A copyright is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the exclusive right to copy, distribute, adapt, display, and perform a creative work, usually for a limited time. The creative work may be in a literary, artistic, educational, or musical form. Copyright is intended to protect the original expression of an idea in the form of a creative work, but not the idea itself. A copyright is subject to limitations based on public interest considerations, such as the fair use doctrine in the United States.
The Universal Copyright Convention (UCC), adopted in Geneva, Switzerland, in 1952, is one of the two principal international conventions protecting copyright; the other is the Berne Convention.
The World Intellectual Property Organization Copyright Treaty is an international treaty on copyright law adopted by the member states of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) in 1996. It provides additional protections for copyright to respond to advances in information technology since the formation of previous copyright treaties before it. As of August 2021, the treaty has 110 contracting parties. The WCT and WIPO Performances and Phonograms Treaty, are together termed WIPO "internet treaties".

The World Intellectual Property Organization is one of the 15 specialized agencies of the United Nations (UN). Pursuant to the 1967 Convention Establishing the World Intellectual Property Organization, WIPO was created to promote and protect intellectual property (IP) across the world by cooperating with countries as well as international organizations. It began operations on 26 April 1970 when the convention entered into force. The current Director General is Singaporean Daren Tang, former head of the Intellectual Property Office of Singapore, who began his term on 1 October 2020.
In the copyright law of the United States, a work made for hire is a work subject to copyright that is created by an employee as part of their job, or some limited types of works for which all parties agree in writing to the WFH designation. Work for hire is a statutorily defined term, so a work for hire is not created merely because parties to an agreement state that the work is a work for hire. It is an exception to the general rule that the person who actually creates a work is the legally recognized author of that work. According to copyright law in the United States and certain other copyright jurisdictions, if a work is "made for hire", the employer—not the employee—is considered the legal author. In some countries, this is known as corporate authorship. The entity serving as an employer may be a corporation or other legal entity, an organization, or an individual.
List of international public law topics:

"All rights reserved" is a copyright formality indicating that the copyright holder reserves, or holds for its own use, all the rights provided by copyright law. Originating in the Buenos Aires Convention of 1910, it is unclear if it has any legal effect in any jurisdiction. However, it is still used by many copyright holders.
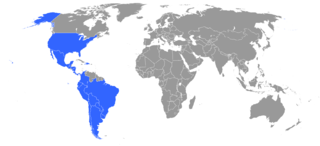
The Buenos Aires Convention is an international copyright treaty signed in Buenos Aires, Argentina, on 11 August 1910, providing mutual recognition of copyrights where the work carries a notice containing a statement of reservation of rights (Art. 3). This was commonly done with the phrase "All rights reserved" next to the copyright notice. This implementation varied as US law only required the author and year of publishing. Copyright protection under the convention is granted for the shorter of the terms of the protecting country and the source country of the work. The rather vague nature of the requirement for a statement of reservation led to the development of longer and more legalistic wordings, which have persisted despite the developments in international copyright law.
Intellectual property rights (IPRs) have been acknowledged and protected in China since the 1980s. China has acceded to the major international conventions on protection of rights to intellectual property. Domestically, protection of intellectual property law has also been established by government legislation, administrative regulations, and decrees in the areas of trademark, copyright, and patent. This has led to the creation of a comprehensive legal framework to protect both local and foreign intellectual property. Despite this, copyright violations are extremely common in the PRC. The American Chamber of Commerce in China surveyed over 500 of its members doing business in China regarding IPR for its 2016 China Business Climate Survey Report, and found that IPR enforcement is improving, but significant challenges still remain. The results show that the laws in place exceed their actual enforcement, with patent protection receiving the highest approval rate, while protection of trade secrets lags far behind. Many US companies have claimed that the Chinese government has stolen their intellectual property sometime in 2009–2019.

The Uruguay Round Agreements Act is an Act of Congress in the United States that implemented in U.S. law the Marrakesh Agreement of 1994. The Marrakesh Agreement was part of the Uruguay Round of negotiations which transformed the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) into the World Trade Organization (WTO). One of its effects is to give United States copyright protection to foreign works that had previously been in the public domain in the United States.
The rule of the shorter term, also called the comparison of terms, is a provision in international copyright treaties. The provision allows that signatory countries can limit the duration of copyright they grant to foreign works under national treatment to no more than the copyright term granted in the country of origin of the work.

The Organisation Africaine de la Propriété Intellectuelle or OAPI is an intellectual property organization, headquartered in Yaoundé, Cameroon. The organisation was created by Bangui Agreement of March 2, 1977. The Bangui Agreement was subsequently amended in 1999.

The Berne Convention for the Protection of Literary and Artistic Works, usually known as the Berne Convention, is an international agreement governing copyright, which was first accepted in Berne, Switzerland, in 1886. The Berne Convention has 179 contracting parties, most of which are parties to the Paris Act of 1971.

The Convention for the Protection of Producers of Phonograms Against Unauthorized Duplication of Their Phonograms, also known as the Geneva Phonograms Convention, is a 1971 international agreement relating to copyright protection for sound recordings.
The copyright law of New Zealand is covered by the Copyright Act 1994 and subsequent amendments. It is administered by Business Law Policy Unit of the Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment (MBIE). In June 2017, a review of the existing legislation was announced.
Iran is a member of the WIPO since 2001 and has acceded to several WIPO intellectual property treaties. Iran joined the Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property in 1959. In December 2003 Iran became a party to the Madrid Agreement and the Madrid Protocol for the International Registration of Marks. In 2005 Iran joined the Lisbon Agreement for the Protection of Appellations of Origin and their International Registration, which ensures the protection of geographical names associated with products. As at February 2008 Iran had yet to accede to The Hague Agreement for the Protection of Industrial Designs.
Copyright law of South Korea is regulated by the Copyright Act of 1957. It has been amended several times, with a recent 2009 revision introducing a three strikes policy for online copyright infringement.

The copyright law of Moldova regulates the copyright laws of Moldova. The first official decree related to copyright in the country was made on 25 November 1991, shortly after its independence on 27 August of the same year. On 25 May 1991, the State Agency on the Protection of Industrial Property (AGEPI) was created, making it the second copyright agency in the country together with the State Agency for Copyright (ADA). In 1993, Moldova signed an agreement on cooperation in the protection of copyright and the related rights between it and other countries, all members of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), which only came into force in 1999. By the time of this year, Moldova had already created its official copyright law: Law No. 293-XIII, from 1994 but applied since 1995.









