Related Research Articles

The counties of Ireland are historic administrative divisions of the island. They began as Norman structures, and as the powers exercised by the Cambro-Norman barons and the Old English nobility waned over time, new offices of political control came to be established at a county level. The number of counties varied depending on the time period, however thirty-two is the traditionally accepted and used number.
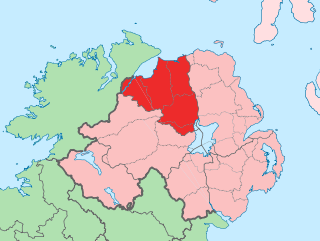
County Londonderry, also known as County Derry, is one of the six counties of Northern Ireland, one of the thirty two counties of Ireland and one of the nine counties of Ulster. Before the partition of Ireland, it was one of the counties of the Kingdom of Ireland from 1613 onward and then of the United Kingdom after the Acts of Union 1800. Adjoining the north-west shore of Lough Neagh, the county covers an area of 2,118 km2 (818 sq mi) and today has a population of about 252,231.
A county corporate or corporate county was a type of subnational division used for local government in England, Wales, and Ireland.

Douglas is a suburb, with a village core, in Cork city, Ireland. Douglas is also the name of the townland, Roman Catholic parish, Church of Ireland parish and civil parish in which it is contained.
Cork City was a parliamentary constituency in Ireland, represented in the Parliament of the United Kingdom. From 1880 to 1922 it returned two members of parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. From 1922 it was not represented in the UK Parliament, as it was no longer in the UK.
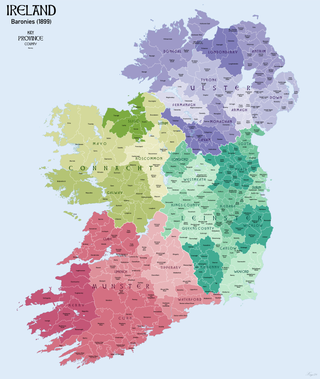
In Ireland, a barony is a historical subdivision of a county, analogous to the hundreds into which the counties of England were divided. Baronies were created during the Tudor reconquest of Ireland, replacing the earlier cantreds formed after the original Norman invasion. Some early baronies were later subdivided into half baronies with the same standing as full baronies.
Cork City was a constituency represented in the Irish House of Commons until its abolition on 1 January 1801.

Cork is the second largest city in the Republic of Ireland, third largest on the island of Ireland, and largest in the province of Munster. At the 2022 census, it had a population of 222,526.
In Ireland, the term city has somewhat differing meanings in Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland.

The North West Liberties of Londonderry is a barony in County Londonderry, Northern Ireland. It is bordered by two other baronies in Northern Ireland: Tirkeeran to the east, across Lough Foyle, and Strabane Lower to the south. It also borders two baronies in County Donegal in the Republic of Ireland. It borders Raphoe North, to the south-west; and Inishowen West to the north.


Kilculliheen is a civil parish, electoral division and barony in Ireland, on the north bank of the River Suir across from the centre of Waterford City. Historically, it has been transferred several times between the county of the city of Waterford and the counties of Kilkenny and Waterford. It now contains the only part of Waterford city on the left bank of the River Suir. The Parliamentary Gazetteer of 1846 states "as it lies on the left bank of the Suir, which, for the most part, divides co. Waterford from co. Kilkenny, most topographists mistakingly assign it to the barony of Ida, co. Kilkenny". It is now partly in County Kilkenny and partly in Waterford City. Of the barony's eleven townlands, five are entirely in Kilkenny and six are split between Kilkenny and Waterford. The city portion contains the formerly rural village of Ferrybank, which gives its name to a wider suburb which has spread across the county boundary.
Philip de Barry, was a Cambro-Norman warrior from Manorbier in Pembrokeshire who participated in the colonisation of Kingdom of Desmond following the Norman invasion of Ireland. He was the founder of the Barry or De Barry family in County Cork, and common ancestor of the barons Barry and earls of Barrymore.
Cork City is a barony in County Cork, Ireland. It contains seven civil parishes.

The Cathedral of Saint Mary and Saint Anne, also known as Saint Mary's Cathedral, The North Cathedral or The North Chapel, is a Roman Catholic cathedral located at the top of Shandon Street in Cork, Ireland. It is the seat of the Bishop of Cork and Ross, and the mother church of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Cork and Ross. Its name derived from the fact that it encompassed the ecclesiastical parish of St. Mary and the civil parish of St. Anne.
Dublin is one of the baronies of Ireland, an historical geographical unit of land. Its chief town is Donnybrook. It was created by the 1840 Acts from lands that were previously liberties in the county of the City of Dublin. Its name and area were confirmed by the Dublin Baronies Act 1842.
Fermoy is a historical barony in County Cork in Ireland. It is bordered by the baronies of Orrery and Kilmore to the north-west; Duhallow to the west; Barretts to the south-west; Barrymore to the south; Condons and Clangibbon to the east; and Coshlea, County Limerick to the north. It is bounded to the south by the Nagle Mountains and the valley of the Munster Blackwater. The Ballyhoura Mountains mark the northern boundary. A tributary of the Blackwater, the Awbeg has two branches in its upper stretches; one branch forms the northern boundary while the other near Buttevant, forms the western limit. To the east, lies another Blackwater tributary, the Funcheon. Anomalously, the namesake town of Fermoy is actually in the barony of Condons and Clangibbon. The town with the greatest population in the barony is Mallow.
The North Liberties or North Liberties of Limerick is a barony of County Limerick in Ireland, on the north bank of the River Shannon, between the centre of Limerick City to the east and County Clare to the north and west. It comprises parts of 17 townlands in three civil parishes: Killeely, St. Munchin's, and St. Nicholas.

Galway is a barony in Ireland, comprising Galway city and surrounding parts of County Galway. The barony is coterminous with the former County of the Town of Galway, a county corporate created by the town's 1610 charter and abolished by the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898.
References
From "Irish placenames database". logainm.ie (in English and Irish). Department of Community, Rural and Gaeltacht Affairs. Retrieved 11 November 2011.:
- 1 2 "Cork". Archived from the original on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ↑ "Cork: Civil parishes". Archived from the original on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ↑ "Rathcooney". Archived from the original on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ↑ "St. Michael's". Archived from the original on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ↑ "Dunbulloge". Archived from the original on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ↑ "Kilcully". Archived from the original on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ↑ "St. Anne's, Shandon". Archived from the original on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ↑ "St. Mary's, Shandon". Archived from the original on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ↑ "Whitechurch". Archived from the original on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ↑ "Currykippane". Archived from the original on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ↑ "Carrigrohane". Archived from the original on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ↑ "St. Finbar's". Archived from the original on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ↑ "Kilnaglory". Archived from the original on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ↑ "St. Nicholas". Archived from the original on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ↑ "Inishkenny". Archived from the original on 25 April 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ↑ "Ballinaboy". Archived from the original on 26 April 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ↑ "Killanully". Archived from the original on 26 April 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ↑ "Carrigaline". Archived from the original on 3 May 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
From other sources:
- 1 2 3 "Cork". The Parliamentary gazetteer of Ireland: adapted to the new poor-law, franchise, municipal and ecclesiastical arrangements, and compiled with a special reference to the lines of railroad and canal communication, as existing in 1814-45. Vol. I. A. Fullarton and co. 1846. pp. 515–516.
- ↑ "Charters". Cork City Council . Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- 1 2 Joyce, P.W. (c. 1880). "County Cork". Philips' Handy Atlas of the Counties of Ireland. London: George Philips & Son. p. 7. Archived from the original on 10 July 2011. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
