↑ "MoMA | The Collection | James White, William Heise. Fatima's Coochee-Coochee Dance. 1986". moma.org. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ↑ "Fatima's Coochee-Coochee Dance (1896) - IMDb". imdb.com. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ↑ Hanania, R. (2005). Arabs of Chicagoland. Arcadia. p. 10. ISBN 9780738534176 . Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ↑ Sonny Watson. "Hootchy-Cootchy Dance - aka Dance du ventre, Hoochi Koochi, Risque - Fatima, Little Egypt". streetswing.com. Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ↑ Stencell, A.W. (1999). Girl Show: Into the Canvas World of Bump and Grind. ECW Press. p. 7. ISBN 9781550223712 . Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ↑ Browne, R.B. (1979). The Alabama Folk Lyric: A Study in Origins and Media of Dissemination. Bowling Green University Popular Press. p. 220. ISBN 9780879721299 . Retrieved 2015-03-24.
- ↑ "Ella Fitzgerald Lyrics: Coochi-Coochi-Coo Lyrics - HotLyrics.net". Archived from the original on 2012-08-02. Retrieved 2010-10-25.
- ↑ Eve Ensler (1996) The Vagina Monologues: The V-Day Edition, pp.11, 76-82, 153-4, 180
- ↑ Ultramontane Associates (1999) Culture Wars, Volume 19, p.94