
Pachacuti Inca Yupanqui, also called Pachacútec, was the ninth Sapa Inca of the Chiefdom of Cusco, which he transformed into the Inca Empire. Most archaeologists now believe that the famous Inca site of Machu Picchu was built as an estate for Pachacuti.

Huayna Capac was the third Sapa Inca of Tawantinsuyu, the Inca Empire. He was the son of and successor to Túpac Inca Yupanqui., the sixth Sapa Inca of the Hanan dynasty, and eleventh of the Inca civilization. He was born in Tumipampa and tutored to become Sapa Inca from a young age.

Cajamarca, also known by the Quechua name, Kashamarka, is the capital and largest city of the Cajamarca Region as well as an important cultural and commercial center in the northern Andes. It is located in the northern highlands of Peru at approximately 2,750 m (8,900 ft) above sea level in the valley of the Mashcon river. Cajamarca had an estimated population of about 226,031 inhabitants in 2015, making it the 13th largest city in Peru.

Arequipa is a department and region in southwestern Peru. It is the sixth largest department in Peru, after Puno, Cuzco, Madre de Dios, Ucayali, and Loreto, its sixth most populous department, and its eleventh least densely populated department. It is bordered by the departments of Ica, Ayacucho, Apurímac and Cusco in the north, the Department of Puno in the east, the Department of Moquegua in the south, and the Pacific Ocean in the west. Its capital, also called Arequipa, is Peru's second-largest city.

Moquegua is a department and region in southern Peru that extends from the coast to the highlands. Its capital is the city of Moquegua, which is among the main Peruvian cities for its high rates of GDP and national education.

The Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire, also known as the Conquest of Peru, was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. After years of preliminary exploration and military skirmishes, 168 Spanish soldiers under conquistador Francisco Pizarro, along with his brothers in arms and their indigenous allies, captured the last Sapa Inca, Atahualpa, at the Battle of Cajamarca in 1532. It was the first step in a long campaign that took decades of fighting but ended in Spanish victory in 1572 and colonization of the region as the Viceroyalty of Peru. The conquest of the Inca Empire, led to spin-off campaigns into present-day Chile and Colombia, as well as expeditions to the Amazon Basin and surrounding rainforest.

Topa Inca Yupanqui or Túpac Inca Yupanqui, also Topa Inga Yupangui, erroneously translated as "noble Inca accountant" was the tenth Sapa Inca (1471–93) of the Inca Empire, fifth of the Hanan dynasty. His father was Pachacuti, and his son was Huayna Capac. Topa Inca belonged to the Qhapaq Panaca. His quya was his older sister, Mama Ocllo.

Moquegua is a city in southern Peru, located in the Department of Moquegua, of which it is the capital. It is also capital of Mariscal Nieto Province and Moquegua District. It is located 1144 kilometers south of the capital city of Lima.
Qullasuyu was the southeastern provincial region of the Inca Empire. Qullasuyu is the region of the Qulla and related specifically to the native Qulla Quechuas who primarily resided in areas such as Cochabamba and Potosí. Most Aymara territories which are now largely incorporated into the modern South American states of northern Chile, Peru, Bolivia and the Argentine northwest were annexed during the reign of Sapa Inca Huayna Cápac in the sixteenth century.

The Chincha culture was the culture of a Native Peruvian people living near the Pacific Ocean in south west Peru. The Chincha Kingdom and their culture flourished in the Late Intermediate Period, also known as the regional states period of pre-Columbian Peru. They became part of the Inca Empire around 1480. They were prominent as sea-going traders and lived in a large and fertile oasis valley. La Centinela is an archaeological ruin associated with the Chincha. It is located near the present-day city of Chincha Alta.

Mayta Qhapaq was the fourth Sapa Inca of the Kingdom of Cuzco and a member of the Hurin dynasty.

The Battle of Arica, also known as Assault and Capture of Cape Arica, was a battle in the War of the Pacific. It was fought on 7 June 1880, between the forces of Chile and Peru.

PeruRail is a railway operator providing tourist, freight, and charter services in southern Peru. It was founded in 1999 by two Peruvian entrepreneurs and the British company Sea Containers.

The Incas were most notable for establishing the Inca Empire which was centered in modern-day South America in Peru and Chile. It was about 4,000 kilometres (2,500 mi) from the northern to southern tip. The Inca Empire lasted from 1438 to 1533. It was the largest Empire in America throughout the Pre-Columbian era. The Inca state was known as the Kingdom of Cuzco before 1438. Over the course of the Inca Empire, the Inca used conquest and peaceful assimilation to incorporate the territory of modern-day Peru, followed by a large portion of western South America, into their empire, centered on the Andean mountain range. However, shortly after the Inca Civil War, the last Sapa Inca (emperor) of the Inca Empire was captured and killed on the orders of the conquistador Francisco Pizarro, marking the beginning of Spanish rule. The remnants of the empire retreated to the remote jungles of Vilcabamba and established the small Neo-Inca State, which was conquered by the Spanish in 1572.
Lagunas de Mejía National Sanctuary is a protected area on the coastal plain of Peru, in Islay Province, Arequipa, in the mouth of the Tambo River. It is a sanctuary for migratory and resident birds, and was designated a Ramsar site in 1992.

The Inca army was the multi-ethnic armed forces used by the Tawantin Suyu to expand its empire and defend the sovereignty of the Sapa Inca in its territory.

The Battle of Los Ángeles was a military action fought on 22 March 1880 between the Chilean and Peruvian armies during the Tacna and Arica Campaign of the War of the Pacific. The Chilean forces under Commander in chief Manuel Baquedano assaulted and defeated the Allied stronghold guided by Andrés Gamarra garrisoned at Los Angeles hill top.
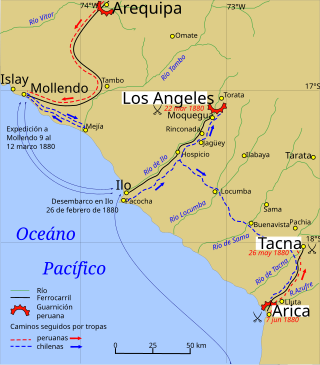
The Tacna and Arica campaign is known as the stage of the War of the Pacific after the Chilean conquest of the Peruvian department of Tarapacá, ending with Chilean domination of the Moquegua department in southern Peru. During this campaign Bolivia retired from the war after the Battle of Tacna, and Peru lost the port of Arica. Also, Manuel Baquedano assumed command as the new Commander in Chief of the Chilean Army, and the Allied Presidents were thrown out of office and replaced by Nicolas de Pierola in Peru and General Narciso Campero in Bolivia.

Osmore River system flows northeast to southwest in the Moquegua Region of southern coastal Peru. The river has its origin in the snow peaks of the Chuqi Ananta and Arundane mountains, at an elevation of 5,100 metres (16,700 ft) above sea level. It changes names as it descends from the Andes: From its origin it is called the Moquegua, then Osmore in the middle valley as Rio Coscori and Rio Tumilaca including where the river disappears into subterranean channels, and further down in the lower reaches as Rio Ilo.


























