Maps
- Berne ConventionRatifications of the Convention as of 2019
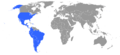
- Buenos Aires ConventionSignatories to the Buenos Aires Convention
- TRIPSWTO members (where the TRIPS agreement applies)Parties to the Agreement where also the membership of the European Union appliesObservers to the WTO