
Corydalis Alkaloids are categorized as natural products of the isoquinoline alkaloid type. [1]

Corydalis Alkaloids are categorized as natural products of the isoquinoline alkaloid type. [1]
Corydalis alkaloids are primarily located within the roots of Corydalis cava and various other Corydalis species. [1]
The representatives of Corydalis alkaloids include d-tetrahydrocoptisine (also known as d- or (+)-stylopine), d-canadine, and hydrohydrastinine. [2] [3]
Corydalis alkaloids exhibit certain narcotic and muscle-paralyzing effects. Historically, the powdered rhizomes of Corydalis alkaloid-containing plants enjoyed popularity as a vermifuge and menstrual stimulant. [1]

Corydalis is a genus of about 540 species of annual and perennial herbaceous plants in the family Papaveraceae, native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere and the high mountains of tropical eastern Africa. They are most diverse in China and the Himalayas, with at least 357 species in China.

Scoulerine, also known as discretamine and aequaline, is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (BIA) that is derived directly from (S)-reticuline through the action of berberine bridge enzyme. It is a precursor of other BIAs, notably berberine, noscapine, (S)-tetrahydropalmatine, and (S)-stylopine, as well as the alkaloids protopine, and sanguinarine. It is found in many plants, including opium poppy, Croton flavens, and certain plants in the genus Erythrina.

Toxiferine is a curare toxin. It is a bisindole alkaloid derived from Strychnos toxifera and a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. This alkaloid is the main toxic component of Calabash curare, and one of the most toxic plant alkaloids known. The lethal dose (LD50) for mice has been determined as 10 - 60 µg/kg by intravenous administration. It is a muscle relaxant that causes paralysis of skeletal muscle, which takes approximately 2 hours to recovery for a moderate dose, and 8 hours of total paralysis with a 20-fold paralytic dose. The paralysis can be antagonized by neostigmine

(S)-Canadine, also known as (S)-tetrahydroberberine and xanthopuccine, is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (BIA), of the protoberberine structural subgroup, and is present in many plants from the family Papaveraceae, such as Corydalis yanhusuo and C. turtschaninovii.

Steroidal alkaloids have the basic steroidal skeleton with nitrogen-based functional groups attached to the skeleton. More specifically, they are distinguished by their tetracyclic cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene skeleton that marks their close relationship with sterols. They fall in two major categories: Solanum alkaloids and Veratrum alkaloids. A Steroidal alkaloid has also been found in Chonemorpha fragrans, 'chonemorphine' was used to treat intestinal infections in Wistar rats..

(S)-Cheilanthifoline is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (BIA) which has been isolated from Corydalis dubia and Argemone mexicana. (S)-Cheilanthifoline is metabolically derived from (S)-reticuline, a pivotal intermediate in the biosynthesis of numerous BIAs. (S)-Cheilanthifoline is the immediate precursor of the BIA (S)-stylopine ((S)-stylopine synthase/CYP719A20), which is the precursor for the alkaloids protopine and sanguinarine.

Corydalis cava is a species of flowering plant in the family Papaveraceae, native to moist, shady, woodland habitats throughout most of mainland Europe, although commonest in central and southeast Europe. Its range extends from Spain in the west to Ukraine, Belarus and the Caucasus in the east and as far north as Sweden. It is absent from Iceland, the UK, the Netherlands, Norway, Finland, Russia and Greece.

Piperidine alkaloids are naturally occurring chemical compounds from the group of alkaloids, which are chemically derived from piperidine.

Quinolizidine alkaloids are natural products that have a quinolizidine structure; this includes the lupine alkaloids.
Erythrina alkaloids, generally containing benzyl-tetrahydroisoquinoline structure, are widely distributed in Erythrina species, a genus of plants which belong to the Fabaceae family in tropical and subtropical regions. The Erythrina alkaloids can be found in several organs of Erythrina trees but are primarily found in their seeds. They display several unique properties, and are the subject of active scientific research relating to their synthesis and bioactivity.

The carbazole alkaloids are natural products of the indole alkaloid type, derived from carbazole.
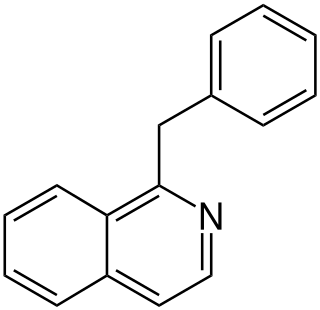
The benzylisoquinoline alkaloids are natural products that can be classified as isoquinoline alkaloidss and are derived from benzylisoquinoline. They also include the benzyl(tetrahydro)isoquinoline alkaloids.

Cephalotaxus alkaloids are natural products characterized by pentacyclic structure.

Indolizidine alkaloids are natural products from various alkaloid groups whose structure can be derived from indolizidine.
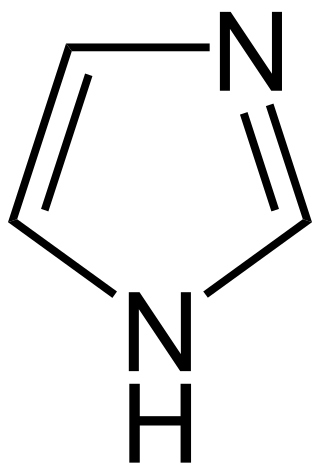
Imidazole alkaloids are a group of alkaloidss whose basic structure contains the imidazole ring system.

Diterpene alkaloids are natural products of the terpene alkaloid type.

Dendrobium alkaloids are natural products and so-called pseudoalkaloids.

The pyrrolidine alkaloids are natural products chemically derived from pyrrolidine.

Areca alkaloids are a group of piperidine alkaloids found in the areca nut, the seeds of the areca palm.
Apocynaceae alkaloids are natural products found in the plant family of the dogbane family (Apocynaceae).