
Saqqara, also spelled Sakkara or Saccara in English, is an Egyptian village in the markaz (county) of Badrashin in the Giza Governorate, that contains ancient burial grounds of Egyptian royalty, serving as the necropolis for the ancient Egyptian capital, Memphis. Saqqara contains numerous pyramids, including the Pyramid of Djoser, sometimes referred to as the Step Tomb, and a number of mastaba tombs. Located some 30 km (19 mi) south of modern-day Cairo, Saqqara covers an area of around 7 by 1.5 km.

The tomb of Tutankhamun, also known by its tomb number, KV62, is the burial place of Tutankhamun, a pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of ancient Egypt, in the Valley of the Kings. The tomb consists of four chambers and an entrance staircase and corridor. It is smaller and less extensively decorated than other Egyptian royal tombs of its time, and it probably originated as a tomb for a non-royal individual that was adapted for Tutankhamun's use after his premature death. Like other pharaohs, Tutankhamun was buried with a wide variety of funerary objects and personal possessions, such as coffins, furniture, clothing and jewelry, though in the unusually limited space these goods had to be densely packed. Robbers entered the tomb twice in the years immediately following the burial, but Tutankhamun's mummy and most of the burial goods remained intact. The tomb's low position, dug into the floor of the valley, allowed its entrance to be hidden by debris deposited by flooding and tomb construction. Thus, unlike other tombs in the valley, it was not stripped of its valuables during the Third Intermediate Period.

Tomb KV17, located in Egypt's Valley of the Kings and also known by the names "Belzoni's tomb", "the Tomb of Apis", and "the Tomb of Psammis, son of Nechois", is the tomb of Pharaoh Seti I of the Nineteenth Dynasty. It is one of the most decorated tombs in the valley, and is one of the largest and deepest tombs in the Valley of the Kings. It was uncovered by Italian archaeologist and explorer Giovanni Battista Belzoni on 16 October, 1817.

The ancient Egyptians had an elaborate set of funerary practices that they believed were necessary to ensure their immortality after death. These rituals included mummifying the body, casting magic spells, and burials with specific grave goods thought to be needed in the afterlife.

Tomb KV43 is the tomb of Pharaoh Thutmose IV in the Valley of the Kings in Luxor, Egypt. It has a dog-leg shape, typical of the layout of early 18th Dynasty tombs. KV43 was rediscovered in 1903 by Howard Carter, excavating on behalf of Theodore M. Davis.

Tomb KV36, located in the Valley of the Kings in Egypt, was used for the burial of the noble Maiherpri from the Eighteenth Dynasty.

Tomb KV57 is the royal tomb of Horemheb, the last pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty and is located in the Valley of the Kings, Egypt.

Tomb KV40 is located in the Valley of the Kings, in Egypt. Artifacts from the tomb attribute it to 18th Dynasty royal family members, though human remains from the later 22nd Dynasty were interred. Although the tomb was excavated by Victor Loret in 1899, no report was published.

KV44 is an ancient Egyptian tomb located in the Valley of the Kings, Egypt. It was discovered and excavated by Howard Carter in 1901 and was re-examined in 1991 by Donald P. Ryan. The single chamber accessed by a shaft contained three intact Twenty-second Dynasty burials; the remains of seven mummies from the original interment were found within the fill. The original cutting of the tomb is dated to the Eighteenth Dynasty.

Tomb KV50 is located in the Valley of the Kings, in Egypt. It was discovered in 1906 by Edward R. Ayrton excavating on behalf of Theodore M. Davis. Together with KV51 and KV52, it forms a group known as the "Animal Tombs". It contained the burial of a dog mummy and a mummified monkey and is probably associated with the nearby tomb of Amenhotep II (KV35).
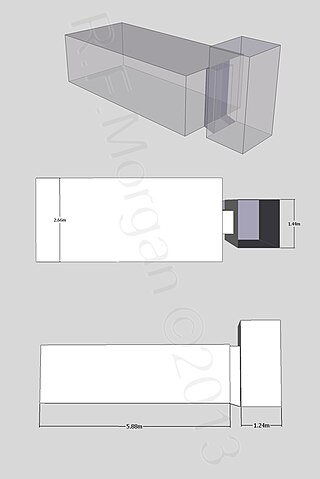
Tomb KV51 is located in the Valley of the Kings, in Egypt. It was discovered in 1906 by Edward R. Ayrton excavating on behalf of Theodore M. Davis. The tomb, together with KV50 and KV52 forms a group of three known as the "Animal Tombs". It contained the burials of three monkeys, one baboon, one ibis and three ducks, and is probably associated with the nearby tomb of Amenhotep II (KV35).

Tomb KV54 is located in the Valley of the Kings, in Egypt. It was originally excavated by Edward R. Ayrton on behalf of the American lawyer Theodore M. Davis, who funded the work.

The Valley of the Kings, also known as the Valley of the Gates of the Kings, is an area in Egypt where, for a period of nearly 500 years from the Eighteenth Dynasty to the Twentieth Dynasty, rock-cut tombs were excavated for pharaohs and powerful nobles under the New Kingdom of ancient Egypt.

TT1 is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official Sennedjem and members of his family. It is located in Deir el-Medina, on the west bank of the Nile opposite Luxor.
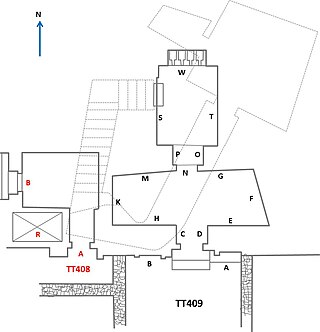
The Theban Tomb TT409 is located in El-Assasif, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian Samut called Kyky, who was Accountant of Cattle of the Amun domain, during the reign of Ramesses II during the Nineteenth Dynasty.
The majority of the 65 numbered tombs in the Valley of the Kings can be considered minor tombs, either because at present they have yielded little information or because the results of their investigation was only poorly recorded by their explorers, while some have received very little attention or were only cursorily noted. Most of these tombs are small, often only consisting of a single burial chamber accessed by means of a shaft or a staircase with a corridor or a series of corridors leading to the chamber, but some are larger, multiple chambered tombs. These minor tombs served various purposes, some were intended for burials of lesser royalty or for private burials, some contained animal burials and others apparently never received a primary burial. In many cases these tombs also served secondary functions and later intrusive material has been found related to these secondary activities. While some of these tombs have been open since antiquity, the majority were discovered in the 19th and early 20th centuries during the height of exploration in the valley.

Hornedjitef was an ancient Egyptian priest in the Temple of Amun at Karnak during the reign of Ptolemy III. He is known from his elaborate coffins, mummy mask and mummy, dating from the Early Ptolemaic Period and excavated from Asasif, Thebes, Egypt, which are all held in the British Museum. These related objects were chosen as the first of the hundred objects selected by British Museum Director Neil MacGregor in the 2010 BBC Radio 4 series A History of the World in 100 Objects.

The mask of Tutankhamun is a gold funerary mask of the 18th-dynasty ancient Egyptian pharaoh Tutankhamun. After being buried for over 3,000 years, it was excavated by Howard Carter in 1925 from tomb KV62 in the Valley of the Kings and is now in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo. The death mask is one of the best-known works of art in the world and a prominent symbol of ancient Egypt.
The archaeology of Ancient Egypt is the study of the archaeology of Egypt, stretching from prehistory through three millennia of documented history. Egyptian archaeology is one of the branches of Egyptology.


















