
Perth is the capital city of Western Australia. It is the fourth most populous city in Australia, with a population of over 2.3 million within Greater Perth as of 2023. It is part of the South West Land Division of Western Australia, with most of Perth's metropolitan area on the Swan Coastal Plain between the Indian Ocean and the Darling Scarp. The city has expanded outward from the original British settlements on the Swan River, upon which its central business district and port of Fremantle are situated.

The Armadale line is a suburban railway service in Perth, Western Australia, operated by the Public Transport Authority as part of the Transperth system. The Armadale line is 30.4 kilometres (18.9 mi) long, and starts at Perth station, heading south-east of there to serve Perth's south-eastern suburbs, terminating at Armadale station.

Oats Street railway station is a temporarily-closed Transperth suburban railway station in Western Australia, located in the Perth suburbs of Carlisle and East Victoria Park. The station was served by the Armadale and Thornlie lines prior to its closure in November 2023.

Carlisle railway station is a temporarily-closed suburban railway station on the Transperth network in Western Australia. It is in the Perth suburbs of Carlisle and East Victoria Park, and was predominantly served by Thornlie line services prior to its closure in November 2023.

Joondalup is a suburb of Perth, Western Australia, approximately 26 kilometres (16 mi) north of Perth's central business district. It contains the central business district of the regional City of Joondalup and acts as the primary urban centre of Perth's outer northern suburbs.

The Mandurah line is a commuter railway and service on the Transperth network in Western Australia that runs from Perth south to the state's second largest city Mandurah. The service is operated by Transperth Train Operations, a division of the Public Transport Authority. The line is 70.1 kilometres (43.6 mi) long and has 12 stations. At its northern end, the line begins as a continuation of the Joondalup line at Perth Underground, and ends as a continuation of the Joondalup line at Elizabeth Quay. The first 1.3 kilometres (0.81 mi) of the line is underground, passing under the Perth central business district. The line surfaces and enters the median of the Kwinana Freeway just north of the Swan River. It continues south down the freeway's median for 30 kilometres (19 mi), before veering south-west towards Rockingham. The final stretch of the line goes south from Rockingham to Mandurah.
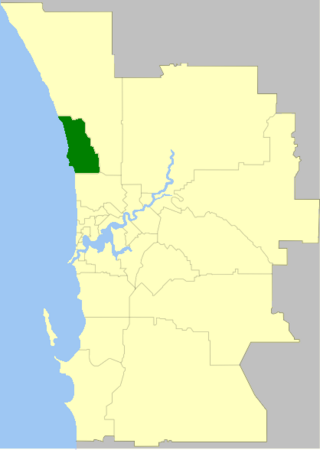
The City of Joondalup is a local government area in Perth, Western Australia. Its central business district is located in the suburb Joondalup, and it includes the town centres of Hillarys and Warwick.

Great Eastern Highway Bypass is a limited-access dual carriageway linking Great Eastern Highway and Roe Highway in Perth, Western Australia. Together with a section of Roe Highway, it bypasses the historical Guildford and Midland localities, through which the original, urban and slower Great Eastern Highway passes.
The South East Queensland Regional Plan 2009-2031 is a statutory plan designed to guide regional growth and development in South East Queensland, Australia. It was established under the Integrated Planning Act 1997, which has now been replaced by The Sustainable Planning Act 2009.
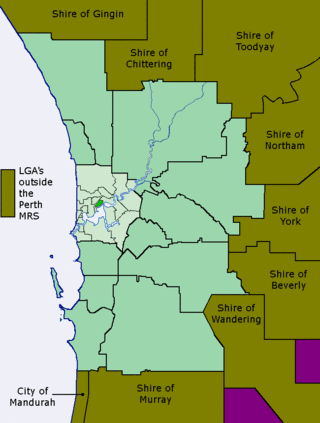
The Metropolitan Region Scheme (MRS) provides the legal basis for land use planning within the Perth metropolitan region. It classifies land into broad zones and reservations and is administered by the Western Australian Planning Commission. It is one of three regional schemes in Western Australia. The MRS is updated via an ongoing process of amendments. Amendments to the MRS are typically informed by a series of strategic plans prepared by the Department of Planning, Lands and Heritage. Detailed land use planning within the area of the MRS is undertaken by local governments and other statutory authorities which prepare one or more local planning schemes within their administrative boundaries. Local plannings schemes must be consistent with the MRS and require the approval of the WAPC. The acquisition of land reserved under the MRS is funded by a hypothecated land tax called the Metropolitan Region Improvement Tax.
Gordon Stephenson was a British-born town planner and architect. He is best known for his role in shaping the modern growth and development of Perth, Western Australia.

Paul Ritter was a Western Australian architect, town planner, sociologist, artist and author. In his roles as the first city planner of the City of Perth and subsequent two decades spent serving as Councillor for East Perth, Ritter is remembered as a brilliant, eccentric and often controversial public figure who consistently fought to preserve and enhance the character and vitality of the central city district. Today he is primarily remembered for his involvement in preserving many of Perth's heritage buildings at a time of rapid redevelopment and preventing the construction of an eight-lane freeway on the Swan River foreshore. Ritter's later career was blighted by a 3-year prison sentence for making misleading statements in applying for export marketing grants.

Railways in Perth, the capital city of Western Australia, have existed since 1881, when the Eastern Railway was opened between Fremantle and Guildford. Today, Perth has seven Transperth commuter rail lines and 75 stations.

Transperth is the public transport system for Perth and surrounding areas in Western Australia. It is managed by the Public Transport Authority (PTA), a state government organisation, and consists of train, bus and ferry services. Bus operations are contracted out to Swan Transit, Path Transit and Transdev. Ferry operations are contracted out to Captain Cook Cruises. Train operations are done by the PTA through their Transperth Train Operations division.
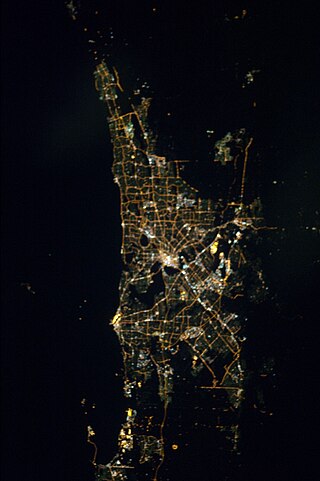
The Perth metropolitan region or the Perth metropolitan area is the administrative area and geographical extent of the Western Australian capital city of Perth and its conurbation.

The Sydney Region Outline Plan (SROP) was a land use and infrastructure scheme for metropolitan New South Wales released by the State Planning Authority in March 1968. The SROP superseded the 1948 County of Cumberland planning scheme. Whereas the Cumberland scheme echoed contemporary plans for London, the SROP adopted a Scandinavian model of town centres arranged along existing railway corridors.

The 1955 Plan for the Metropolitan Region, Perth and Fremantle was prepared for the Government of Western Australia by Gordon Stephenson and Alistair Hepburn. The plan was the first regional plan for Perth, and provided the basis for land use zoning under the Metropolitan Region Scheme. Even though not every recommendation of the report was adopted it is considered to have provided the underlying template for the modern development of Perth. The plan was superseded by the Corridor Plan for Perth in 1970.

Jandakot Regional Park is a conservation park approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) south of Perth, Western Australia, located within the Cities of Armadale, Canning, Cockburn, Gosnells and Kwinana as well as the Shire of Serpentine-Jarrahdale. The park, established in 1997 as the Jandakot Botanic Park, covers a non-continuous area of 2,362 hectares and is managed by the Cities of Armadale, Cockburn and Kwinana. It stretches from the southern end of Jandakot Airport to south of Casuarina Prison.

The railway passenger service between Perth and Fremantle was closed from 2 September 1979 to 29 July 1983 by the Charles Court government of Western Australia.
Directions 2031 is an overarching strategic plan for the Perth metropolitan area published by the Western Australian Planning Commission. It replaced the draft 2004 Network City and was the first strategic plan to be formally adopted since Metroplan in 1991. Detailed sub-regional planning frameworks containing comprehensive spatial maps were published separately as Perth and Peel @ 3.5 million, extending the strategic timeframe out to 2050. These frameworks, covering Perth’s Central, North-West, North-East and Southern regions, included specific population targets for each local government area. Collectively these targets accommodate an additional 800,000 people in the metropolitan area by 2030.
















