Related Research Articles

Aquitaine, archaic Guyenne or Guienne, is a historical region of Southwestern France and a former administrative region. Since 1 January 2016 it has been part of the administrative region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine. It is situated in the southwest corner of metropolitan France, along the Atlantic Ocean and the Pyrenees mountain range on the border with Spain; for most of its written history Bordeaux has been a vital port and administrative centre. It is composed of the five departments of Dordogne, Lot-et-Garonne, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, Landes and Gironde. Gallia Aquitania was established by the Romans in ancient times and in the Middle Ages, Aquitaine was a kingdom and a duchy, whose boundaries fluctuated considerably.

Guyenne or Guienne was an old French province which corresponded roughly to the Roman province of Aquitania Secunda and the archdiocese of Bordeaux.
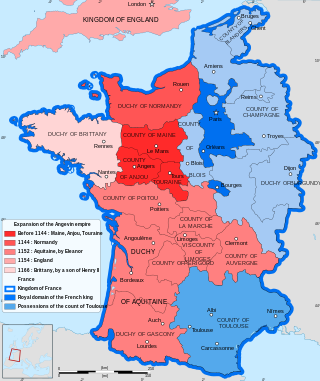
The Duke of Aquitaine was the ruler of the medieval region of Aquitaine under the supremacy of Frankish, English, and later French kings.

The Duchy of Aquitaine was a historical fiefdom in western, central, and southern areas of present-day France to the south of the river Loire, although its extent, as well as its name, fluctuated greatly over the centuries, at times comprising much of what is now southwestern France (Gascony) and central France.
The County of Armagnac, situated between the Adour and Garonne rivers in the lower foothills of the Pyrenées, was a historic county of the Duchy of Gascony, established in 601 in Aquitaine. In 960, the title of 'Count of Armagnac' was established, and thus the County of Armagnac was created. In 1751, following the death of childless Charles de Lorraine, Comte d'Armagnac, the county was absorbed into the Crown lands of France and the King, then Louis XV took the title of 'Count of Armagnac'. In 1791, following the Decree dividing France into departments, the county was disestablished, but remains an important natural region of France.
The history of Toulouse, in Occitania, southern France, traces back to ancient times. After Roman rule, the city was ruled by the Visigoths and Merovingian and Carolingian Franks. Capital of the County of Toulouse during the Middle Ages, today it is the capital of the Midi-Pyrénées region.

Alamannia, or Alemannia, was the kingdom established and inhabited by the Alemanni, a Germanic tribal confederation that had broken through the Roman limes in 213.
Seguin or Séguín is a French and Gascon name. It may be a Frankish name, from Germanic origin. Seghin, Sigiwinus, Siguvinus, Siguinus, Siguin, Sigiwin, Sigwin, Sigoin and Segouin are alternate variants. According to Jean de Jaurgain quoting primary source Saint Andrew of Bordeaux, the original Vascon name written in Latin was Sihiminum, related to Basque Seme(no), meaning 'son'. It is also spelled Scimin, Skimin, Scemenus, Semen, Semeno, Xemen, or Ximen and gave rise to the Castilian Ximeno and Jimeno. Both Semen and Seguin, unrelated names, are found in sources.
Seguin II, called Mostelanicus, was the Count of Bordeaux and Saintes from 840 and Duke of Gascony from 845. He was either the son or grandson of Seguin I, the duke appointed by Charlemagne.
Sancho II Sánchez or Sans II Sancion succeeded his brother Aznar Sánchez as count of Vasconia Citerior (Gascony) in 836, in spite of the objections of King Pepin I of Aquitaine.
García II Sánchez, called the Bent, was Duke of Gascony from sometime before 887 to his death.
William II Sánchez, Duke of Gascony from circa 961 at least until 996, was the younger illegitimate son of duke Sancho IV and successor, around 961, of his childless elder brother, Duke Sancho V. He united the County of Bordeaux with the Gascony. Documents of his reign state that his grandfather came from Iberia, lending credence to "phantasmagorical" genealogies placing the origins of García II Sánchez across the Pyrenees. He died in 996 or 997 and was succeeded by his son, Bernard William.
Bernard William, sometimes Bernard I, was the Duke of Gascony and Count of Bordeaux from c.997 to his death. During his time, Gascony was effectively independent, its duke a sovereign and any connection to the Kingdom of France theoretical. His reign fell during a period of relative peace and prosperity: the Peace of God movement had originated in Gascony in his father's time, monastic reform was introduced during his reign and the period of Viking attacks was over. Nonetheless, it was also a period of increasing feudal fragmentation, and Bernard died a violent death.
Seguin I Lupo was Duke of Gascony from 812 until 816, when Louis the Pious deposed him "because of his boundless arrogance and wicked ways", according to the contemporary Frankish chroniclers. The "Basques across the Garonne and around the Pyrenees" rebelled against the removal of their duke, but the Frankish king received the submission of the rebels in Dax. The emperor crossed the Pyrenees and "settled matters" in Pamplona. This could imply that the Gascony of Seguin's day was trans-Pyrenean, i.e., comprised lands on both sides of the mountains.

The Duchy of Gascony or Duchy of Vasconia was a duchy located in present-day southwestern France and northeastern Spain, an area encompassing the modern region of Gascony. The Duchy of Gascony, then known as Wasconia, was originally a Frankish march formed to hold sway over the Basques. However, the duchy went through different periods, from its early years with its distinctively Basque element to the merger in personal union with the Duchy of Aquitaine to the later period as a dependency of the Plantagenet kings of England.

The County of Vasconia Citerior was a medieval domain attested as of 824. It may have comprised the lands between the western Pyrenees and the river Adour.
Lupus I was the duke of Gascony and part of Aquitaine in the Merovingian kingdom during the 670s. He may have started a dynasty, since the next-known duke of Gascony was Lupus II . Lupus was probably the successor of Felix, whose duchy seemed to encompass almost an identical territory to the kingdom of Charibert II. Sometime after 658, Lupus rebelled against Felix and later succeeded him. According to the Miracles of Saint Martial, the rebellion occurred during the mayorship of Ebroin.
The Charte d'Alaon is a spurious and fraudulent charter purporting to provide a genealogy of the house of Odo the Great, Duke of Aquitaine. The 19th-century French historian Joseph-François Rabanis proved it to be a hoax fabricated in the 17th century. His research thus rendered a good deal of "known" Gascon and Navarrese genealogy meaningless.
References
- ↑ Charles Higounet, Bordeaux pendant le Haut Moyen Âge (Bordeaux: 1963), pp. 303–05.