
Aachen is the 13th-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia and the 27th-largest city of Germany, with around 252,000 inhabitants.

Charlemagne was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the Holy Roman Emperor from 800, all until his death in 814. Charlemagne succeeded in uniting the majority of Western and Central Europe, and he was the first recognized emperor to rule Western Europe after the fall of the Western Roman Empire approximately three centuries earlier. Charlemagne's rule saw a program of political and societal changes that had a lasting impact on Europe in the Middle Ages.

Filioque, a Latin term meaning "and from the Son," was added to the original Niceno-Constantinopolitan Creed, and has been the subject of great controversy between Eastern and Western Christianity. The term refers to the Son, Jesus Christ, with the Father, as the one shared origin of the Holy Spirit. It is not in the original text of the Creed, attributed to the First Council of Constantinople (381), which says that the Holy Spirit proceeds "from the Father", without additions of any kind, such as "and the Son" or "alone".

Louis I, better known as Louis the Pious, also called the Fair and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aquitaine from 781. As the only surviving son of Charlemagne and Hildegard, he became the sole ruler of the Franks after his father's death in 814, a position that he held until his death except from 833 to 834, when he was deposed.

The Second Council of Nicaea is recognized as the last of the first seven ecumenical councils by the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church. In addition, it is also recognized as such by the Old Catholics, the Anglican Communion, and others. Protestant opinions on it are varied.
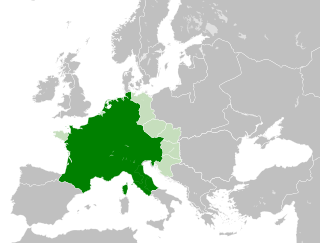
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lombards in Italy from 774. In 800, the Frankish king Charlemagne was crowned emperor in Rome by Pope Leo III in an effort to transfer the Roman Empire from the Byzantine Empire to Western Europe. The Carolingian Empire is sometimes considered the first phase in the history of the Holy Roman Empire.
Pope Nicholas I, called Nicholas the Great, was the bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 24 April 858 until his death. He is remembered as a consolidator of papal authority, exerting decisive influence on the historical development of the papacy and its position among the Christian nations of Western Europe. Nicholas I asserted that the pope should have suzerainty over all Christians, even royalty, in matters of faith and morals.
Albert of Aix(-la-Chapelle) or Albert of Aachen; Latin: Albericus Aquensis; fl. c. 1100) was a historian of the First Crusade and the early Kingdom of Jerusalem. He was born during the later part of the 11th century, and afterwards became canon (priest) and custos (guardian) of the church of Aachen.
The East–West Schism, also known as the Great Schism or Schism of 1054, is the ongoing break of communion between the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches since 1054. A series of ecclesiastical differences and theological disputes between the Greek East and Latin West preceded the formal split that occurred in 1054. Prominent among these were the procession of the Holy Spirit (Filioque), whether leavened or unleavened bread should be used in the Eucharist, the Pope's claim to universal jurisdiction, and the place of the See of Constantinople in relation to the pentarchy.

Saint Paulinus II was a priest, theologian, poet, and one of the most eminent scholars of the Carolingian Renaissance. From 787 to his death, he was the Patriarch of Aquileia. He participated in a number of synods which opposed Spanish Adoptionism and promoted both reforms and the adoption of the Filioque into the Nicene Creed. In addition, Paulinus arranged for the peaceful Christianisation of the Avars and the alpine Slavs in the territory of the Aquileian patriarchate. For this, he is also known as the apostle of the Slovenes.
Ecclesiastical polity is the operational and governance structure of a church or of a Christian denomination. It also denotes the ministerial structure of a church and the authority relationships between churches. Polity relates closely to ecclesiology, the study of doctrine and theology relating to church organization.
Amalarius (c. 775–c. 850) was a Frankish prelate and courtier, temporary bishop of Trier (812–13) and Lyon (835–38), and an accomplished liturgist. He was close to Charlemagne and a partisan of his successor, Louis the Pious, throughout the latter's tumultuous reign.
Arles in the south of Roman Gaul hosted several councils or synods referred to as Concilium Arelatense in the history of the early Christian church.

In the history of Christianity, the first seven ecumenical councils include the following: the First Council of Nicaea in 325, the First Council of Constantinople in 381, the Council of Ephesus in 431, the Council of Chalcedon in 451, the Second Council of Constantinople in 553, the Third Council of Constantinople from 680–681 and finally, the Second Council of Nicaea in 787. All of the seven councils were convened in what is now the country of Turkey.
Christianity became the official religion of the Roman Empire when Emperor Theodosius I issued the Edict of Thessalonica in 380, which recognized the catholic orthodoxy of Nicene Christians in the Great Church as the Roman Empire's state religion. Most historians refer to the Nicene church associated with emperors in a variety of ways: as the catholic church, the orthodox church, the imperial church, the imperial Roman church, or the Byzantine church, although some of those terms are also used for wider communions extending outside the Roman Empire. The Eastern Orthodox Church, Oriental Orthodoxy, and the Catholic Church all claim to stand in continuity from the Nicene church to which Theodosius granted recognition.

The Synods of Aachen between 816 and 819 were a landmark in regulations for the monastic life in the Frankish realm. The Benedictine Rule was declared the universally valid norm for communities of monks and nuns, while canonical orders were distinguished from monastic communities and unique regulations were laid down for them: the Institutio canonicorum Aquisgranensis. The synods of 817 and 818/819 completed the reforms. Among other things, the relationship of church properties to the king was clarified.

In canon law, a canon designates some law promulgated by a synod, an ecumenical council, or an individual bishop.

Leidrad was the bishop of Lyon from 797 and its first archbishop from 804 until 814. He was a courtier of Charlemagne before he was a bishop. As bishop, he helped resolve the adoptionist controversy. He also began a programme of building and renovation in his diocese, turning Lyon into a centre of learning. Of his writings, two letters and a treatise on baptism survive.
The Carolingian Church encompasses the practices and institutions of Christianity in the Frankish kingdoms under the rule of the Carolingian dynasty (751-888). In the eighth and ninth centuries, Western Europe witnessed decisive developments in the structure and organisation of the church, relations between secular and religious authorities, monastic life, theology, and artistic endeavours. Christianity was the principal religion of the Carolingian Empire. Through military conquests and missionary activity, Latin Christendom expanded into new areas, such as Saxony and Bohemia. These developments owed much to the leadership of Carolingian rulers themselves, especially Charlemagne and Louis the Pious, whose courts encouraged successive waves of religious reform and viewed Christianity as a unifying force in their empire.









