
The Royal Abbey of Our Lady of Fontevraud or Fontevrault was a monastery in the village of Fontevraud-l'Abbaye, near Chinon, in the former French duchy of Anjou. It was founded in 1101 by the itinerant preacher Robert of Arbrissel. The foundation flourished and became the center of a new monastic Order, the Order of Fontevraud. This order was composed of double monasteries, in which the community consisted of both men and women — in separate quarters of the abbey — all of whom were subject to the authority of the Abbess of Fontevraud. The Abbey of Fontevraud itself consisted of four separate communities, all managed by the same abbess.

Robert II, called the Pious or the Wise, was King of the Franks from 996 to 1031, the second from the Capetian dynasty.

Odo was the elected King of West Francia from 888 to 898. He was the first king from the Robertian dynasty. Before assuming the kingship, Odo was the count of Paris. His reign marked the definitive separation of West Francia from the Carolingian Empire, which would never reunite.

Robert I was the elected King of West Francia from 922 to 923. Before his election to the throne he was Count of Poitiers, Count of Paris and Marquis of Neustria and Orléans. He succeeded the overthrown Carolingian king Charles the Simple, who in 898 had succeeded Robert's brother, king Odo.

Count of Paris was a title for the local magnate of the district around Paris in Carolingian times. After Hugh Capet was elected King of France in 987, the title merged into the crown and fell into disuse. However, it was later revived by the Orléanist pretenders to the French throne in an attempt to evoke the legacy of Capet and his dynasty.

Maine is one of the traditional provinces of France. It corresponds to the former County of Maine, whose capital was also the city of Le Mans. The area, now divided into the departments of Sarthe and Mayenne, counts about 857,000 inhabitants.
Theobald III of Blois (1012–1089) was count of Blois, Meaux and Troyes. He was captured in 1044 by Geoffrey II, Count of Anjou, and exchanged the county of Touraine for his freedom. Theobald used his nephew's involvement with the Norman invasion of England, to gain authority over the County of Champagne. He died in 1089.

The County of Blois was a feudal principality centred on Blois, south of Paris, France. It was created just after king Clovis I conquered Roman Gaul around AD 500. Between the 8th and the 13th centuries, it was amongst the most powerful vassal counties within the Kingdom of France, after having succeeded in surrounding the Capetian dynasty's lands of France since Blois annexed the Champagne.
Odo II was the count of Blois, Chartres, Châteaudun, Beauvais and Tours from 1004 and count of Troyes and Meaux from 1022. He twice tried to make himself a king: first in Italy after 1024 and then in Burgundy after 1032.
In medieval history, West Francia or the Kingdom of the West Franks refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by Charlemagne. It was the forerunner of the future Kingdom of France and existed from 843 to 987. West Francia emerged from the partition of the Carolingian Empire in 843 under the Treaty of Verdun following the death of Charlemagne's son, Louis the Pious. It is considered the first separate polity in French history.
Louis of Lower Lorraine, Frankish royalty and a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was a younger son of Charles, Duke of Lower Lorraine, through his second wife, Adelaide.
Hugh the Abbot was a member of the Welf family, a son of Conrad I of Auxerre and Adelaide. After his father's death, his mother apparently married Robert the Strong, the margrave of Neustria. On Robert's death in 866, Hugh became the regent and guardian for Robert's sons, Odo and Robert.
Theobald I (913–975), called the Trickster, was first Viscount of Blois and Viscount of Tours, and then from 956, Count of Blois, Chartres and Châteaudun, as well as Count of Tours.
The Marches of Neustria were two marches created in 861 by the Carolingian king of West Francia Charles the Bald. They were ruled by officials appointed by the Monarchy of France, known as wardens, prefects or margraves. One march, was created as a buffer against the Bretons and the other against the Norsemen.
The Robertians are the proposed Frankish family which was ancestral to the Capetian dynasty, and thus to the royal families of France and of many other countries. The Capetians appear first in the records as powerful nobles serving under the Carolingian dynasty of Charlemagne in West Francia, which later became France. As their power increased, they came into conflict with the older royal family and attained the crown several times before the eventual start of the continuous rule of the descendants of Hugh Capet.

Bourgueil Abbey was a Benedictine monastery located at Bourgueil, historically in Anjou, currently in Indre-et-Loire and the diocese of Angers. The founder was Emma of Blois, daughter of Theobald I of Blois, and by her marriage, duchess of Aquitaine.
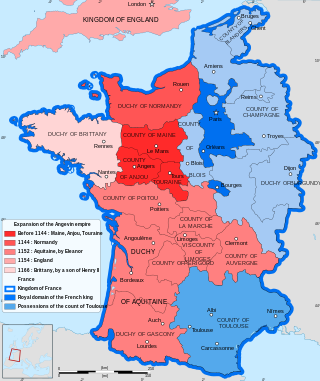
The County of Anjou was a small French county that was the predecessor to the better-known Duchy of Anjou. Its capital was Angers, and its area was roughly co-extensive with the diocese of Angers. Anjou was bordered by Brittany to the west, Maine to the north, Touraine to the east and Poitou to the south. The adjectival form is Angevin, and inhabitants of Anjou are known as Angevins. In 1360, the county was raised into the Duchy of Anjou within the Kingdom of France. This duchy was later absorbed into the French royal domain in 1482 and remained a province of the kingdom until 1790.
The County of Châteaudun was held in the 9th century by counts who also held the County of Blois. Theobald I created the first viscount of Châteaudun with the appointment of Geoffrey I, founder of the House of Châteaudun. The viscounts were entrusted with the government of the county of Châteaudun, records of whom are continuous from the mid-10th century. The actual rule of Châteaudun between the late 9th and the mid-10th centuries, and the relationships between the count and viscounts, is uncertain. The county was revived in 1439 when the region was recreated as the County of Dunois and granted to Jean Levieux Valois des Orléans, the illegitimate son of Louis I, Duke of Orléans, son of Charles V of France.
Hubert of Vendôme was the bishop of Angers between 1006 and 1047. He was the son of Hubert, viscount of Vendôme, and Emma.