Related Research Articles
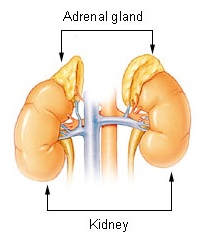
The adrenal glands are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three main zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.

Vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travels down the axon of that cell, which terminates in the posterior pituitary, and is released from vesicles into the circulation in response to extracellular fluid hypertonicity (hyperosmolality). AVP has two primary functions. First, it increases the amount of solute-free water reabsorbed back into the circulation from the filtrate in the kidney tubules of the nephrons. Second, AVP constricts arterioles, which increases peripheral vascular resistance and raises arterial blood pressure.

The renin–angiotensin system (RAS), or renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), is a hormone system that regulates blood pressure and fluid and electrolyte balance, as well as systemic vascular resistance.

Angiotensin is a peptide hormone that causes vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure. It is part of the renin–angiotensin system, which regulates blood pressure. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex to promote sodium retention by the kidneys.

Cortisol is a steroid hormone, in the glucocorticoid class of hormones. When used as a medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
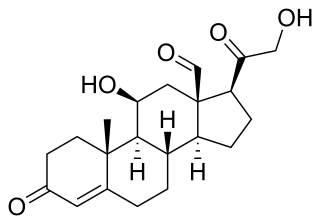
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays a central role in the homeostatic regulation of blood pressure, plasma sodium (Na+), and potassium (K+) levels. It does so primarily by acting on the mineralocorticoid receptors in the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the nephron. It influences the reabsorption of sodium and excretion of potassium (from and into the tubular fluids, respectively) of the kidney, thereby indirectly influencing water retention or loss, blood pressure and blood volume. When dysregulated, aldosterone is pathogenic and contributes to the development and progression of cardiovascular and kidney disease. Aldosterone has exactly the opposite function of the atrial natriuretic hormone secreted by the heart.

Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) or atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) is a natriuretic peptide hormone secreted from the cardiac atria that in humans is encoded by the NPPA gene. Natriuretic peptides are a family of hormone/paracrine factors that are structurally related. The main function of ANP is causing a reduction in expanded extracellular fluid (ECF) volume by increasing renal sodium excretion. ANP is synthesized and secreted by cardiac muscle cells in the walls of the atria in the heart. These cells contain volume receptors which respond to increased stretching of the atrial wall due to increased atrial blood volume.
The baroreflex or baroreceptor reflex is one of the body's homeostatic mechanisms that helps to maintain blood pressure at nearly constant levels. The baroreflex provides a rapid negative feedback loop in which an elevated blood pressure reflexively causes the heart rate to decrease and also causes blood pressure to decrease. Decreased blood pressure decreases baroreflex activation and causes heart rate to increase and to restore blood pressure levels. The baroreflex can begin to act in less than the duration of a cardiac cycle and thus baroreflex adjustments are key factors in dealing with postural hypotension, the tendency for blood pressure to decrease on standing due to gravity.

The subfornical organ (SFO) is one of the circumventricular organs of the brain. Its name comes from its location on the ventral surface of the fornix near the interventricular foramina, which interconnect the lateral ventricles and the third ventricle. Like all circumventricular organs, the subfornical organ is well-vascularized, and like all circumventricular organs except the subcommissural organ, some SFO capillaries have fenestrations, which increase capillary permeability. The SFO is considered a sensory circumventricular organ because it is responsive to a wide variety of hormones and neurotransmitters, as opposed to secretory circumventricular organs, which are specialized in the release of certain substances.
Secondary hypertension is a type of hypertension which by definition is caused by an identifiable underlying primary cause. It is much less common than the other type, called essential hypertension, affecting only 5-10% of hypertensive patients. It has many different causes including endocrine diseases, kidney diseases, and tumors. It also can be a side effect of many medications.

11-Deoxycorticosterone (DOC), or simply deoxycorticosterone, also known as 21-hydroxyprogesterone, as well as desoxycortone (INN), deoxycortone, and cortexone, is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal gland that possesses mineralocorticoid activity and acts as a precursor to aldosterone. It is an active (Na+-retaining) mineralocorticoid. As its names indicate, 11-deoxycorticosterone can be understood as the 21-hydroxy-variant of progesterone or as the 11-deoxy-variant of corticosterone.
Follistatin also known as activin-binding protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FST gene. Follistatin is an autocrine glycoprotein that is expressed in nearly all tissues of higher animals.

Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as both a hormone and neurotransmitter. The name "noradrenaline", derived from Latin roots meaning "at/alongside the kidneys", is more commonly used in the United Kingdom; in the United States, "norepinephrine", derived from Greek roots having that same meaning, is usually preferred. "Norepinephrine" is also the international nonproprietary name given to the drug. Regardless of which name is used for the substance itself, parts of the body that produce or are affected by it are referred to as noradrenergic.
Chronic stress is the response to emotional pressure suffered for a prolonged period of time in which an individual perceives they have little or no control. It involves an endocrine system response in which corticosteroids are released. While the immediate effects of stress hormones are beneficial in a particular short-term situation, long-term exposure to stress creates a high level of these hormones. This may lead to high blood pressure, damage to muscle tissue, inhibition of growth, and damage to mental health.

Urodilatin (URO) is a hormone that causes natriuresis by increasing renal blood flow. It is secreted in response to increased mean arterial pressure and increased blood volume from the cells of the distal tubule and collecting duct. It is important in oliguric patients as it lowers serum creatinine and increases urine output.

Inhibin, beta A, also known as INHBA, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the INHBA gene. INHBA is a subunit of both activin and inhibin, two closely related glycoproteins with opposing biological effects.

Natriuretic peptide precursor C, also known as NPPC, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NPPC gene. The precursor NPPC protein is cleaved to the 22 amino acid peptide C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP).

Inhibin, alpha, also known as INHA, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the INHA gene.
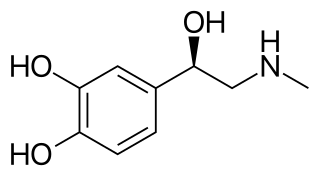
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions. Adrenaline is normally produced both by the adrenal glands and by a small number of neurons in the medulla oblongata. It plays an important role in the fight-or-flight response by increasing blood flow to muscles, output of the heart by acting on SA Node, pupil dilation response and blood sugar level. It does this by binding to alpha and beta receptors. It is found in many animals and some single-celled organisms. Polish physiologist Napoleon Cybulski first isolated adrenaline in 1895.

Ventricular natriuretic peptide or brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), also known as B-type natriuretic peptide, is a hormone secreted by cardiomyocytes in the heart ventricles in response to stretching caused by increased ventricular blood volume.
References
- ↑ Beall, C.; Ashford, M. L.; McCrimmon, R. J. (2011). "The physiology and pathophysiology of the neural control of the counterregulatory response". AJP: Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology. 302 (2): R215-23. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00531.2011. PMID 22071156.
- ↑ Stein BC, Levin RI (May 1998). "Natriuretic peptides: Physiology, therapeutic potential, and risk stratification in ischemic heart disease". Am Heart J. 135 (5): 914–23. doi:10.1016/s0002-8703(98)70054-7. PMID 9588425.[ verification needed ]
- ↑ Hurwitz JM, Santoro N (August 2004). "Inhibins, activins, and follistatin in the aging female and male". Semin Reprod Med. 22 (3): 209–17. doi:10.1055/s-2004-831896. PMID 15319823.[ verification needed ]
- ↑ Nicks KM, Perrien DS, Akel NS, Suva LJ, Gaddy D (2009-10-30). "Regulation of osteoblastogenesis and osteoclastogenesis by the other reproductive hormones, Activin and Inhibin". Mol Cell Endocrinol. 310 (1–2): 11–20. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2009.07.001. PMC 2951729 . PMID 19615428.