
Smoke is a collection of airborne particulates and gases emitted when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwanted by-product of fires, but may also be used for pest control (fumigation), communication, defensive and offensive capabilities in the military, cooking, or smoking. It is used in rituals where incense, sage, or resin is burned to produce a smell for spiritual or magical purposes. It can also be a flavoring agent and preservative.

An aerosol is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog or mist, dust, forest exudates, and geyser steam. Examples of anthropogenic aerosols include particulate air pollutants, mist from the discharge at hydroelectric dams, irrigation mist, perfume from atomizers, smoke, steam from a kettle, sprayed pesticides, and medical treatments for respiratory illnesses. When a person inhales the contents of a vape pen or e-cigarette, they are inhaling an anthropogenic aerosol.
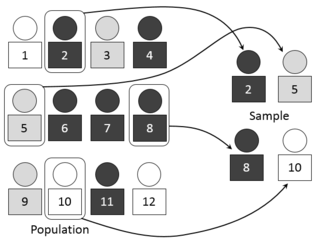
In statistics, quality assurance, and survey methodology, sampling is the selection of a subset of individuals from within a statistical population to estimate characteristics of the whole population. Statisticians attempt to collect samples that are representative of the population in question. Sampling has lower costs and faster data collection than measuring the entire population and can provide insights in cases where it is infeasible to measure an entire population.
In chemistry, a mixture is a material made up of two or more different chemical substances which are not chemically bonded. A mixture is the physical combination of two or more substances in which the identities are retained and are mixed in the form of solutions, suspensions and colloids.

A nephelometer or aerosol photometer is an instrument for measuring the concentration of suspended particulates in a liquid or gas colloid. A nephelometer measures suspended particulates by employing a light beam and a light detector set to one side of the source beam. Particle density is then a function of the light reflected into the detector from the particles. To some extent, how much light reflects for a given density of particles is dependent upon properties of the particles such as their shape, color, and reflectivity. Nephelometers are calibrated to a known particulate, then use environmental factors (k-factors) to compensate lighter or darker colored dusts accordingly. K-factor is determined by the user by running the nephelometer next to an air sampling pump and comparing results. There are a wide variety of research-grade nephelometers on the market as well as open source varieties.
Pierre Maurice Gy was a chemist and statistician. Born in Paris, France, to Felix and Clemence, Gy graduated in chemical engineering from ESPCI ParisTech in 1946.
Protein purification is a series of processes intended to isolate one or a few proteins from a complex mixture, usually cells, tissues or whole organisms. Protein purification is vital for the specification of the function, structure and interactions of the protein of interest. The purification process may separate the protein and non-protein parts of the mixture, and finally separate the desired protein from all other proteins. Separation of one protein from all others is typically the most laborious aspect of protein purification. Separation steps usually exploit differences in protein size, physico-chemical properties, binding affinity and biological activity. The pure result may be termed protein isolate.
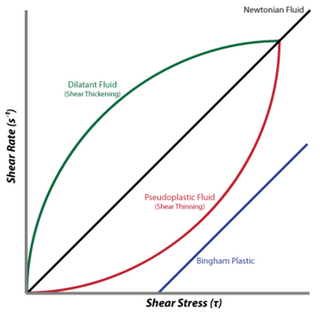
A dilatant material is one in which viscosity increases with the rate of shear strain. Such a shear thickening fluid, also known by the initialism STF, is an example of a non-Newtonian fluid. This behaviour is usually not observed in pure materials, but can occur in suspensions.
Density and dense usually refer to a measure of how much of some entity is within a fixed amount of space. Types of density include:
Total suspended solids (TSS) is the dry-weight of suspended particles, that are not dissolved, in a sample of water that can be trapped by a filter that is analyzed using a filtration apparatus known as sintered glass crucible. TSS is a water quality parameter used to assess the quality of a specimen of any type of water or water body, ocean water for example, or wastewater after treatment in a wastewater treatment plant. It is listed as a conventional pollutant in the U.S. Clean Water Act. Total dissolved solids is another parameter acquired through a separate analysis which is also used to determine water quality based on the total substances that are fully dissolved within the water, rather than undissolved suspended particles.

An electrostatic precipitator (ESP) is a filterless device that removes fine particles, like dust and smoke, from a flowing gas using the force of an induced electrostatic charge minimally impeding the flow of gases through the unit.
Soil texture is a classification instrument used both in the field and laboratory to determine soil classes based on their physical texture. Soil texture can be determined using qualitative methods such as texture by feel, and quantitative methods such as the hydrometer method based on Stokes' law. Soil texture has agricultural applications such as determining crop suitability and to predict the response of the soil to environmental and management conditions such as drought or calcium (lime) requirements. Soil texture focuses on the particles that are less than two millimeters in diameter which include sand, silt, and clay. The USDA soil taxonomy and WRB soil classification systems use 12 textural classes whereas the UK-ADAS system uses 11. These classifications are based on the percentages of sand, silt, and clay in the soil.
Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, or diffuse reflection spectroscopy, is a subset of absorption spectroscopy. It is sometimes called remission spectroscopy. Remission is the reflection or back-scattering of light by a material, while transmission is the passage of light through a material. The word remission implies a direction of scatter, independent of the scattering process. Remission includes both specular and diffusely back-scattered light. The word reflection often implies a particular physical process, such as specular reflection.
A particulate matter sampler is an instrument for measuring the properties of particulates in the ambient air.

The particle-size distribution (PSD) of a powder, or granular material, or particles dispersed in fluid, is a list of values or a mathematical function that defines the relative amount, typically by mass, of particles present according to size. Significant energy is usually required to disintegrate soil, etc. particles into the PSD that is then called a grain size distribution.
Gy's sampling theory is a theory about the sampling of materials, developed by Pierre Gy from the 1950s to beginning 2000s in articles and books including:
Continuous particulate air monitors (CPAMs) have been used for years in nuclear facilities to assess airborne particulate radioactivity (APR). In more recent times they may also be used to monitor people in their homes for the presence of manmade radioactivity. These monitors can be used to trigger alarms, indicating to personnel that they should evacuate an area. This article will focus on CPAM use in nuclear power plants, as opposed to other nuclear fuel-cycle facilities, or laboratories, or public-safety applications.
The riffle splitter is a static and fractional sub-sampling device that can be used for dividing a lot of dry particulate material into two half-lots. The device is usually constructed with steel sheet and should be designed to have an even number of opposing inclined chutes, with each chute having the same width. The recommended chute width should be at least 2.5× the size of the maximum particle diameter that can be found in the lot to be split. Riffle splitters are typically used in assay and analytical laboratories to reduce the size of samples provided from other sources to a lot size that is appropriate for the next stage of analytical sample preparation.

The characterization of nanoparticles is a branch of nanometrology that deals with the characterization, or measurement, of the physical and chemical properties of nanoparticles. Nanoparticles measure less than 100 nanometers in at least one of their external dimensions, and are often engineered for their unique properties. Nanoparticles are unlike conventional chemicals in that their chemical composition and concentration are not sufficient metrics for a complete description, because they vary in other physical properties such as size, shape, surface properties, crystallinity, and dispersion state.
The concept of the representative layer came about though the work of Donald Dahm, with the assistance of Kevin Dahm and Karl Norris, to describe spectroscopic properties of particulate samples, especially as applied to near-infrared spectroscopy. A representative layer has the same void fraction as the sample it represents and each particle type in the sample has the same volume fraction and surface area fraction as does the sample as a whole. The spectroscopic properties of a representative layer can be derived from the spectroscopic properties of particles, which may be determined by a wide variety of ways. While a representative layer could be used in any theory that relies on the mathematics of plane parallel layers, there is a set of definitions and mathematics, some old and some new, which have become part of representative layer theory.







