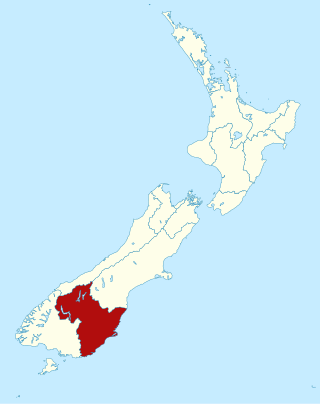
Otago is a region of New Zealand located in the southern half of the South Island administered by the Otago Regional Council. It has an area of approximately 32,000 square kilometres (12,000 sq mi), making it the country's second largest local government region. Its population was 254,600 in June 2023.

The Otago Peninsula is a long, hilly indented finger of land that forms the easternmost part of Dunedin, New Zealand. Volcanic in origin, it forms one wall of the eroded valley that now forms Otago Harbour. The peninsula lies south-east of Otago Harbour and runs parallel to the mainland for 20 km, with a maximum width of 9 km. It is joined to the mainland at the south-west end by a narrow isthmus about 1.5 km wide.

Larnach Castle is a mock castle on the ridge of the Otago Peninsula within the limits of the city of Dunedin, New Zealand, close to the small settlement of Pukehiki. It is one of a few houses of this scale in New Zealand. The house was built by the prominent entrepreneur and politician, William Larnach. Since 1967, the castle has been privately owned by the Barker family, and opened as a tourist attraction, as "New Zealand's only castle".

Hocken Collections (Māori: Uare Taoka o Hākena, formerly the Hocken Library) is a research library, historical archive, and art gallery based in Dunedin, New Zealand. Its library collection, which is of national significance, is administered by the University of Otago.

Moturata, also called Taieri Island, is an island in the mouth of the Taieri River in southern New Zealand. It is connected to the mainland by a sandy causeway at low tide.

Taiaroa Head is a headland at the end of the Otago Peninsula in New Zealand, overlooking the mouth of the Otago Harbour. It lies within the city limits of Dunedin. The nearest settlement, Otakou, lies three kilometres to the south.

Lawyers Head is a prominent landmark on the coast of Otago, New Zealand. Located within the city of Dunedin, this rocky headland juts into the Pacific Ocean at the eastern end of the city's main beach, Saint Kilda Beach. It is named for the likeness of the cliff face to the profile of a lawyer in traditional legal wig.
The Weller brothers, Englishmen of Sydney, Australia, and Otago, New Zealand, were the founders of a whaling station on Otago Harbour and New Zealand's most substantial merchant traders in the 1830s.

Kaimata, or Cape Saunders, is the prominent headland on the Pacific Ocean coast of Muaupoko, the Otago Peninsula, in the far south-east of Aotearoa New Zealand's Te Wai Pounamu, the South Island. It is home to the Cape Saunders Lighthouse.

The settlement of Harington Point lies within the boundaries of the city of Dunedin, New Zealand. It is located at the Otago Heads, at the northeastern end of Otago Peninsula, close to the entrance of Otago Harbour. The mouth of the harbour is at its narrowest at Harington Point, only some 400 metres separating the point from the mudflats at Aramoana on the opposing coast.

Toko Mouth is a settlement close to the south bank of the mouth of the Tokomairaro River, some 50 kilometres (31 mi) south of Dunedin and 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) southeast of Milton in Otago, New Zealand.

Ocean Beach is a long sandy beach which runs along the Pacific Ocean coast of south Dunedin, New Zealand. It stretches for some three kilometres from Saint Clair in the southwest along the coast of Saint Kilda to the foot of Lawyers Head in the east. The beach is a popular recreation area for swimming, surfing, and walking.

Dunedin Chinese Garden is a Chinese garden located in Dunedin, New Zealand.

Victory Beach is located on the Pacific Ocean coast of the Otago Peninsula, in the South Island of New Zealand, 24 kilometres (15 mi) by road from Dunedin city centre and 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) from the nearby town of Portobello. The longest beach on the peninsula, Victory Beach is located northeast of the entrance to Papanui Inlet and stretches for 3.2 kilometres (2.0 mi). The beach's name derives from the wreck of the SS Victory on the beach in 1861.

Taranakite is a hydrated alkali iron-aluminium phosphate mineral with chemical formula (K,Na)3(Al,Fe3+)5(PO4)2(HPO4)6·18 H2O. It forms from the reaction of clay minerals or aluminous rocks with solutions enriched in phosphate derived from bat or bird guano or, less commonly, from bones or other organic matter. Taranakite is most commonly found in humid, bat inhabited caves near the boundary of guano layers with the cave surface. It is also found in perennially wet coastal locations that have been occupied by bird colonies. The type location, and its namesake, the Sugar Loaf Islands off Taranaki, New Zealand, is an example of a coastal occurrence.

Huriawa, commonly known as Huriawa Peninsula or Karitane Peninsula, is a headland on the coast of Otago, New Zealand. It is located 35 kilometres north of Dunedin city centre, immediately to the southeast of the settlement of Karitane.

Blackhead is a promontory on the coast of Otago, New Zealand. It lies within the city limits of Dunedin, some 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) southwest of the city centre. The promontory extends some 500 metres into the ocean, and rises to a height of a little over 100 metres (330 ft). Māori names for Blackhead include Te Wai o Tinarau and Makereatu.

The Southern District Health Board was a district health board which provided healthcare to an area covering the southern half of the South Island of New Zealand. In July 2022, the Southern DHB was dissolved as part of a nationwide overhaul of the district health board system. Its former functions and responsibilities were taken over by Te Whatu Ora.

















