Vale Canada Limited is a wholly owned subsidiary of the Brazilian mining company Vale. Vale's nickel mining and metals division is headquartered in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It produces nickel, copper, cobalt, platinum, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium, gold, and silver. Prior to being purchased by CVRD in 2006, Inco was the world's second largest producer of nickel, and the third largest mining company outside South Africa and Russia of platinum group metals. It was also a charter member of the 30-stock Dow Jones Industrial Average formed on October 1, 1928.

In mineralogy, a pseudomorph is a mineral or mineral compound that appears in an atypical form, resulting from a substitution process in which the appearance and dimensions remain constant, but the original mineral is replaced by another. The name literally means "false form".

Chuquicamata, or "Chuqui" as it is more familiarly known, is by excavated volume the largest open pit copper mine in the world, located in the north of Chile, just outside Calama at 2,850 m (9,350 ft) above sea level, 215 km (134 mi) northeast of Antofagasta and 1,240 km (770 mi) north of the capital, Santiago. Flotation and smelting facilities were installed in 1952, and expansion of the refining facilities in 1968 made 500,000 ton annual copper production possible in the late 1970s. Previously part of Anaconda Copper, the mine is now owned and operated by Codelco, a Chilean state enterprise, since the Chilean nationalization of copper in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Its depth of 850 metres (2,790 ft) makes it the second deepest open-pit mine in the world.

Lake Poopó is a large saline lake located in a shallow depression in the Altiplano Mountains in Oruro Department, Bolivia, at an altitude of approximately 3,700 m (12,100 ft). Because the lake was long and wide, it made up the eastern half of the department, known as a mining region in southwest Bolivia. The permanent part of the lake body covered approximately 1,000 square kilometres (390 sq mi) and it was the second-largest lake in the country. The lake received most of its water from the Desaguadero River, which flows from Lake Titicaca at the north end of the Altiplano. Since the lake lacked any major outlet and had a mean depth of less than 3 m (10 ft), the surface area differed greatly on a seasonal basis.

Shogakukan Inc. is a Japanese publisher of dictionaries, literature, manga, non-fiction, DVDs, and other media in Japan.
Antofagasta plc is a Chilean business that operates in various sectors of the economy. It is one of the most important conglomerates of Chile with equity participation in Antofagasta Minerals, the railroad from Antofagasta to Bolivia, Twin Metals in Minnesota and other exploration joint ventures in different parts from the world.

Ilo is a port city in southern Peru, with 66,118 inhabitants. It is the second largest city in the Moquegua Region and capital of the Ilo Province.

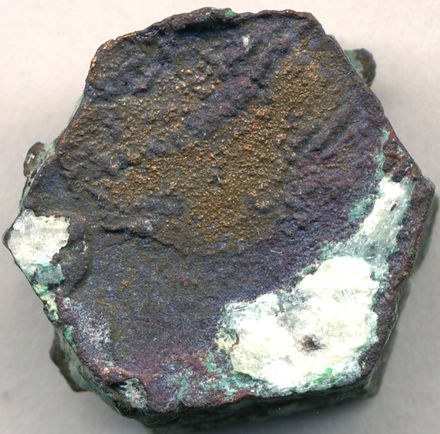
Native copper is an uncombined form of copper that occurs as a natural mineral. Copper is one of the few metallic elements to occur in native form, although it most commonly occurs in oxidized states and mixed with other elements. Native copper was an important ore of copper in historic times and was used by pre-historic peoples.

Pacajes is a province in the Bolivian department of La Paz. Its capital is Coro Coro.

The Territorial Prelature of Corocoro is a territorial prelature located in the city of Coro Coro in the Ecclesiastical province of La Paz in Bolivia.

Desaguadero or Chaka Marka is a town on the Bolivian-Peruvian border. On the Bolivian side it is situated in the La Paz Department, Ingavi Province, Desaguadero Municipality, Desaguadero Canton. On the Peruvian side it lies in the Puno Region, Chucuito Province, Desaguadero District. Both parts of the town are united by a binational bridge.
Apex Silver Mines, founded by Thomas Kaplan, from Denver, Colorado was a US-American transnational mining corporation with a tax haven address in the Cayman Islands. Following its reorganization under Chapter 11 bankruptcy in 2009, it re-emerged as Golden Minerals Corporation.

Desaguadero Municipality is the fourth municipal section of Ingavi Province in La Paz Department, Bolivia. Its capital is Desaguadero.
Mining in Bolivia has been a dominant feature of the Bolivian economy as well as Bolivian politics since 1557. Colonial era silver mining in Bolivia, particularly in Potosí, played a critical role in the Spanish Empire and the global economy. Tin mining supplanted silver by the twentieth century and the central element of Bolivian mining, and wealthy tin barons played an important role in national politics until they were marginalized by the industry's nationalization into the Bolivian Mining Corporation that followed the 1952 revolution. Bolivian miners played a critical part to the country's organized labor movement from the 1940s to the 1980s.

Coro Coro is a small town in the La Paz Department in Bolivia. It is the seat of the Coro Coro Municipality, the first municipal section of the Pacajes Province, and it is the seat of the province. Coro Coro, also known as Corocoro, was one of the most important mining areas in Bolivia because of its copper deposits and was home to the Corocoro United Copper Mines. That changed after 1985 when due to various economic and political reasons the mining center was closed and its workers left the area. Since then, the development of the town has been stagnant. Coro Coro contains in its territory several natural heritage landmarks, such as Kuntur Jipiña, the salt lake of Jayuma Llallawa and the church of Qaqinkura (Caquingora).
The Ch'alla Jawira which upstream is named Ch'api K'uchu and downstream successively is called Tupa Jawira and Qura Jawira is a river in the La Paz Department in Bolivia. It is a right affluent of the Aqhuya Jawira whose waters flow to the Desaguadero River.

Wila Qullu is a 4,658-metre-high (15,282 ft) mountain in the southern part of the Chilla-Kimsa Chata mountain range in the Andes of Bolivia. It is located in the La Paz Department, Pacajes Province, Waldo Ballivián Municipality. This is where the Ch'alla Jawira originates. Its waters flow to the Desaguadero River.
The Llallawa Jawira which upstream successively is named Patu Uma, Ch'alla Jawira, Jach'a Qura, Lupipi and Chuqi Phuju is a river in the La Paz Department in Bolivia. It is a left tributary of the Desaguadero River.
Toribio Ticona Porco is a Bolivian prelate of the Catholic Church. He was Prelate of the Territorial Prelature of Corocoro from 1992 to 2012 after serving as Auxiliary Bishop of Potosí from 1986 to 1992. Pope Francis made him a cardinal on 28 June 2018.














