
Rioja [] is a wine region in Spain, with Denominación de Origen Calificada. Rioja wine is made from grapes grown in the autonomous communities of La Rioja and Navarre, and the Basque province of Álava. Rioja is further subdivided into three zones: Rioja Alta, Rioja Oriental and Rioja Alavesa. Many wines have traditionally blended fruit from all three regions, though there is a slow growth in single-zone wines.

Mediana is an important archeological site from the late Roman period, located in the eastern suburb of the Serbian city of Niš. It represents a luxurious residence with a highly organised economy. Excavations have revealed a villa with peristyle, thermae, granary and water tower. The residence dates to the reign of Constantine the Great 306 to 337. Although Roman artifacts can be found scattered all over the area of present-day Niš, Mediana represents the best-preserved part of Roman Naissus. In 1979, Mediana was added to the Archaeological Sites of Exceptional Importance list, protected by Republic of Serbia.

Ranatra is a genus of slender predatory insects of the family Nepidae, known as water scorpions or water stick-insects. There are around 100 Ranatra species found in freshwater habitats around the world, both in warm and temperate regions, with the highest diversity in South America and Asia. Fewer are found elsewhere, but include several African, some in North America, three from Australia and three from the Palearctic, notably the relatively well-known European R. linearis. These brown insects are primarily found in stagnant or slow-moving water like ponds, marshes and canals, but can also be seen in streams. Exceptionally they have been recorded from hypersaline lakes and brackish lagoons.

Lachenalia is a genus of bulbs in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae, which are usually found in Namibia and South Africa. Most of these plants have a dormancy period, and the new roots of these plants will always grow every year. Lachenalia is named after the Swiss botanist Werner de Lachenal (1736-1800). Species are sometimes known as "Cape cowslip" though they are not directly related to the true cowslip Primula veris.

Eucalyptus tereticornis is a species of tree native to eastern Australia. E. tereticornis has several common names, including forest red gum, blue gum, flooded gum, grey gum, mountain gum, Queensland blue gum, red gum, bastard box, red ironbark, red irongum and slaty gum.
Mediana de Voltoya is a municipality located in the province of Ávila, Castile and León, Spain. According to the 2006 census (INE), the municipality has a population of 107 inhabitants.
Tolbaños is a municipality located in the province of Ávila, Castile and León, Spain. According to the 2004 census (INE), the municipality has a population of 111 inhabitants.
Mediana de Aragón is a municipality located in the province of Zaragoza, Aragon, Spain. According to the 2004 census (INE), the municipality has a population of 504 inhabitants.

The tortrix moth, genus Pammene, belongs to the tribe Grapholitini of the subfamily Olethreutinae.

Philornis is a genus of around 50 species of fly from Central and South America. Their larvae are subcutaneous parasites of nestling birds. They parasitize a wide range of bird species including macaws at the Tambopata research site.

Alive is an album by Chick Corea, released in 1991 through the record label GRP. The album peaked at number three on Billboard's Top Jazz Albums chart.
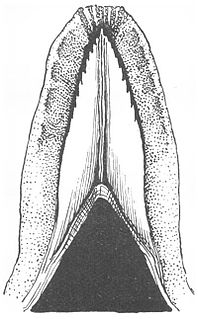
The sublingua ("under-tongue") is a muscular secondary tongue found below the primary tongue in tarsiers and living strepsirrhine primates, which includes lemurs and lorisoids. Although it is most fully developed in these primates, similar structures can be found in some other mammals, such as marsupials, treeshrews, and colugos. This "second tongue" lacks taste buds, and in lemuriforms, it is thought to be used to remove hair and other debris from the toothcomb, a specialized dental structure used to comb the fur during oral grooming.
Cotaena phlegyropa is a species of sedge moths in the genus Cotaena. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1915. It is found in Guyana and French Guiana.
Mordellistena mediana is a species of beetle in the Mordellidae family which is in the Tenebrionoidea superfamily. It was discovered in 1977 and can be found in Croatia, Greece and Hungary.
Chrostosoma mediana is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Schaus in 1928. It is found in Paraguay.
Clarkeulia mediana is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in Paraná, Brazil.
Orthocomotis mediana is a species of moth of the Tortricidae family. It is found in Ecuador and Peru.
Megachile mediana is a species of bee in the family Megachilidae. It was described by Pasteels in 1965.

Chondrorrhina is a genus of fruit and flower chafers belonging to the family Scarabaeidae, subfamily Cetoniinae.











